Navegação por Autores IPEN "ABE, ALFREDO"
- Página inicial
- →
- Navegação por Autores IPEN
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação por Autores IPEN "ABE, ALFREDO"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 25
-
. Analysis of the combined effects on the fuel performance of UO2-BeO as fuel and iron-based alloy as cladding. In: WATER REACTOR FUEL PERFORMANCE MEETING, September 10-14, 2017, Jeju Island, Korea. Proceedings... 2017. p. 1-9. Abstract: Iron-based alloys have been considered as promising candidate material to replace zirconium-based alloys as fuel cladding based on the previous experience of the first generation of pressurized water reactors (PWR). Moreover, the safety margins of nuclear fuels can be improved by means of additives in the fuel pellet, as beryllium oxide (BeO), due to the increase of the fuel thermal conductivity. These efforts are part of the accident tolerant fuel (ATF) program which aims to develop nuclear fuel systems with enhanced performance under normal operation, design-basis accident and severe-accident conditions. This paper addresses the combined effects on the fuel performance considering the BeO additive in the fuel pellet and stainless steel 348 as cladding material under steady-state and loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) scenario. The fuel performance simulation and assessment are conducted using modified versions of well-known fuel performance codes (FRAPCON/FRAPTRAN). The obtained results have shown that the studied fuel system (stainless steel cladding and UO2-BeO) enables an improvement in the main parameters associated to the fuel safety margins under steady-state irradiation as well as LOCA scenario.. Analysis of the combined effects on the fuel performance of UO2-BeO as fuel and iron-based alloy as cladding. In: WATER REACTOR FUEL PERFORMANCE MEETING, September 10-14, 2017, Jeju Island, Korea. Proceedings... 2017. p. 1-9. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29131. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Assessment of minimum allowable thickness of advanced steel (FeCrAl) cladding for accident tolerant fuel. Nuclear Engineering and Design, v. 415, p. 1-7, 2023. DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2023.112707 Abstract: The ferritic iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy cladding is considered to be the most promising for near-term application in the ATF framework to replace existing zirconium alloy cladding. Although FeCrAl cladding presents several advantages, it is well known that there are at least two main drawbacks, one is the increased thermal neutron absorption cross-section compared to the current Zr-based cladding resulting in a neutronic penalty and another is tritium higher permeation. In the present study, the minimum allowable thickness of cladding is addressed considering neutronic penalty reduction and the mechanical-structural behavior under the LOCA accident condition. The neutronic penalty assessment was performed using the Monte Carlo code and mechanical-structural performance of the FeCrAl cladding using the TRANSURANUS fuel code, which was modified to consider properly the FeCrAl cladding.. Assessment of minimum allowable thickness of advanced steel (FeCrAl) cladding for accident tolerant fuel. Nuclear Engineering and Design, v. 415, p. 1-7, 2023. DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2023.112707. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/34371. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Assessment of stainless steel 348 fuel rod performance against literature available data using TRANSURANUS code. EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies, v. 2, p. 1-8, 2016. DOI: 10.1051/epjn/2016017 Abstract: Early pressurized water reactors were originally designed to operate using stainless steel as cladding material, but during their lifetime this material was replaced by zirconium-based alloys. However, after the Fukushima Daiichi accident, the problems related to the zirconium-based alloys due to the hydrogen production and explosion under severe accident brought the importance to assess different materials. In this sense, initiatives as ATF (Accident Tolerant Fuel) program are considering different material as fuel cladding and, one candidate is iron-based alloy. In order to assess the fuel performance of fuel rods manufactured using iron-based alloy as cladding material, it was necessary to select a specific stainless steel (type 348) and modify properly conventional fuel performance codes developed in the last decades. Then, 348 stainless steel mechanical and physics properties were introduced in the TRANSURANUS code. The aim of this paper is to present the obtained results concerning the verification of the modified TRANSURANUS code version against data collected from the open literature, related to reactors which operated using stainless steel as cladding. Considering that some data were not available, some assumptions had to be made. Important differences related to the conventional fuel rods were taken into account. Obtained results regarding the cladding behavior are in agreement with available information. This constitutes an evidence of the modified TRANSURANUS code capabilities to perform fuel rod investigation of fuel rods manufactured using 348 stainless steel as cladding material.
Palavras-Chave: stainless steels; fuel rods; t codes; comparative evaluations; reactors; cladding; data; performance
. Assessment of stainless steel 348 fuel rod performance against literature available data using TRANSURANUS code. EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies, v. 2, p. 1-8, 2016. DOI: 10.1051/epjn/2016017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/26913. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Assessment of uranium dioxide fuel performance with the addition of beryllium oxide. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 22-27, 2017, Belo Horizonte, MG. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2017. Abstract: The Fukushima Daiichi accident in 2011 pointed the problem related to the hydrogen generation under accident scenarios due to the oxidation of zirconium-based alloys widely used as fuel rod cladding in water-cooled reactors. This problem promoted research programs aiming the development of accident tolerant fuels (ATF) which are fuels that under accident conditions could keep longer its integrity enabling the mitigation of the accident effects. In the framework of the ATF program, different materials have been studied to be applied as cladding to replace zirconium-based alloy; also efforts have been made to improve the uranium dioxide thermal conductivity doping the fuel pellet. This paper evaluates the addition of beryllium oxide (BeO) to the uranium dioxide in order to enhance the thermal conductivity of the fuel pellet. Investigations performed in this area considering the addition of 10% in volume of BeO, resulting in the UO2-BeO fuel, have shown good results with the improvement of the fuel thermal conductivity and the consequent reduction of the fuel temperatures under irradiation. In this paper, two models obtained from open literature for the thermal conductivity of UO2- BeO fuel were implemented in the FRAPCON 3.5 code and the results obtained using the modified code versions were compared. The simulations were carried out using a case available in the code documentation related to a typical pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel rod irradiated under steady state condition. The results show that the fuel centerline temperatures decrease with the addition of BeO, when compared to the conventional UO2 pellet, independent of the model applied.
Palavras-Chave: beryllium oxides; comparative evaluations; computerized simulation; f codes; fuel pellets; fuel rods; nuclear fuels; performance; pwr type reactors; steady-state conditions; thermal conductivity; uranium dioxide
. Assessment of uranium dioxide fuel performance with the addition of beryllium oxide. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 22-27, 2017, Belo Horizonte, MG. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28186. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Best estimate plus uncertainty analysis of metal-water reaction transient experiment. Nuclear Engineering and Design, v. 411, p. 1-12, 2023. DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2023.112414 Abstract: Uncertainty analysis is applied in the licensing process for nuclear installations to complement best estimate analysis and to verify that the upper bound value is less than the threshold corresponding to the safety parameter of interest. Metal-water reaction is a critical safety phenomenon of water-cooled nuclear reactors at accident conditions, e.g. Loss-Of-Coolant Accidents (LOCA). AISI 348 cladding is able to increase the accident tolerance comparing to Zr-based alloys and differently from other accident tolerant fuel cladding options, there is operational experience of nuclear power plants with stainless steel. In this study, a transient oxidation experiment of AISI 348 by steam was conducted and the major sources of uncertainty were addressed. An evaluation model was developed to calculate the evolution of mass gain during the experiment. Meanwhile, uncertainty propagation of experimental data was performed. The results show that the mass gain predicted by the transient metal-water reaction model lays within the experimental data uncertainty band. Furthermore, the selection of the oxidation kinetics model seems to be important whether the analysis wills to provide conservative results.. Best estimate plus uncertainty analysis of metal-water reaction transient experiment. Nuclear Engineering and Design, v. 411, p. 1-12, 2023. DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2023.112414. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/34372. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Critical loading configurations of the IPEN/MB-01 reactor with UOsub(2)GDsun(2)Osub(3) burnable poison rods. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 9th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 16th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 1st, September 27 - October 2, 2009, Rio de Janeiro, RJ. Proceedings... Sao Paulo: ABEN, 2009, 2009.
Palavras-Chave: burnable poisons; control rod drives; experimental data; fuel rods; gadolinium oxides; ipen-mb-1 reactor; k codes; m codes; monte carlo method; multiplication factors; reactor cores; uranium dioxide
. Critical loading configurations of the IPEN/MB-01 reactor with UOsub(2)GDsun(2)Osub(3) burnable poison rods. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 9th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 16th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 1st, September 27 - October 2, 2009, Rio de Janeiro, RJ. Proceedings... Sao Paulo: ABEN, 2009, 2009. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/16612. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Development and application of modified fuel performance code based on stainless steel as cladding under steady state, transient and accident conditions. In: . Fuel Modelling in Accident Conditions (FUMAC). Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2019. p. 55-81, (IAEA-TECDOC-1889 - ANNEX II). Abstract: The IPEN/CNEN proposal for FUMAC-CRP was to modified fuel performance codes (FRAPCON and FRAPTRAN) in order to assess the behavior of fuel rod using stainless steel as cladding and compare to zircaloy cladding performance under steady state and accident condition. The IFA 650- 9, IFA-650-10 and UFA-650-11experiments were modelled to perform the LOCA accident simulation considering the original cladding and compared to stainless steel cladding.
Palavras-Chave: cladding; comparative evaluations; computer codes; fuel rods; loss of coolant; reactor accident simulation; stainless steels; steady-state conditions; zircaloy
. Development and application of modified fuel performance code based on stainless steel as cladding under steady state, transient and accident conditions. In: . Fuel Modelling in Accident Conditions (FUMAC). Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2019. p. 55-81. (IAEA-TECDOC-1889 - ANNEX II). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30879. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Effectiveness of Ni-based and Fe-based cladding alloys in delaying hydrogen generation for small modular reactors with increased accident tolerance. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, v. 55, n. 1, p. 156-168, 2023. DOI: 10.1016/j.net.2022.09.002 Abstract: This study investigates the high temperature oxidation behaviour of a Ni–20Cr-1.2Si (wt.%) alloy in steam from 1200 °C to 1350 °C by Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). The results demonstrate that exposed Ni-based alloy developed a thin oxide scale, consisted mainly of Cr2O3. The oxidation kinetics obtained from the experimental results was applied to evaluate the hydrogen generation considering a simplified reactor core model with different cladding alloys following an unmitigated Loss-Of-Coolant Accident (LOCA) scenario in a hypothetical Small Modular Reactor (SMR). Overall, experimental data and simulations results show that both Fe-based and Ni-based alloys may enhance cladding survivability, delaying its melting, as well as reducing hydrogen generation under accident conditions compared to Zr-based alloys. However, a substantial neutron absorption occurs when Ni-based alloys are used as cladding for current uranium-dioxide fuel systems, even when compared to Fe-based alloys.
Palavras-Chave: fuel-cladding interactions; nickel alloys; stainless steels; oxidation; temperature range 0400-1000 k; cladding
. Effectiveness of Ni-based and Fe-based cladding alloys in delaying hydrogen generation for small modular reactors with increased accident tolerance. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, v. 55, n. 1, p. 156-168, 2023. DOI: 10.1016/j.net.2022.09.002. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/33996. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Evaluation of corrosion on the fuel performance of stainless steel cladding. EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies, v. 2, n. 40, p. 1-6, 2016. DOI: 10.1051/epjn/2016033 Abstract: In nuclear reactors, the use of stainless steel (SS) as the cladding material offers some advantages such as good mechanical and corrosion resistance. However, its main advantage is the reduction in the amount of the hydrogen released during loss-of-coolant accident, as observed in the Fukushima Daiichi accident. Hence, research aimed at developing accident tolerant fuels should consider SS as an important alternative to existing materials. However, the available computational tools used to analyze fuel rod performance under irradiation are not capable of assessing the effectiveness of SS as the cladding material. This paper addresses the SS corrosion behavior in a modified fuel performance code in order to evaluate its effect on the global fuel performance. Then, data from the literature concerning to SS corrosion are implemented in the specific code subroutines, and the results obtained are compared to those for Zircaloy-4 (Zy-4) under the same power history. The results show that the effects of corrosion on SS are considerably different from those on Zy-4. The thickness of the oxide layer formed on the SS surface is considerably lower than that formed on Zy-4. As a consequence of this, the global fuel performance of SS under irradiation should be less affected by the corrosion.
Palavras-Chave: comparative evaluations; computerized simulation; corrosion resistance; f codes; feasibility studies; fuel cans; fuel rods; performance; pwr type reactors; stainless steels; zircaloy 4
. Evaluation of corrosion on the fuel performance of stainless steel cladding. EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies, v. 2, n. 40, p. 1-6, 2016. DOI: 10.1051/epjn/2016033. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27169. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Heavy steel reflector evaluation using diffusion theory. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 11th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 18th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 3rd, November 24-29, 2013, Recife, PE. Proceedings... Sao Paulo: ABEN, 2013, 2013.
Palavras-Chave: absorption; c codes; cross sections; distribution; eigenvalues; h codes; ipen-mb-1 reactor; neutron flux; neutron reflectors; performance; reactor cores; stainless steels;
. Heavy steel reflector evaluation using diffusion theory. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 11th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 18th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 3rd, November 24-29, 2013, Recife, PE. Proceedings... Sao Paulo: ABEN, 2013, 2013. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/17204. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Modification of fuel performance code to evaluate iron-based alloy behavior under loca scenario. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 22-27, 2017, Belo Horizonte, MG. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2017. Abstract: Accident tolerant fuels (ATF) has been studied since the Fukushima Daiichi accident in the research efforts to develop new materials which under accident scenarios could maintain the fuel rod integrity for a longer period compared to the cladding and fuel system usually utilized in Pressurized Water Reactors (PWR). The efforts have been focused on new materials applied as cladding, then iron-base alloys appear as a possible candidate. The aim of this paper is to implement modifications in a fuel performance code to evaluate the behavior of ironbased alloys under Loss-of-Coolant Accident (LOCA) scenario. For this, initially the properties related to the thermal and mechanical behavior of iron-based alloys were obtained from the literature, appropriately adapted and introduced in the fuel performance code subroutines. The adopted approach was step by step modifications, where different versions of the code were created. The assessment of the implemented modification was carried out simulating an experiment available in the open literature (IFA-650.5) related to zirconium-based alloy fuel rods submitted to LOCA conditions. The obtained results for the iron-based alloy were compared to those obtained using the regular version of the fuel performance code for zircaloy-4. The obtained results have shown that the most important properties to be changed are those from the subroutines related to the mechanical properties of the cladding. The results obtained have shown that the burst is observed at a longer time for fuel rods with iron-based alloy, indicating the potentiality of this material to be used as cladding with ATF purposes.
Palavras-Chave: accident-tolerant nuclear fuels; cladding; computerized simulation; f codes; fuel rods; iron alloys; loss of coolant; performance; pwr type reactors; stainless steel-348
. Modification of fuel performance code to evaluate iron-based alloy behavior under loca scenario. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 22-27, 2017, Belo Horizonte, MG. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28187. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Neutron flux intercomparison and ex-core neutron detector optimization in a SMR reactor using MCNP6 code and MAVRIC sequence. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 21-25, 2019, Santos, SP. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2019. p. 4144-4163. Abstract: Ex-core neutron detectors are commonly referred as a detector placed outside the reactor pressure vessel and in a typical SMR design its use is employed to reactor control. Due to its position (far from core) neutron flux calculation for ex-core detector purposes is challenging when using Monte Carlo codes, therefore this work presents an intercomparison between two Monte Carlo codes and also a neutron flux analysis (axially and radially) to better positioning the ex-core neutron detectors. Discrepancies regarding energy treatment can be evaluated as the MAVRIC sequence uses a set of cross sections in a multigroup energy structure while MCNP6 uses continuous energy. In this work, neutron flux intercomparison is mostly focused on variance reduction techniques since these codes presents different approaches, mainly because the MAVRIC sequence uses a hybrid approach combining deterministic and probabilistic methods and MCNP6 code uses traditional variance reduction methods. Some Monte Carlo variables such as figure-of-merit, CPU-time and error distributions maps are evaluated, and neutron flux magnitudes compared. To do so, a typical small modular reactor is modeled with the aid of MCNP6 code and the MAVRIC sequence in two different situations: one being a deep subcritical state with an external neutron source for variance reduction techniques comparison and the other a generic start up procedure (control rods removal) for detector position optimization.
Palavras-Chave: comparative evaluations; control elements; cross sections; finite difference method; graphite moderated reactors; m codes; monte carlo method; neutron detectors; neutron flux; neutron sources; optimization; reactor cores
. Neutron flux intercomparison and ex-core neutron detector optimization in a SMR reactor using MCNP6 code and MAVRIC sequence. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 21-25, 2019, Santos, SP. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2019. p. 4144-4163. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30692. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Neutronic screening of potential candidate for accident tolerant fuel. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Resumo expandido... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files).
Palavras-Chave: accident-tolerant nuclear fuels; beryllium oxides; cladding; fuel rods; monte carlo method; pwr type reactors; reactivity; stainless steels; uranium dioxide; uranium silicides; zircaloy
. Neutronic screening of potential candidate for accident tolerant fuel. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Resumo expandido... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31922. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Nuclear criticality safety parameter evaluation for uranium metallic alloy. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 11th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 18th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 3rd, November 24-29, 2013, Recife, PE. Proceedings... Sao Paulo: ABEN, 2013, 2013.
Palavras-Chave: uranium alloys; nuclear fuels; criticality; safety analysis; s codes; monte carlo method
. Nuclear criticality safety parameter evaluation for uranium metallic alloy. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 11th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 18th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 3rd, November 24-29, 2013, Recife, PE. Proceedings... Sao Paulo: ABEN, 2013, 2013. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/17324. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Preliminary assessment of iron alloy cladding as accident tolerant fuel cladding. In: TECHNICAL MEETING ON MODELLING OF FUEL BEHAVIOUR IN DESIGN BASIS ACCIDENTS AND DESIGN EXTENSION CONDITIONS, May 13-16, 2019, Shenzhen, China. Apresentação... 2019.
Palavras-Chave: waste water; liquid wastes; industrial wastes; accelerators; portable equipment; electron beams
. Preliminary assessment of iron alloy cladding as accident tolerant fuel cladding. In: TECHNICAL MEETING ON MODELLING OF FUEL BEHAVIOUR IN DESIGN BASIS ACCIDENTS AND DESIGN EXTENSION CONDITIONS, May 13-16, 2019, Shenzhen, China. Apresentação... 2019. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32194. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Preliminary neutronic assessment of iron based alloy fuel cladding. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files). Abstract: Nowadays two important nuclear fuel performance requirements have been addressed: high burnup in order to improve fuel cycle economic aspect and accident tolerant fuel to enhance the safety under accident condition. The accident tolerant fuel particularly becomes very important issue after Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident in 2011. The initiatives of R&D program toward to accident tolerant fuel comprises different countries, organizations and including fuel vendors. The Accident Tolerant Fuel (ATF) can be defined as enhanced fuel which can tolerate loss of active cooling system capability for a considerably longer time period and the fuel/cladding system can be maintained without significant degradation and can also improve the fuel performance during normal operations and transients, as well as design-basis accident (DBA) and beyond design-basis (BDBA) accident. Different materials have been proposed as fuel cladding candidates considering thermo-mechanical properties and lower reaction kinetic with steam and slower hydrogen production, besides that an evaluation of the neutronic aspects for several cladding candidates is important and shall be evaluated. Depending of the outcome of this evaluation, the fuel enrichment level changes to higher than actual level shall be necessary to overcome the neutron absorption penalty. The aim of this work is to perform a preliminary neutronic assessment of fuel cladding based on iron alloy considering a standard PWR fuel rod (fuel pellet and dimension). The main purpose of the assessment is to quantify the penalty due to increase of neutron absorption in the cladding materials and some others fuel parameters are evaluated in order to overcome such penalty. In addition to neutronic assessment, the criticality safety aspects due to increase of fuel enrichment level are briefly presented and discussed.
Palavras-Chave: absorption; accident-tolerant nuclear fuels; beyond-design-basis accidents; cooling systems; design-basis accidents; enrichment; fuel cycle; fuel pellets; fuel rods; iron alloys; pwr type reactors; radiation accidents; reactor accidents; safety
. Preliminary neutronic assessment of iron based alloy fuel cladding. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31920. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Preliminary neutronic assessmento for ATF (Accident Tolerant Fuel) based on iron alloy. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 12th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 19th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 4th, October 4-9, 2015, São Paulo, SP. Proceedings... 2015.
Palavras-Chave: fuel rods; cladding; iron alloys; loss of coolant; monte carlo method; neutron absorbers; nuclear fuels; pwr type reactors; tolerance; zirconium alloys
. Preliminary neutronic assessmento for ATF (Accident Tolerant Fuel) based on iron alloy. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 12th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 19th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 4th, October 4-9, 2015, São Paulo, SP. Proceedings... 2015. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/24029. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Reactivity experiments with different boric acid concentrations in the IPEN/MB-01 reactor. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 10th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 17th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 2nd, October 24-28, 2011, Belo Horizonte, MG. Proceedings... São Paulo: ABEN, 2011, 2011.
Palavras-Chave: ipen-mb-1 reactor; reactor cores; boric acid; monte carlo method
. Reactivity experiments with different boric acid concentrations in the IPEN/MB-01 reactor. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE; MEETING ON NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS, 10th; MEETING ON REACTOR PHYSICS AND THERMAL HYDRAULICS, 17th; MEETING ON NUCLEAR INDUSTRY, 2nd, October 24-28, 2011, Belo Horizonte, MG. Proceedings... São Paulo: ABEN, 2011, 2011. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/16161. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Revisiting stainless steel as PWR fuel rod cladding after Fukushima daiichi accident. Journal of Energy and Power Engineering, v. 8, p. 973-980, 2014.
Palavras-Chave: stainless steels; cladding; fuel rods; pwr type reactors; zircaloy; steady-state conditions; p codes; performance
. Revisiting stainless steel as PWR fuel rod cladding after Fukushima daiichi accident. Journal of Energy and Power Engineering, v. 8, p. 973-980, 2014. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/23372. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Sensitivity analysis of fuel rod parameters in steady state condition using TRANSURANUS code. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 21-25, 2019, Santos, SP. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2019. p. 4936-4942. Abstract: In this paper, a simulation of steady state conditions using TRANSURANUS code applied to Arkansas Nuclear One Unit 2 (PWR) fuel rod is presented. The fuel rod considered in this work was exposed to a peak rod average burnup of 64 GWd/TU, which corresponds to a batch-average exposure of about 53 GWd/TU. TRANSURANUS code offers two different approach for sensitivity analysis: Numerical Noise Analysis and Monte Carlo. In this work, sensitivity analysis using Monte Carlo approach was considered in the range of fuel rod manufacturing parameters, such as internal and external radius of the cladding, external radius of the fuel, and filling gas pressure of the fuel rod, in order to verify some existing correlation with fuel centerline temperature, internal cladding temperature, average tangential stress in the cladding, average permanent tangential strain in the cladding, internal pressure, and fission gas release.
Palavras-Chave: arkansas-2 reactor; burnup; computerized simulation; fuel rods; monte carlo method; neutron flux; sensitivity analysis; steady-state conditions; t codes
. Sensitivity analysis of fuel rod parameters in steady state condition using TRANSURANUS code. In: INTERNATIONAL NUCLEAR ATLANTIC CONFERENCE, October 21-25, 2019, Santos, SP. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro: Associação Brasileira de Energia Nuclear, 2019. p. 4936-4942. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30705. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 25
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

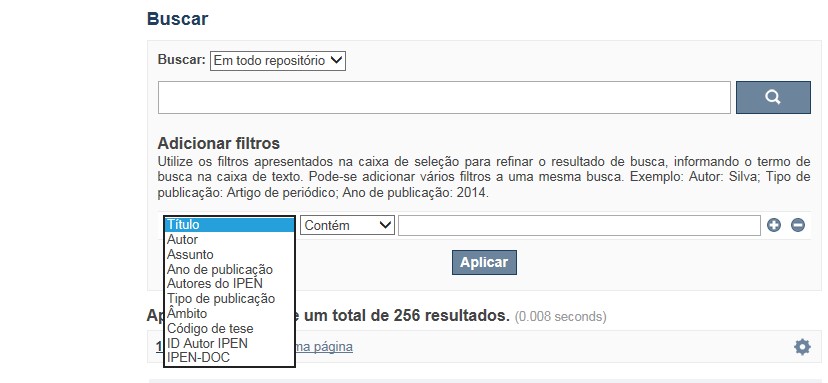
A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
