Navegação Periódicos - Artigos por ano de publicação "2020"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Periódicos - Artigos
- →
- Navegação Periódicos - Artigos por ano de publicação
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Periódicos - Artigos por ano de publicação "2020"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 348
-
. Yeast-TiO2 biotemplate for oxytetracycline solar photodecomposition. Journal of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, v. 8, n. 7, p. 12-26, 2020. DOI: 10.4236/msce.2020.87002 Abstract: The detection of the pharmaceutical compounds used in human and veterinary medicine is in several environmental matrices (surface waters, effluents, groundwater, soils, and sediments), and such presence promotes the resistance bacteria development, making them ineffective in some diseases treatment. The research project promotes the TiO2 synthesis using yeast culture as biotemplate, the step followed by the microstructure characterization with surface area enhancement; such properties are responsible for the improvement of solar photodecomposition processes of the veterinary antibiotic oxytetracycline. In such simple and standard process conditions the system reaches about 84% of removal percentage with a better agreement with the pseudo-first-order with the Pearson coefficient in the range from 0.82 to 0.94 and K1 = 0.035 M−1∙s−1. The degradation rate constant increased with the increasing initial Yeast-TiO2 dosage until the maximum mass of 0.1 g or with the decreasing of initial oxytetracycline concentration. The solar light used as a sustainable irradiation source is abundant and low cost in tropical countries, perfect to be applied in water treatment to decompose the pharmaceuticals pollutants, as the veterinarian antibiotics. The study demonstrates that solar photodecomposition is an efficient treatment technology for the removal of antibiotics from polluted water and provides insightful information on the potential practical application of this technology to treat contaminated water, possibly also in rural, distant areas.
Palavras-Chave: decomposition; titanium oxides; oxytetracycline; yeasts; solar energy; solar radiation; antibiotics
. Yeast-TiO2 biotemplate for oxytetracycline solar photodecomposition. Journal of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, v. 8, n. 7, p. 12-26, 2020. DOI: 10.4236/msce.2020.87002. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31801. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Yb:KGW self-Raman laser with 89 cm(−1) Stokes shift and more than 32% diode-to-Stokes optical efficiency. Optics and Laser Technology, v. 121, p. 1-4, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105835 Abstract: We report on a Yb3+:KGW self-Raman laser operating at 1096 nm. A 100 μm fiber-coupled diode end-pumped configuration is used to generate a fundamental emission wavelength that strongly depends on internal resonator losses. Stokes emission at 1096 nm is achieved with a slope efficiency of 42 ± 8%, an optical conversion efficiency of more than 32% and a maximum output power of 4.5W for quasi-continuous operation (1 ms pulses). The explored Stokes conversion of 89 cm−1 shows excellent laser characteristics, indicating that this still little explored Stokes shift could pave the way to continuous-wave Raman frequency-comb lasers.
Palavras-Chave: lasers; raman effect; doped materials; solid state lasers; raman spectra; stokes parameters; wavelengths; crystals
. Yb:KGW self-Raman laser with 89 cm(−1) Stokes shift and more than 32% diode-to-Stokes optical efficiency. Optics and Laser Technology, v. 121, p. 1-4, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105835. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30351. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Visible-light photocatalytic activity and recyclability of N-doped TiO2 films grown by MOCVD / Atividade fotocatalítica sob luz visível e reutilização de filmes de TiO2 dopados com N crescidos por MOCVD. Cerâmica, v. 66, n. 380, p. 451-459, 2020. DOI: 10.1590/0366-69132020663802957 Abstract: Nitrogen-doped TiO2 films were grown on borosilicate glass substrates at 400 °C by the metallorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) for removing dye from water under visible light. The effect of N-doping on the structural, surface, and photocatalytic properties of films was evaluated. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses revealed that 1.56 and 2.44 at% of nitrogen were incorporated into the films by varying the NH3 flux during the growth. Methyl orange dye degradation experiments showed that the N-doped films presented photoactivity under visible light. The film containing 2.44 at% of nitrogen exhibited the best photocatalytic behavior, with 55% of efficiency. Recyclability tests under visible light showed that the film efficiency dropped gradually after each test. N-TiO2 films grown by MOCVD have the potential to be used in environmental applications by removing pollutants using a green method under sunlight or even under internal illumination, although its reuse is limited.
Palavras-Chave: photocatalysis; titanium oxides; thin films; nanostructures; chemical vapor deposition; organometallic compounds; nitrogen; doped materials; recycling; x-ray spectra
. Visible-light photocatalytic activity and recyclability of N-doped TiO2 films grown by MOCVD. Cerâmica, v. 66, n. 380, p. 451-459, 2020. DOI: 10.1590/0366-69132020663802957. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31786. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Variations in essential elements after malignant transformation of kidney epithelial tubular cells. Medical & Clinical Research, v. 5, n. 6, p. 114-117, 2020. DOI: 10.33140/MCR.05.06.04 Abstract: Cell line-based research is a valuable tool for the study of cancer physiopathology and the discovery of new drugs for use in clinical practice. In this study, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to estimate Ca, Co, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na, P, S, Se, and Zn in epithelial tubular cells (HK-2) and kidney tumor cells (Caki-1 cells). The most relevant difference was a decrease in the contents of Ca, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na, P, S, and Zn. A significant accumulation of Co was also detected in Caki-1 cells. The fold change variation of each element concentration between HK-2 and Caki-1 cells was Ca (‒0.40), Co (1.37), Cu (‒0.68), Fe (‒0.56), K (‒0.40), Mg (‒0.41), Mn (-0.54), Na (‒0.33), P (‒0.31), S (‒0.26), and Zn (‒0.73). These findings indicate that the elements mainly affect the metabolic pathways of epithelial kidney cells. Thus, our findings open a new avenue for RCC target therapy
Palavras-Chave: kidneys; carcinomas; elements; transition elements; icp mass spectroscopy; transformations; tumor cells; lyophilization
. Variations in essential elements after malignant transformation of kidney epithelial tubular cells. Medical & Clinical Research, v. 5, n. 6, p. 114-117, 2020. DOI: 10.33140/MCR.05.06.04. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31420. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Variability: surface intensity distribution of large-area reference sources. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, v. 160, p. 1-7, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109108 Abstract: In this paper we present the impact of variability, a surface source parameter, on the efficiency evaluation of surface contamination monitors. This study was based on two source uniformity correction methodologies and data from real surface source distributions. Surface source intensity distribution has been changed by rearranging the cells (portions of the active area of each LARS) while keeping the same source uniformity value. Instrument efficiencies have been calculated for different sets of uniformities and variabilities. This study led to emphasize the importance of variability, a differential source intensity distribution parameter, over the uniformity, an integral source intensity distribution parameter, and reinforced the importance of the source uniformity correction procedure on the course of surface contamination monitor calibration.
Palavras-Chave: surface contamination; surface contamination monitors; variations; calculation methods; variational methods; radiation sources; calibration; monte carlo method
. Variability: surface intensity distribution of large-area reference sources. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, v. 160, p. 1-7, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2020.109108. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31345. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Utilização do lítio na indústria nuclear gera parceria entre universidade e empresa no Brasil. Revista Facto, v. 62, p. 18-19, 2020.
Palavras-Chave: nuclear industry; lithium; technology impacts; isotopes; research programs; educational facilities
. Utilização do lítio na indústria nuclear gera parceria entre universidade e empresa no Brasil. Revista Facto, v. 62, p. 18-19, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32388. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Uso de modelagem computacional para avaliação da exposição médica e ocupacional durante procedimento de cardiologia intervencionista. Brazilian Journal of Radiation Sciences, v. 8, n. 1A, p. 1-12, 2020. DOI: 10.15392/bjrs.v8i1A.1086 Abstract: A cardiologia intervencionista (CI) é uma modalidade comum que utiliza imagens fluoroscópicas para o diagnóstico e a terapia de problemas cardiovasculares. Embora os equipamentos de fluoroscopia mais modernos empreguem sistema de redução de dose, além de feixes bem colimados, a radiação espalhada atinge órgãos circundantes do paciente que não estão localizados no feixe primário de radiação. A radiação espalhada pelo corpo do paciente acarreta a exposição ocupacional do médico intervencionista. A avaliação das exposições ocupacional e médica é importante para a determinação dos riscos e das consequências biológicas em diferentes órgãos e tecidos. Neste trabalho, a avalição foi feita por meio do conceito de coeficiente de conversão (CC). Para quantificar os valores de CC, foi utilizado o programa computacional MCNPX e o simulador antropomórfico masculino virtual adulto (MASH3), para representar o paciente e o médico. Os resultados comprovaram a eficiência da proteção dos equipamentos suspensos. Quando não utilizados, um aumento dos valores de CC de dose efetiva podem ser superiores a 1000%.
Palavras-Chave: cardiovascular diseases; computerized simulation; effective radiation doses; equivalent radiation doses; lenses; medical personnel; monte carlo method; occupational exposure; patients; phantoms; photon beams; radiation protection
. Uso de modelagem computacional para avaliação da exposição médica e ocupacional durante procedimento de cardiologia intervencionista. Brazilian Journal of Radiation Sciences, v. 8, n. 1A, p. 1-12, 2020. DOI: 10.15392/bjrs.v8i1A.1086. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31462. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Use of plasma reactor to viabilise the volumetric reduction of radioactive wastes. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, v. 168, p. 1-4, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108625 Abstract: Nuclear reactors, hospitals, industries and research institutes generate considerable amounts of radioactive waste every day. To dispose this waste in a safe and costeffective manner, it must be treated by immobilising the radionuclides and, for better stocking capacity, it must be volumetrically reduced as much as possible. To this end, plasma technology, among other promising technologies for radioactive waste treatment, exposes radioactive waste to temperatures above 1400 °C, thereby substantially reducing its volume. In the planning and managing of radioactive waste, the challenges related to plasma technology are presented as a motivation factor for the possible implantation of plasma reactors in nuclear plants and research centres, thereby improving radioactive waste management. In this study, a thermal plasma treatment process was established, and a plasma reactor was used for compactable waste processing. After 30 min of thermal plasma treatment, the volume reduction factor reached 1:99. The results demonstrate the viability of using a thermal plasma process for the volumetric reduction of radioactive waste in a safe and cost-effective manner.
Palavras-Chave: radioactive materials; radioactive wastes; radioactive waste management; plasma; reactors; radioactive waste storage; reduction; slags; volume; brazilian cnen; plasma technology
. Use of plasma reactor to viabilise the volumetric reduction of radioactive wastes. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, v. 168, p. 1-4, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108625. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31099. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Use of Monte Carlo simulation and the Shadow-Cone Method to evaluate the neutron scattering correction at a calibration laboratory. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, v. 170, p. 1-4, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108624 Abstract: The calibration of radiation detectors is performed with the aim of ensuring accurate measurements of different types of radiation. Due to scattering neutrons, the neutron beam spectrum will not be the same spectrum as that emitted by the neutron source, thus influencing the reading of the instrument to be calibrated and causing a systematic error in the calibration of the neutron measurement devices. The objective of the present work was to estimate the contribution of scattering neutron radiation to fluence and mean energy using the Monte Carlo simulation and the Shadow-Cone Method with the objective of obtaining direct and scattering counting rates. The counting rates obtained at the Neutron Calibration Laboratory at IPEN, using the Bonner sphere spectrometer, were inserted into the NeuraLN program, which uses the UTA-4 response matrix and has 81 bins of energy used to determine the spectrum, fluence rate, and mean energy at the source-detector distances of 100 cm and 150 cm.
Palavras-Chave: monte carlo method; scattering; calibration; neutron detectors; neutron beams; neutron spectra; neutron sources; cones; shadow effect
. Use of Monte Carlo simulation and the Shadow-Cone Method to evaluate the neutron scattering correction at a calibration laboratory. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, v. 170, p. 1-4, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108624. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31440. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Use of calcium alginate beads and Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biosorption of 241Am. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, v. 223-224, p. 1-10, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2020.106399 Abstract: Calcium alginate beads, inactivated Saccharomyces cerevisiae and inactivated S. cerevisiae immobilized in calcium alginate beads (S. cerevisiae–calcium alginate beads) are examined as potential biosorption materials as regards their capacity to remove 241Am. In this study, initial experiments were carried out to evaluate the effects of pH (2 and 4) and 241Am initial concentration: 75, 150, and 300 Bq mL-1. The experiments were conducted in a batch reactor. Higher removal capacity was observed at pH 2 with the use of S. Cerevisiae, whereas pH 4 performed better for the essays with calcium alginate beads and S. Cerevisiae-calcium alginate beads. The pseudo-first-order kinetic model described the kinetics of biosorption. Calcium alginate was the adsorbent of choice to further experiments with synthetic organic liquid waste. A lower removal rate was observed in the organic waste, although calcium alginate beads have also been able to achieve high sorption capacity in less than 4 h. With the organic waste, the highest value of sorption capacity of 241Am was 4.38 × 10−7 mmol g−1 with an initial 241Am concentration of 2.31 × 10−8 mmol L−1.
Palavras-Chave: bioadsorbents; sorption; adsorbents; americium 241; saccharomyces cerevisiae; calcium; alginates; ph value
. Use of calcium alginate beads and Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biosorption of 241Am. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, v. 223-224, p. 1-10, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2020.106399. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31615. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Uptake of silver, gold, and hybrids silver-iron, gold-iron and silver-gold aminolevulinic acid nanoparticles by MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, v. 32, p. 1-10, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.102080 Abstract: Background. Nanoparticles show promise for theranostic applications in cancer. The metal-based nanoparticles can be used both as photosensitizers and delivery vehicles. In bimetallic particles based on gold or silver and iron, a combination of the plasmonic features of the gold or silver components with the magnetic properties of the iron makes these hybrid nanomaterials suitable for both imaging and therapeutic applications. Herein, we discuss toxicity and cell internalization of metallic (silver and gold) and bimetallic (silver-iron, gold-iron, and silver-gold) aminolevulinic acid (ALA) nanoparticles. ALA can control the production of an intracellular photosensitizer, protoporphyrin IX (PpIX), commonly used in photodynamic therapy. Methods. Nanoparticles were synthesized by photoreduction method and characterized by UV/Vis spectra, Zeta potential, FTIR, XRD, and transmission electron microscopy. The amount of singlet oxygen generation by a yellow LED, and ultrasound was studied for gold, gold-iron, and silver-gold nanoparticles. Cytotoxicity assays of MCF-7 in the presence of nanoparticles were performed, and PpIX fluorescence was quantified by high content screening (HCS). Results. Red fluorescence observed after 24 h of nanoparticles incubation on MCF-7 cells, indicated that the ALA in surface of nanoparticles was efficiently converted to PpIX. The best results for singlet oxygen generation with LED or ultrasound irradiation were obtained with ALA:AgAuNPs. Conclusions. The studied nanoparticles present the potential to deliver aminolevulinic acid to breast cancer cells efficiently, generate singlet oxygen, and convert ALA into PpIX inside the cells allowing photodiagnosis and therapies such as photodynamic and sonodynamic therapies.
Palavras-Chave: gold; silver; nanoparticles; mammary glands; neoplasms; drug delivery; reduction; therapy; aminolevulinic acid
. Uptake of silver, gold, and hybrids silver-iron, gold-iron and silver-gold aminolevulinic acid nanoparticles by MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, v. 32, p. 1-10, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.102080. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31812. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Unveiling the high‑temperature dielectric response of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3. Scientific Reports, v. 10, n. 1, p. 1-11, 2020. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-75859-z Abstract: Understanding the physics behind changes in dielectric permittivity and mechanical response with temperature and frequency in lead-free ferroic materials is a fundamental key to achieve optimal properties and to guarantee good performance in the technological applications envisaged. In this work, dense Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 (BNT) electroceramics were prepared through solid-state reaction of highgrade oxide reagents, followed by sintering at high temperature (1393 K for 3 h). In good agreement with previous reports in the literature, the thermal behaviour of dielectric response from these BNT materials showed the occurrence of a high-temperature diffuse-like permittivity peak, whose origin has been so far controversial. Thermally stimulated depolarization current, impedance and mechanical spectroscopies measurements were here conducted, over a wide range of temperature and frequency, to get a deep insight into the mechanism behind of this event. The approach included considering both as-sintered and reduced BNT samples, from which it is demonstrated that the broad high-temperature dielectric peak originates from interfacial polarization involving oxygen vacancies-related spacecharge effects that develop at the grain-to-grain contacts. This mechanism, that contributes to the anomalous behavior observed in the mechanical response at low frequencies, could also be responsible for the presence of ferroelastic domains up to high temperatures.
Palavras-Chave: lead compounds; titanates; zirconium compounds; ceramics; thermal analysis; impedance
. Unveiling the high‑temperature dielectric response of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3. Scientific Reports, v. 10, n. 1, p. 1-11, 2020. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-75859-z. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31819. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Ultrahigh temperature in situ transmission electron microscopy based bicrystal coble creep in Zirconia II: interfacial thermodynamics and transport mechanisms. Acta Materialia, v. 200, p. 1008-1021, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.070 Abstract: This work uses a combination of stress dependent single grain boundary Coble creep and zero-creep ex- periments to measure interfacial energies, along with grain boundary point defect formation and migra- tion volumes in cubic ZrO 2 . These data, along with interfacial diffusivities measured in a companion paper are then applied to analyzing two-particle sintering. The analysis presented indicates that the large acti- vation volume, v ∗= v f + v m primarily derives from a large migration volume and suggests that the grain boundary rate limiting defects are delocalized, possibly due to electrostatic interactions between charge compensating defects. The discrete nature of the sintering and creep process observed in the small-scale experiments supports the hypothesis that grain boundary dislocations serve as sources and sinks for grain boundary point defects and facilitate strain during sintering and Coble creep. Model two-particle sintering experiments demonstrate that initial-stage densification follows interface reaction rate-limited kinetics.
Palavras-Chave: grain boundaries; creep; transmission electron microscopy; temperature range 0400-1000 k; zirconium oxides; sintering; bicrystals; thermodynamics
. Ultrahigh temperature in situ transmission electron microscopy based bicrystal coble creep in Zirconia II: interfacial thermodynamics and transport mechanisms. Acta Materialia, v. 200, p. 1008-1021, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.070. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31586. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Ultrahigh temperature in situ transmission electron microscopy based bicrystal coble creep in zirconia I: nanowire growth and interfacial diffusivity. Acta Materialia, v. 199, p. 530-541, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.069 Abstract: This work demonstrates novel in situ transmission electron microscopy-based microscale single grain boundary Coble creep experiments used to grow nanowires through a solid-state process in cu- bic ZrO 2 between ≈1200 °C and ≈2100 °C. Experiments indicate Coble creep drives the for- mation of nanowires from asperity contacts during tensile displacement, which is confirmed by phase field simulations. The experiments also facilitate efficient measurement of grain boundary diffusivity and surface diffusivity. 10 mol% Sc 2 O 3 doped ZrO 2 is found to have a cation grain boundary diffusivity of D gb = ( 0 . 056 ±0 . 05 ) exp ( −380 , 0 0 0 ±41 , 0 0 0 RT ) m 2 s −1 , and surface diffusivity of D s = ( 0 . 10 ±0 . 27 ) exp ( −380 , 0 0 0 ±28 , 0 0 0 RT ) m 2 s −1 .
Palavras-Chave: creep; temperature range 0400-1000 k; transmission electron microscopy; transmission; zirconium oxides; nanowires; grain boundaries
. Ultrahigh temperature in situ transmission electron microscopy based bicrystal coble creep in zirconia I: nanowire growth and interfacial diffusivity. Acta Materialia, v. 199, p. 530-541, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.069. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31587. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Two-phase flow void fraction estimation based on bubble image segmentation using Randomized Hough Transform with Neural Network (RHTN). Progress in Nuclear Energy, v. 118, p. 1-21, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2019.103133 Abstract: The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has been encouraging the use of passive cooling systems in new designs of nuclear power plants. Next nuclear reactor generations are intended to have simpler and robust safety resources. Natural Circulation based systems hold an undoubtedly prominent position among these. The study of limiting conditions of these systems has led to instability behavior analysis where many different two-phase flow patterns are present. Void fraction is a key parameter in thermal transfer analysis of these flow instability conditions. This work presents a new method to estimate void fraction from images captured of an experimental two-phase flow circuit. The method integrates a set of Artificial Neural Networks with a modified Randomized Hough Transform to make multiple scans over acquired images, using crescent-sized masks. This method was called Randomized Hough Transform with Neural Network (RHTN). Each different mask size is chosen according with bubble sizes, which are the main ‘objects of interest’ in this image analysis. Images are segmented using fuzzy inference with different parameters adjusted based on acquisition focus. Void fraction calculation considers the volume of the imaged geometrical section of flow inside cylindrical glass tubes considering the acquisition depth-of-field used. The bubble volume is estimated based on geometrical parameters inferred for each detected bubble. The image database is obtained from experiments performed on a vertical two-phase flow circuit made of cylindrical glass where flow-patterns visualization is possible. The results have shown that the estimation method had good agreement with increasing void fraction experimental values. RHTN has been very efficient as bubble detector with very low ‘false-positive’ cases (< 0.004%) due robustness obtained through integration between Artificial Neural Networks with Randomized Hough Transforms.
Palavras-Chave: two-phase flow; void fraction; neural networks; image processing; bubbles; fuzzy logic; transformations; nuclear power plants; pattern recognition; natural convection; randomness
. Two-phase flow void fraction estimation based on bubble image segmentation using Randomized Hough Transform with Neural Network (RHTN). Progress in Nuclear Energy, v. 118, p. 1-21, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2019.103133. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30353. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Tribological and mechanical behaviour of 45S5 Bioglass®-based compositions containing alumina and strontium. Ceramics International, v. 46, n. 15, p. 24347-24354, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.216 Abstract: Although bioactive glasses have been widely used for the surfaces of orthopaedic and dental implants, its limited mechanical strength, low toughness and wear resistance have prevented their use as load-bearing devices. Considering that even a small variation in the composition of such materials can deeply modify their features, inducing very different physicochemical or mechanical properties, the present research was conducted by modifying the glass network of 45S5 Bioglass® by adding Al2O3 and SrO to obtain a highly bioactive glass with improved mechanical and tribological performance for biomedical applications. The addition of 2% Al2O3 and 2% SrO produced a dense material with the same elastic modulus as 45S5 (~50 GPa). Moreover, the bending strength increased by 60% and the toughness doubled. The wear rate obtained against steel was found to be three times lower than that of 45S5. From the results, it can be assumed that both alumina and strontium synergistically play crucial roles in the mechanical and tribological properties of these new bioactive glasses.
Palavras-Chave: glass; biological materials; silicates; strontium oxides; wear resistance; coefficient of performance; friction; mechanical properties
. Tribological and mechanical behaviour of 45S5 Bioglass®-based compositions containing alumina and strontium. Ceramics International, v. 46, n. 15, p. 24347-24354, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.216. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31399. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Trace element leaf accumulation in native trees from the remaining Semideciduous Atlantic Forest in Brazil. Atmospheric Pollution Research, v. 11, n. 5, p. 871-879, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.apr.2020.01.015 Abstract: Remnants of Semideciduous Atlantic Forest surrounded by numerous industries, intense road traffic and agricultural lands in Southeast Brazil have been affected by trace elements. We implemented a passive biomonitoring with the three most abundant native tree species (Astronium graveolens, Croton floribundus and Piptadenia gonoacantha) to answer these questions: 1) which species has the greatest potential to accumulate trace elements?; 2) does the leaf accumulation level of trace elements vary between the edge and interior of the forest remnants, between dry and wet periods or due to the distance from the industrial area?; 3) which species, among the most abundant in the forest remnants, would better indicate the spatial variations in trace elements pollution and which elements would be the most relevant for such spatial discrimination? Leaf samples were collected during the dry and wet seasons, at the edge and interior of four forest remnants. Trace elements were determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP MS). Few edge effects were evidenced in the leaf concentrations in all species. Higher concentrations of most trace elements were measured during dry season. Although C. floribundus showed the most accumulating capacity, A. graveolens was the most appropriate species to discriminate spatial variations. The forest closer to the industrial area was distinguished from the others by Mn and Ni from oil burning, but the metal pollution from the industrial area did not interfere on the leaf concentrations in A. graveolens sampled in the urban and rural forests.
Palavras-Chave: air pollution; particulates; deposition; air pollution monitoring; biological indicators; trace amounts; elements; forests; brazil; trees; monitoring; leaves; environment; mass spectroscopy; plasma
. Trace element leaf accumulation in native trees from the remaining Semideciduous Atlantic Forest in Brazil. Atmospheric Pollution Research, v. 11, n. 5, p. 871-879, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.apr.2020.01.015. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31348. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Toxicity and color reduction of a textile effluent containing reactive red 239 dye by electron beam irradiation. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, v. 172, p. 1-5, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108765 Abstract: Textile effluents are a mixture of dyestuff, surfactants, dispersants, acids, alkalis and bleaching agents, among other compounds, and some of these are highly soluble and relatively recalcitrant. Suitable improvement of textile effluents may require combined treatment processes, such as Conventional Treatments and Advanced Oxidative Process (AOPs). Electron beam irradiation (EBI) has been proposed as a possible technology for the treatment of textile effluents. In this context, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficiency of an Electron Beam treatment applied to toxicity and color reduction of a textile effluent containing reactive Red 239 dye. Effluent COD and TOC were also evaluated. The assessed effluents were submitted to EBI treatment at doses ranging from 0.5 to 15 kGy. Vibrio fischeri bacteria and Daphnia similis crustaceans were exposed to both irradiated and non-irradiated effluents, the toxicity was evaluated through EC50 (median effective concentration) calculations. EB irradiation successfully reduced effluent toxicity and color. The EC50 for D. similis(48h) were of 6.31% ± 3.19 (non-irradiated) and 27.56% ± 9.31 (10 kGy), and for V. fischeri(15min), of 7.41% ± 1.52 (nonirradiated) and 31.89% ± 10.99 (10 kGy), respectively. Approximately 70% toxicity reduction was obtained for both organisms, while 95% color reduction was obtained by applying 5 kGy.
Palavras-Chave: toxicity; textiles; effluents; dyes; color; electron beams; textile industry; bacteria; crustaceans; experimental data; environmental impacts; toxic materials; decomposition
. Toxicity and color reduction of a textile effluent containing reactive red 239 dye by electron beam irradiation. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, v. 172, p. 1-5, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108765. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31098. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Total and partial loss of coolant experiments in an instrumented fuel assembly of IEA-R1 research reactor. Nuclear Engineering and Design, v. 363, p. 1-11, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2020.110610 Abstract: The safety of nuclear facilities has been a growing global concern, mainly after the Fukushima nuclear accident. Studies on nuclear research reactor accidents such as the Loss of Coolant Accident (LOCA), many times considered a design basis accident, are important for ensure the integrity of the plant. A LOCA may lead to the partial or complete uncovering of the fuel assemblies and it is necessary to assure the decay heat removal as a safety condition. This work aimed to perform, in a safe way, partial and complete uncovering experiments for an Instrumented Fuel Assembly (IFA), in order to measure and compare the actual fuel temperatures behavior for LOCA in similar conditions to research reactors. A test section for experimental simulation of Loss of Coolant Accident named STAR was designed and built. The IFA was irradiated in the IEA-R1 core and positioned in the STAR, which was totally immersed in the reactor pool. Thermocouples were installed in the IFA to measure the clad and fluid temperatures in several axial and radial positions. Experiments were carried out for five levels of uncovering of IFA, being one complete uncovering and four partial uncovering, in two different conditions of decay heat. It was observed that the cases of complete uncovering of the IFA were the most critical ones, that is, those cases presented higher clad temperatures when compared with partial uncovering cases, for the specific conditions of heat decay intensity and dissipation analyzed. The maximum temperatures reached in all experiments were quite below the fuel blister temperature, which is around 500 °C. The STAR has proven to be a safe and reliable experimental apparatus for conducting loss of coolant experiments.
Palavras-Chave: computer codes; computerized simulation; data covariances; fuel assemblies; loss of coolant; natural convection; r codes; radiosensitivity effects; reactor accident simulation; research reactors; sensitivity analysis
. Total and partial loss of coolant experiments in an instrumented fuel assembly of IEA-R1 research reactor. Nuclear Engineering and Design, v. 363, p. 1-11, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2020.110610. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31409. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. TL/OSL signal of CaSO4:Eu,Ag samples produced by variations of the slow evaporation route. Radiation Measurements, v. 135, p. 1-8, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2020.106334 Abstract: The aim of this work was to produce crystals of CaSO4 doped with europium (Eu) and silver (Ag) nanoparticles, by means of three different preparation routes, and to study their applicability in radiation dosimetry by the TL and OSL techniques. The crystals were produced by variations of the slow evaporation route. Samples of CaSO4: Eu,Ag(a) were obtained using europium oxide and silver particles as dopants. For the growth of the crystals of CaSO4:Eu,Ag(b), silver was incorporated in nitrate form. CaSO4:Eu,Ag(c) phosphorus were synthetized mixing europium oxide in a colloidal suspension of silver nanoparticles. Optical characterization confirmed the presence of Eu3þ/Eu2þ in the crystal matrix. Dosimetric characteristics were evaluated after the exposure of the samples to a90Sr/90Y source. The CaSO4:Eu,Ag(a) and CaSO4:Eu,Ag(b) composites presented the most intense signals, the lowest detectable doses, and showed a linear and reproducible dose response, but the CaSO4:Eu,Ag(a) samples showed the best potential for application in TL/OSL dosimetry.
Palavras-Chave: thermoluminescence; photoluminescence; nanoparticles; dosimetry; radiation sources; synthesis; calcium sulfates; x-ray diffraction; dosemeters
. TL/OSL signal of CaSO4:Eu,Ag samples produced by variations of the slow evaporation route. Radiation Measurements, v. 135, p. 1-8, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2020.106334. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31422. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 348
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
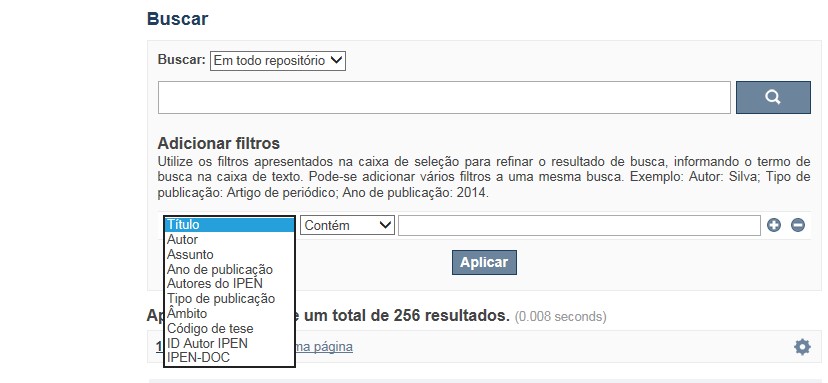
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
