JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
Navegação Periódicos - Artigos por autor "10118"
-
ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.
 ; PARRA, JOAO P.R.L.L.; VALLCORBA, ORIOL; PERAL, INMA; YOSHITO, WALTER K.
; PARRA, JOAO P.R.L.L.; VALLCORBA, ORIOL; PERAL, INMA; YOSHITO, WALTER K.
 ; SAEKI, MARGARIDA J.; TURRILLAS, XAVIER; MARTINEZ, LUIS G.
; SAEKI, MARGARIDA J.; TURRILLAS, XAVIER; MARTINEZ, LUIS G..
Cation distribution of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles using pair distribution function analysis and resonant X-ray scattering.
EPL,
v. 124,
n. 5,
p. 56001-p1 - 56001-p5,
2018.
DOI:
10.1209/0295-5075/124/56001
Abstract:
Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles were synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method
and analysed using X-ray synchrotron diffraction data. Pair distribution function (PDF) analysis
was used to probe the local structure and revealed that the first-neighbour distances of Fe-Fe and
Mn-Zn in the 3.0 up to 3.5˚A range are different from the ones usually reported in the literature.
For the sample with the best magnetic behaviour, resonant X-ray scattering (RXS) using three
energies close to the absorption edges of Mn, Zn and Fe was applied to determine the cation
distribution which explained the previous result from PDF analysis.
Palavras-Chave:
nanoparticles;
distribution functions;
scattering;
x-ray diffraction;
ferrite;
zinc compounds;
manganese compounds;
magnetic resonance;
nmr imaging;
images
ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.; PARRA, JOAO P.R.L.L.; VALLCORBA, ORIOL; PERAL, INMA; YOSHITO, WALTER K.; SAEKI, MARGARIDA J.; TURRILLAS, XAVIER; MARTINEZ, LUIS G.
Cation distribution of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles using pair distribution function analysis and resonant X-ray scattering.
EPL,
v. 124,
n. 5,
p. 56001-p1 - 56001-p5,
2018.
DOI:
10.1209/0295-5075/124/56001.
Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29931. Acesso em: $DATA.
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Como referenciar este item
-
MARANHAO, W.C.A.
 ; ICHIKAWA, R.U.
; ICHIKAWA, R.U.
 ; TURRILLAS, X.; YOSHITO, W.K.
; TURRILLAS, X.; YOSHITO, W.K.
 ; SAEKI, M.J.; ORLANDO, M.T.D.; MARTINEZ, L.G.
; SAEKI, M.J.; ORLANDO, M.T.D.; MARTINEZ, L.G.

.
Characterization of nanostructured Mn-Zn ferrites synthesized by coprecipitation method using CTAB.
Materials Science Forum,
v. 1012,
p. 207-211,
2020.
DOI:
10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1012.207
Abstract:
In this work it was investigated the influence of CTAB surfactant concentration on the
synthesis of the compound Mn0.75Zn0.25Fe2O4 by the coprecipitation method. It was also compared
the influence of hydrothermal treatment on the synthesized materials. The magnetic properties were
characterized by AC susceptometry for the determination of the magnetic susceptibility and
magnetic density energy. The phases, crystal structure and morphology of the nanoferrites were
determined by Rietveld analysis of X-ray diffraction data. It was found the presence of two phases:
Franklinite and Akaganeite and it was shown that the samples synthesized only by coprecipitation
presented the tendency to increasing the crystallite sizes of the akaganeite phase and decreasing of
crystallite sizes of the Franklinite phase as a function of CTAB concentration. The samples
submitted to subsequent hydrothermal treatment presented a tendency to decreasing the crystallite
sizes of both phases and increasing in Franklinite phase fraction, compared to the samples
synthesized only by coprecipitation, suggesting that the hydrothermal treatment was effective in
obtaining nanostructured materials of smaller particles.
Palavras-Chave:
ferrites;
manganese;
zinc;
nanostructures;
manganese carbides;
zinc oxides;
coprecipitation;
hydrothermal synthesis;
x-ray diffraction;
calculation methods
MARANHAO, W.C.A.; ICHIKAWA, R.U.; TURRILLAS, X.; YOSHITO, W.K.; SAEKI, M.J.; ORLANDO, M.T.D.; MARTINEZ, L.G.
Characterization of nanostructured Mn-Zn ferrites synthesized by coprecipitation method using CTAB.
Materials Science Forum,
v. 1012,
p. 207-211,
2020.
DOI:
10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1012.207.
Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31632. Acesso em: $DATA.
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Como referenciar este item
-
ROJAS-HERNANDEZ, ROCIO E.; RUBIO-MARCOS, FERNANDO; GORNI, GIULIO; MARINI, CARLO; DANILSON, MATI; PASCUAL, LAURA; ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.
 ; HUSSAINOVA, IRINA; FERNANDEZ, JOSE F.
; HUSSAINOVA, IRINA; FERNANDEZ, JOSE F..
Enhancing NIR emission in ZnAl2O4:Nd,Ce nanofibers by co-doping with Ce and Nd: a promising biomarker material with low cytotoxicity.
Journal of Materials Chemistry C,
v. 9,
n. 2,
p. 657-670,
2021.
DOI:
10.1039/d0tc04752j
Abstract:
Development of new near infrared luminescent (NIR) emitters improves our understanding of their fundamental structure–property relationships. The ability to use efficient energy transfer to convert ultraviolet or visible light photons to enhance the NIR emission has attracted a great deal of attention in down-conversion applications. Taking advantage of the sol–gel impregnation process and growth of materials along a support or template, core–shell structured nanofibers of ZnAl2O4 – based ceramic doped with cerium and neodymium were synthesized with the help of an elaborate facile and cost-efficient strategy. The color-tunable emissions make this material a suitable host for a wide range of applications, e.g., bio-imaging, security markers, imaging devices, optical coatings, and solar cells. This research correlates the defects and the remarkable optical properties of the developed structures. Specified conditions of sol–gel processing combined with the incorporation of rare-earth elements in various concentrations provide the possibility of tuning the ratio between Ce3+ and Ce4+ in the nanofibers with an average diameter of 50 nm and, therefore, their functional response. It is important to clarify the role of trivalent and tetravalent cerium cations in the modulation of NIR emission to establish the luminescence mechanism. The NIR emitter luminescent compound ZnAl2O4:Nd,Ce, which adopts a spinel-type structure, is studied using the X-ray absorption near-edge structure technique. For the first time, this study reveals the energy transfer from Ce3+ to Nd3+ and the enhancement of the NIR emission due to the presence of Ce4+ in the ZnAl2O4:Nd,Ce spinel compound. Cytotoxicity analyses suggest the viability of the synthesized nanofibers, which opens new avenues in bio-imaging applications.
Palavras-Chave:
nanofibers;
near infrared radiation;
zinc;
cerium;
neodymium
ROJAS-HERNANDEZ, ROCIO E.; RUBIO-MARCOS, FERNANDO; GORNI, GIULIO; MARINI, CARLO; DANILSON, MATI; PASCUAL, LAURA; ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.; HUSSAINOVA, IRINA; FERNANDEZ, JOSE F.
Enhancing NIR emission in ZnAl2O4:Nd,Ce nanofibers by co-doping with Ce and Nd: a promising biomarker material with low cytotoxicity.
Journal of Materials Chemistry C,
v. 9,
n. 2,
p. 657-670,
2021.
DOI:
10.1039/d0tc04752j.
Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32025. Acesso em: $DATA.
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Como referenciar este item
-
FARIA, MARCELA E.M.
 ; LEITE, MARINA M.; ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.
; LEITE, MARINA M.; ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.
 ; VICHI, FLAVIO M.; TURRILLAS, X.
; VICHI, FLAVIO M.; TURRILLAS, X.
 ; MARTINEZ, L.G.
; MARTINEZ, L.G.

.
Thickness estimation of TiO2-based nanotubes using X-ray diffraction techniques.
Materials Science Forum,
v. 1012,
p. 179-184,
2020.
DOI:
10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1012.179
Abstract:
TiO2-based nanotubes are a very promising material with many applications in solar
cells, biomedical devices, gas sensors, hydrogen generation, supercapacitors, and lithium batteries,
among others. Nanotube thickness is a very important property since it is related to electronic and
surface mechanics. In this sense, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) can be used. However, it
can be difficult to acquire a good TEM image because the transversal section of the nanotubes
needs to be visible. In this work, TiO2-based nanotubes obtained via hydrothermal synthesis were
studied using X-ray line profile analysis. Scherrer and Single-Line methods provided consistent
results for the thickness of the nanotubes (≃ 5 nm) when compared with TEM. Additionally,
Single-Line method was also applied to estimate the microstrain. The advantage of using XRD is
given by the fact that it is a quick and statistically significant analysis when compared with TEM.
The results show that XRD can be used as a rapid and reliable alternative for the thickness
estimation of nanotubes.
Palavras-Chave:
x-ray diffraction;
titanium oxides;
nanotubes;
transmission electron microscopy;
hydrothermal synthesis;
thickness;
equations
FARIA, MARCELA E.M.; LEITE, MARINA M.; ICHIKAWA, RODRIGO U.; VICHI, FLAVIO M.; TURRILLAS, X.; MARTINEZ, L.G.
Thickness estimation of TiO2-based nanotubes using X-ray diffraction techniques.
Materials Science Forum,
v. 1012,
p. 179-184,
2020.
DOI:
10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1012.179.
Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31644. Acesso em: $DATA.
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Como referenciar este item
-
MERIZIO, L.G.; BONTURIM, E.; ICHIKAWA, R.U.
 ; SILVA, I.G.N.; TEIXEIRA, V.C.; RODRIGUES, L.C.V.; BRITO, H.F.
; SILVA, I.G.N.; TEIXEIRA, V.C.; RODRIGUES, L.C.V.; BRITO, H.F..
Toward an energy-efficient synthesis method to improve persistent luminescence of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ materials.
Materialia,
v. 20,
p. 1-10,
2021.
DOI:
10.1016/j.mtla.2021.101226
Abstract:
The synthesis of persistent luminescent materials usually requires a multi-step long time annealing at high temperatures (>1200°C) in a resistive oven, causing a huge energy consumption. Also, to achieve reduced oxidation states of emitter ions (e.g., Eu3+ → Eu2+ ), the H2(g) atmosphere is often used, which can be dangerous and increase the costs of the process. Therefore, the development of a quick and new single-step green strategy, using in-situ low-risk atmosphere (e.g., CO(g)) and a microwave-assisted solid-state (MASS) method has been encouraged. In this work, we present a single-step method to synthesize the compound Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ using the MASS method and the results were compared with those prepared by a conventional ceramic method. The luminescent material was prepared in 25 min of synthesis using carbon as a microwave susceptor and CO(g) atmosphere source at the same time. A higher concentration of Eu2+ emitter was identified by XANES in the MASS method product, which has a significant effect on the luminescence efficiency, as well as an improvement in the optical properties, leading to an emission 100 times more intense. Furthermore, to understand the Eu3+ reduction process under CO(g) atmosphere, we present here the innovative results of in-situ XANES analysis for the Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ material. Finally, the MASS method makes it possible to prepare the materials with less than 5% of the ceramic method's duration in time. The energy-saving and better-quality persistent luminescent properties obtained in the MASS method provide viable applications on anti-counterfeiting markers, solar cell sensitizers, and other luminescent technologies.
Palavras-Chave:
microwave radiation;
synthesis;
rare earths;
solids;
luminescence;
annealing;
synchrotron radiation
MERIZIO, L.G.; BONTURIM, E.; ICHIKAWA, R.U.; SILVA, I.G.N.; TEIXEIRA, V.C.; RODRIGUES, L.C.V.; BRITO, H.F.
Toward an energy-efficient synthesis method to improve persistent luminescence of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ materials.
Materialia,
v. 20,
p. 1-10,
2021.
DOI:
10.1016/j.mtla.2021.101226.
Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32655. Acesso em: $DATA.
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Como referenciar este item
-
ICHIKAWA, R.U.
 ; LINHARES, H.M.S.M.D.; SILVA, A.S.B. da
; LINHARES, H.M.S.M.D.; SILVA, A.S.B. da
 ; TEIXEIRA, M.I.
; TEIXEIRA, M.I.
 ; RANIERI, I.M.
; RANIERI, I.M.
 ; TURRILLAS, X.; MARTINEZ, L.G.
; TURRILLAS, X.; MARTINEZ, L.G.

.
X-ray diffraction analysis of KY3F10 nanoparticles doped with Nd and preliminary studies for its use in high-dose radiation dosimetry.
Brazilian Journal of Radiation Sciences,
v. 7,
n. 2A,
p. 1-13,
2019.
DOI:
10.15392/bjrs.v7i2A.586
Abstract:
In this work, the structure and microstructure of Nd:KY3F10 nanoparticles was probed using X-ray synchrotron diffraction analysis. Rietveld refinement was applied to obtain cell parameters, atomic positions and atomic dis-placement factors to be compared with the ones found in literature. X-ray line profile methods were applied to determine mean crystallite size and crystallite size distribution. Thermoluminescent (TL) emission curves were measured for different radiation doses, from 0.10 kGy up to 10.0 kGy. Dose-response curves were obtained by area integration beneath the peaks from TL. The reproducibility of the results in this work has shown that this material can be considered a good dosimetric material.
Palavras-Chave:
nanoparticles;
x-ray diffraction;
radiation doses;
doped materials;
thermoluminescence;
neodymium;
yttrium fluorides;
critical size;
dose-response relationships;
dosimetry
ICHIKAWA, R.U.; LINHARES, H.M.S.M.D.; SILVA, A.S.B. da; TEIXEIRA, M.I.; RANIERI, I.M.; TURRILLAS, X.; MARTINEZ, L.G.
X-ray diffraction analysis of KY3F10 nanoparticles doped with Nd and preliminary studies for its use in high-dose radiation dosimetry.
Brazilian Journal of Radiation Sciences,
v. 7,
n. 2A,
p. 1-13,
2019.
DOI:
10.15392/bjrs.v7i2A.586.
Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30055. Acesso em: $DATA.
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Como referenciar este item
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
-
Todo o repositório
-
Esta coleção
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do
Buscar no Repositório
, isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em
Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em
Navegar
tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro,
Autores IPEN
apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o
ID Autor IPEN
diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome;
Tipo de acesso
diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

A opção
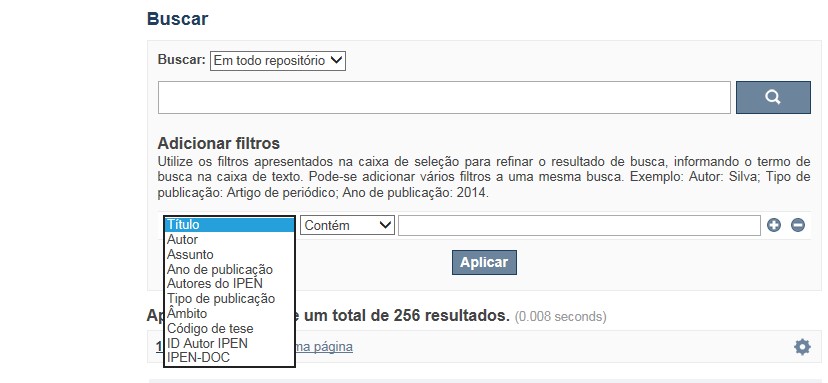
Busca avançada
utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da
International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA
, por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o  significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo  será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI,
clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI,
clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.


![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.