Navegação Periódicos - Resumos por ano de publicação "2017"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Periódicos - Resumos
- →
- Navegação Periódicos - Resumos por ano de publicação
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Periódicos - Resumos por ano de publicação "2017"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 32
-
. Periodontal treatment combined to antimicrobial photodynamic therapy: experimental model. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, v. 49, n. S28, p. 42-43, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/lsm.22650 Abstract: Background: Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (APDT) has been used as an adjuvant treatment for periodontitis. It combines a photosensitizer (PS) with a light source to induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and kill microbial cells. PpNetNI is a protoporphyrin derivate, and it has a chemical binding site at biofilm and great affinity to microbial cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of APDT as an adjuvant treatment for periodontitis. Study: Ten healthy male rats Wistar (Rattus norvegicus) were used in this study (Approved by UNINOVE Ethical committee AN0029/2015). Periodontitis was induced by placing a cotton ligature around the first mandibular molar in a subgingival position. The contralateral mandibular first molar received neither a ligature nor any treatment, and was used as a control. After 7 days, the ligature was removed and all animals received scaling and root planning (SRP) and were divided according to the following treatments: SRP group (received SRP and irrigation with PpNetNI, 10 mM) and PDT group (PpNetNI 10 mM followed by LED irradiation). PDT was performed with a LED (630 nm) with an output power of 400mW (fluence-rate 200mW/cm2; fluence 18 J/cm2). Rats were euthanized at 7 days postoperatively. The bone loss was measured by Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT, THORLABS LTD., Newton, US). Data were analyzed statistically (Mann-Whitney test, p<0.05). in vestibular region of the first molar Results: The animals treated by APDT showed a bone gain of approximately 30% compared to the SRP group following 7 days from the treatment. OCT was able to detect bone loss in the samples and it was nondestructive method for this experimental model. Conclusion: In conclusion, within the parameters used in this study, APDT was an effective alternative to held periodontal health after treatment, and it was able to regenerate supportive periodontal tissue.
Palavras-Chave: experimental data; antimicrobial agents; photosensitivity; dentistry; bone cells; diagnostic techniques
. Periodontal treatment combined to antimicrobial photodynamic therapy: experimental model. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, v. 49, n. S28, p. 42-43, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/lsm.22650. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28802. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Novo fotoabsorvedor para irradiação com laser de Nd:YAG na prevenção de erosão em dentina. Brazilian Oral Research, v. 31, suppl. 2, p. 112-112, 2017. Abstract: A erosão dentária tem sido estudada por ser um fator de risco para o dano dentário. As técnicas de Tomografia por Coerência Óptica (OCT), microdureza e fluorescência de raios-X foram utilizadas para analisar amostras de dentina irradiadas com laser Nd:YAG utilizando uma solução de dentifrício preto como fotoabsorvedor e submetidas a ciclagem erosiva. A utilização de um fotoabsorvedor favorece a absorção da maioria dos fótons na superfície do tecido duro, diminuindo o risco de lesão da polpa dental por aquecimento. 75 blocos de dentina bovina de 8mm2 foram distribuidos em 5 grupos: G1- sem tratamento; G2- aplicação de flúor fosfato acidulado (APF, [F-]=1,23%, pH= 3,3 a 3,9); G3- irradiação com laser de Nd:YAG (1064nm, 0,6W, 10Hz) sem fotoabsorvedor; G4- irradiação com laser de Nd:YAG (1064nm, 0,6W, 10Hz) utilizando pasta de carvão como fotoabsorvedor; G5- irradiação com laser de Nd:YAG (1064nm, 0,6W, 10Hz), utilizando dentifrício (Black is White, Curaprox®) como fotoabsorvedor. Todas as amostras foram submetidas a um desafio erosivo de 3 dias (ácido cítrico 1%, pH = 3,6, 5min, 2x/dia) sob agitação e remineralização (saliva artificial, pH = 7,0, 120min). Após os tratamentos, os valores de microdureza foram maiores nos grupos irradiados com laser e a relação [Ca]/[P] diminuiu nestes mesmos grupos. A avaliação por OCT foi feita antes e após os tratamentos e também após a ciclagem erosiva, a profundidade das lesões de erosão foram menores nos grupos irradiados com laser e fotoabsorvedor.. Novo fotoabsorvedor para irradiação com laser de Nd:YAG na prevenção de erosão em dentina. Brazilian Oral Research, v. 31, p. 112-112, 2017. suppl. 2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29203. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. New methodology for binding Iodine-125 onto silver for brachytherapy sources manufacture. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2828-2828, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304 Abstract: Purpose: Cancer is a major health care problem in Brazil and the world. The Brazil’s National Institute for Cancer estimates around 60,000 new prostate cancer cases for 2017. We are assembling a laboratory for production of iodine-125 sources used in prostate brachytherapy in Brazil, since the imported treatment is extremely expensive, thus only available in the private healthcare sector. There are several challenges when developing a laboratory to produce radioactive sources. From choosing a prototype to radiation safety, the task is enormous. The whole production line is full of new process and innovations. Among those, a new chemical reaction that deposit iodine-125 onto silver (core) was developed. This paper presents a new reaction for binding iodine-125 into a silver core. The fixation percentage was calculated by measuring the activity in an ionization chamber. This methodology will be implemented at the iodine-125 sources manufacture laboratory. Methods: Silver cores are washed with an etching solution (100% sulfuric acid) for 5 minutes with sonication. The cores were then placed in sodium sulfate for at least 3 days. They went from a silver matte to a black color. The reaction was allowed to proceed overnight. Each core was individually measured. Results: The yield was 69.2% 7.1%. Considering the silver attenuation is around 20% the results were consider satisfactory. Conclusion: By maximize the reaction yield, we will be able to generate a less costly product that will be available through our public healthcare.
Palavras-Chave: brachytherapy; iodine 125; silver; neoplasms; therapy
. New methodology for binding Iodine-125 onto silver for brachytherapy sources manufacture. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2828-2828, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31136. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. New method for depth analysis of Y-TZP t-m phase transformation. Dental Materials, v. 33, suppl. 1, p. e6-e6, 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.08.009 Abstract: Purpose/aim: The aim of this studywas to validate the optical coherence tomography (OCT) as a nondestructive method of analysis to evaluate the depth of tetragonal to monoclinic (t-m) transformed zone and to calculate the kinetics of phase transformation of a monolithic Y-TZP after hydrothermal aging. Specifically, to compare the activation energy of t-m transformation calculated by the depth of the transformed zone using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and OCT. Materials and methods: Fully sintered (1450 ◦C/2 h) discs of dentalY-TZP (LAVAPLUS, 3M-ESPE)were aged in hydrothermal pressurized reactor to follow the phase transformation kinetics at 120 to 150 ◦C. Four samples per aging time were analyzed by OCT (OCP930SR, Thorlabs Inc.), = 930 nm, spectral bandwidth (FWHM) of 100 nm, nominal resolution of 6 m (lateral and axial) in air, declared digital resolution 3.09 m (axial). Three areas of 3mm (lateral) were observed to calculate the phase transformation depth (Image J). X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) were performed, Cu-K , 20◦ to 80◦, 2 . The data were refined using the Rietveld method (GSAS). The transversal section of one specimen of each group was submitted to backscattered SEM analysis to calculate the phase transformation depth (Image J). The speed of the transformation zone front was determined plotting the phase transformation depth versus aging time. Results: XRD results indicated that Y-TZP that 66% is the maximum value of monoclinic phase concentration for all aged Y-TZP. The activation energy for the monolithic Y-TZP was 107.53 kJ/mol. One year and 5 years of hydrothermal aging at 37 ◦C will present approximately 4.21% and 15% of monoclinic phase, respectively. The comparison of the depth of the transformed zone using SEM and OCT were similar, showing a linear behavior and providing information that the opaque layer observed by OCT is related to the depth of the transformed zone (Fig. 1), any difference among the results could be a result of the refraction index correction. The energy of activation calculated by SEM and OCT were 114 kJ/mol and 100 kJ/mol, respectively. The speed calculated for the phase transformation into the bulk of the transformed zone estimated for 37 ◦C was 0.04 m/year (SEM) and 0.16 m/year (OCT). Conclusions: The results indicate that activation energy values determined by SEM and OCT observations were similar allowing the use of the OCT as a tool for monolithic Y-TZP t-m phase transformation kinetic evaluation. Moreover, OCT method has the advantage of a shorter analysis time, without the need of sample preparation steps.
Palavras-Chave: crystal-phase transformations; tomography; optical modes; coherence length; scanning electron microscopy; measuring methods
. New method for depth analysis of Y-TZP t-m phase transformation. Dental Materials, v. 33, p. e6-e6, 2017. suppl. 1, DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.08.009. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28641. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. New core configuration for producing Iodine 125 seeds. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2828-2829, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304 Abstract: Purpose: Cancer is one of the most complex public health problems. Prostate cancer is the second most common among men. In prostate brachytherapy use Iodine-125, which is fixated on a silver substrate, then inserted and sealed in a titanium capsule. This work proposes a new source configuration using epoxy resin substrate. Methods: Comparation and analysis methods were used to define the methodology for combining iodine-125 in polymers. The parameters were immersion time, reaction type, concentration of the adsorption solution, specific activity of the radioactive solution, need for carrier and chemical form of radioactive iodine. Results: The methodology developed with an epoxy resin was very good. The final radioactive intake on the resin was higher than 80%. The immobilization of the radioactive solution occurred in the matrix, without any loss or deposition of undesirable materials on its surface, as evidenced by the smear test. The material maintains its integrity when autoclaved at 140 °C. The curing process of the resin was 40 minutes. With the value of the initial activity of the Iodine solution by mass (774.2 lCi/g), it was possible to calculate the immobilization efficiency Average of 680 lCi/g. The immersion test in distilled water at room temperature did not exceed the limit allowed by ISO 9978, which is 5 nCi (185 Bq), proof of no leakage. In a computational simulation by the Monte Carlo Method, PENELOPE, the simulations were consistent with the values adopted by the literature for the GE Healthcare model 6711, which shows the value of the dose rate constant as 0, 965 cGy.U-1.h-1. Conclusion: The effective method for combining iodine-125 in epoxy resin was determinated. The major advantage was the high efficiency percentage fixation, around 82,1 3,2%, and the simplicity and safety of the process.
Palavras-Chave: neoplasms; prostate; iodine 125; polymers; epoxides; resins
. New core configuration for producing Iodine 125 seeds. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2828-2829, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31135. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. A new approach to obtain the catalytic sites region of human sACE with correct fold and activity. Journal of Biotechnology and Biomaterials, v. 7, n. 1, p. 96-96, 2017. DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X.C1.071 Abstract: Angiotensin-converting enzyme I (ACE) is a membrane-bound that catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I to the potent vasopressor angiotensin II. ACE is a key part of the renin-angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure and is widely distributed throughout the body. There are two isoforms of human ACE, including the somatic ACE (sACE) present in somatic tissue and the testicular ACE (tACE) present in male germinal cells. The sACE possesses two domains, N- C- domains, with catalytic sites which exhibit 60% sequence identity. These domains differ in terms of chloride-ion activation profiles, rates of peptide hydrolysis of angiotensin I, bradykinin, Goralatide, Luliberin, substance P, angiotensina, beta-amyloid peptide and sensitivities to various inhibitors. A more detailed analysis shows that these regions are composed of HEMGH and EAIGD sequences that bind zinc ions to facilitate catalytic activity (Fig. 1). Our question is: If the synthesis of catalytic sites with corrects structure and activity could be a good model per si to study new drugs. The objective was to obtain the Ala361 a Gli468 and Ala959 to Ser1066 catalytic regions sACE in a structural conformation that resembles its native form. The catalytic regions were obtained from bacterial system; the expression of this protein in soluble form enables completion of the solubilization/purification steps without the need for refolding. The characterization of Ala959 to Ser1066 region shows that this has an α-helix and β-strand structure, Fig. 1b, which zinc ion (essential for its activity) binds to, and with enzymatic activity. Our conclusion is that the strategy used to obtain the Ala959 to Ser1066 region in the correct structural conformation and with activity was successful.
Palavras-Chave: angiotensin; enzyme inhibitors; zinc ions; bacteria
. A new approach to obtain the catalytic sites region of human sACE with correct fold and activity. Journal of Biotechnology and Biomaterials, v. 7, n. 1, p. 96-96, 2017. DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X.C1.071. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31166. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Microstrutural evolution of nickel-based superalloy processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP). Acta Microscópica, v. 26, Supplement B, p. 71-72, 2017. Abstract: The present work shows the microstructural (under optical microscopy) and Vickers hardness evolution of a nickel-based superalloy Inconel 600 (alloy 600) before and after deformed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) that significantly modified the alloy microstructure and, consequently, its strength. Alloy 600 is an austenitic nickel-based superalloy with 72% nickel, 14-17% chromium and 6-10% iron and it is commonly used in structures and components that work in aggressive environments. The grain size plays a significant role in the mechanical properties in this alloy; so, it is important to understand how processing techniques modify the microstructure of the material. In fact, ECAP is a processing technique involving the application of severe plastic deformation (SPD) used in the manufacture of metals and alloys with ultra-fine grains (UFG) and therefore with extraordinary combinations of both high strength and high ductility [1]. For the research, alloy 600 rods, supplied by Multialloy, with 8 mm diameter, were heat treated at 1200 °C for 6 h (solution), as shown in Figs. 1a and 1b, to achieve a larger grain size. The generated products were machined to the final dimensions of the specimen (6 X 6 X 25 mm) shown in Fig. 1c and then processed by ECAP, at room temperature using route A, in a D2 tool steel die, whose angles Φ and Ψ are 120° and 0° (Fig. 1d). Samples were pressed repetitively through a total of three passes, the microstructural aspect of the samples after each pass are shown in Figs. 2 and 3 with different magnifications. Metallographic preparations were made in the transverse, longitudinal and normal directions, TD, LD and ND of each sample. Sanding step with grit 320, 600 and 1200 were used. Polishing steps included 3 um- and 1 um-diamond paste and 0.05 um-alumina suspension and finally they were etched for optical examination using Marble’s etchant (10 g CuSO4, 50 ml HCl and 50 ml H2O). The micrographs were taken with OLYMPUS optical microscope model BX51M, with magnifications of 100x and 200x. The hardness tests were conducted in a Buehler Micromet 2103 microdurometer in the LD of the samples. For each measurement, a load of 500 g was applied for 15 s. Five separate measurements were taken on each sample at randomly selected points and then averaged. In Figs. 1a and 1b, it is possible to see only 1 phase, a solid solution of Ni-Cr-Fe, a coarsed grain structure and annealing twins. There are slight changes in the microstructure after the first pass, some strain marks are seen. After the second and third passes the microstructure shows highly deformed grains, deformation and transition bands. The values of hardness (Tab. 1) show an increase after each pass. In summary, (1) the micrographs analysis shows all the transformations from an annealed state to a highly-deformed state; (2) the grains are yet elongated after 3 passes and possibly do not show an expected UFG structure; (3) deformation twinning is revealed and is possible to see strain marks, deformation and transition bands; (4) the hardness values increased due to the high strain imposed to the alloy.
Palavras-Chave: heat resisting alloys; microstructure; pressing; vickers hardness
. Microstrutural evolution of nickel-based superalloy processed by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP). Acta Microscópica, v. 26, p. 71-72, 2017. Supplement B. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31242. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Microstructural analysis of composite Cu-Cr-Ag-(CeO2, Al2O3) processing by powder metallurgy. Acta Microscópica, v. 26, B, p. 280-281, 2017. Abstract: Copper has long been used by mankind, since the 20th century they have gained industrial and technological importance [1]. They can be combined with ceramic materials in the synthesis of modern composites, optimized and with balanced properties [2]. The studied composite has a metal as a matrix (copper or copper, chromium and silver), the ceramic oxide as the reinforcing phase (ceria or alumina) and was synthesized by powder metallurgy. A possible application of this material is like anodes in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC), cermets based on rare earth oxides and metals such as copper, silver and nickel have been studied in this component [3]. The objective of this work was the analysis of the particle size by SEM and chemical composition by EDS of the starting material (powders of copper, chromium, silver, ceria and alumina) and the microstructural characterization by MO of copper composites with four compositions: (a) 80% Cu – 8% Cr – 4% Ag – 8% CeO2; (b) 80% Cu – 20% CeO2; (c) 80% Cu – 8% Cr – 4% Ag – 8% Al2O3; (d) 80% Cu – 20% Al2O3. For analysis in the SEM/EDS the powders were fixed in the sample port with carbon paint, for the powders of ceria and alumina was made gold coating for 2 min. The copper powder presented nodular agglomerates; the chromium powder presented large particles with coarse contours and irregular shape; the silver powder presented a dendritic shape; the ceria powder presented very small particles and it was not possible to observe them due to the limitation of the SEM and the alumina powder presented flake-shaped agglomerates, figure 1. The EDS microanalysis results for copper, silver, ceria and alumina powders were adequate, for chromium powder indicated silicon and iron (manufacturer predicted) and calcium impurities (not predicted but with low percentage), figure 1. The powders were weighed on a precision balance (according to each composition), mixed manually and cold-compacted in uniaxial press with 180 MPa pressure and sintered in a tubular furnace with vacuum of 10-7 torr, temperature of 750 °C and time of 6 h. The samples were obtained in laboratory scale with a 31x12x 3.5 mm parallelepipedal shape, hot mounting, grinded (240, 320, 400, 600, 800) and polished (3μm and 1μm diamond and 0.02 μm silica). The optical micrographs indicated coalescence of copper particles, homogeneity, porosity and an unknown (black) phase, possibly related to ceramic materials, figure 2. The sample (c) was the only one that presented different microstructure between the normal and transverse directions, possibly due to segregation of the powders during mixing. It was possible to make an adequate analysis of the particle formats of the copper, chromium, silver and alumina powders; however, the ceria powder needs to be analyzed again in SEM with higher capacity of increase. The results of EDS microanalysis were promising for all powders. The optical micrographs suggest a good adequacy of the compaction and sintering parameters, forming a homogeneous microstructure and with the desired porosity, except for sample (c), that the mixture was not suitable. In order to study the formed phases it is necessary to perform an X-ray mapping on SEM and X-ray diffraction in the samples after sintering.. Microstructural analysis of composite Cu-Cr-Ag-(CeO2, Al2O3) processing by powder metallurgy. Acta Microscópica, v. 26, p. 280-281, 2017. B. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29128. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Methodology for in vivo dosimetry using TLD-100 for radiotherapic treatment. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2898-2899, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304 Abstract: Cancer is a public health problem that affects approximately 27 million people worldwide. The most common type in Brazil among men is prostate cancer with 61 thousand cases. There are two forms of radiotherapy treatments that can be used: teletherapy and brachytherapy. Before starting the teletherapy treatment, a planning is done that makes the acquisition of the anatomical information of the patient to then classify the areas of interest. Dosimetry is performed as a quality control to ensure that the calculated dose is equal to that received by the patient. In vivo dosimetry acts as an independent measurement and this work aims at comparing the dosimetry performed using thermoluminescent dosimeters (LiF: Mg, Ti - TLD - 100) with dose values calculated in the planning system (TPS). Methods: All dosimeters were prepared to be used in an anthropomorphic phantom. A selection of dosimeters, 50 micro TLD’s, selected after heat treatment, were then irradiated and a reading was made. A case planned by TPS was selected and compared the dosimetry performed in an anthropomorphic phantom for the same case. Results: All values obtained were within the deviation ( 5%) allowed by the protocol. The results of this work will help to implement a new quality program in the Radiotherapy Service at Hospital das Cl ınicas de S~ao Paulo. Conclusion: The accurate dosimeter selection provided a feasible and reliable evaluation that enabled the comparison.
Palavras-Chave: neoplasms; prostate; radiotherapy; brachytherapy; thermoluminescent dosimetry
. Methodology for in vivo dosimetry using TLD-100 for radiotherapic treatment. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2898-2899, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31134. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Mechanical properties of Y:TZP/TiO2 coated with hydroxyapatite for dental implants. Dental Materials, v. 33, suppl. 1, p. e54-e54, 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.08.106 Abstract: Purpose/aim: (1) To investigate the effect of titania content in mol% (0, 10 and 30) in the specific surface area (SBET), the size of the agglomerates and the intensity of the peaks corresponding to crystalline phase present in the ceramic powder of Y:TZP/TiO2; (2) to investigate the effect of titania addition (0, 10 and 30 mol%) on the microstructure, relative density (RD), Young’s modulus (E), Poisson’s ratio (PR), flexural strength ( f) andWeibull modulus (m) of a Y:TZP/TiO2 composite; and (3) to investigate the effect of the presence of a biomimetic coating on the microstructure and mechanical properties ( f and m) of Y:TZP/TiO2 composite. Materials and methods: Y:TZP (3mol% of yttria) and Y:TZP/TiO2 composite (10 or 30mol% of titania) were synthesized using a co-precipitation route. The powders were pressed and sintered at 1400 ◦C/2 h. Half of the discs were subjected to biomimetic coating. The powderswere characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), laser scattering, gas adsorption and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The surfaces, with and without biomimetic coating, were characterized by SEM and XRD. The RD was measured by the Archimedes’ principle. E and PRwere measured by ultrasonic pulse-echo method. For the mechanical properties the specimens (n = 30 for each group) were tested in a universal testing machine. Weibull modulus was estimated by the maximum likelihood method and ANOVA with Tukey test (˛ = 5%) was used to evaluate f, E and RD. Results: All powders had a SBET greater than 42m2/g and the titania addition favored the formation of larger agglomerates. Titania addition increased the grain size of the composite and caused a significant decrease in the f in MPa (control: 815.4a; T10: 455.7b and T30: 336.0c), E in GPa (control: 213.4a; T10: 155.8b and T30: 134.0c) and relative density in % (control: 99.0a; T10: 94.4c and T30: 96.3b) of the Y:TZP/TiO2 composite. The presence of 30% titania caused substantial increase in m and PR. Biomimetic coating resulted in the formation of apatite globules heterogeneously distributed on the surface of the material and this treatment did not significantly alter the f and m of the composite (Table 1). Conclusions: The Y:TZP/TiO2 composite coated with a layer of CaP has great potential to be used as implant material. Properties of the powderwere affected by titania addition. Addition of titania toY:TZP caused an increase in grain size, a significant decrease in f, E and RD. The presence of biomimetic coating did not jeopardize the reliability of Y:TZP/TiO2 composite.
Palavras-Chave: titanium oxides; composite materials; apatites; dentistry; implants
. Mechanical properties of Y:TZP/TiO2 coated with hydroxyapatite for dental implants. Dental Materials, v. 33, p. e54-e54, 2017. suppl. 1, DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.08.106. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28642. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Measurement of Iodine-125 radioactive solid waste derived from sources production laboratory for brachytherapy. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2974-2975, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304 Abstract: Purpose: This study aims to present a solid waste management plan for the laboratory of radioactive sources production (LPFR), iodine-125 brachytherapy seeds, located at the Energy and Nuclear Research Institute (IPEN). After the implementation, it is expected to meet a demand of 8000 seeds per month. Methods: Waste from the production of Iodine-125 sources is classified as “Very Low Level Waste Disposal” (T1/2 ≤ 100 days) in the IAEA regulations. Despite that, they have levels of activity above the limits established in standard (CNEN 8.01) needing adequate management in order to guarantee the safety of the installation, operators and environment. The solid waste is generated in Glove box 1, were the fixation reaction (iodine-125 – core) takes place. The wastes from this production are absorbent papers and filters used in surface and air decontamination processes; glass vials, syringes and needles, used in the fixation reaction. Measures of mass, volume and values of activities generated over 5 years of production were performed for each glove box by estimating different scenarios throughout production (supplier switching, variation in activity by radioactive source, etc.). The concentration of activity was also determined in order to meet the criteria established in the standard for safe release of the waste. Results: The final volumes and activities calculated indicated that the laboratory has enough space for temporary storage until the release to the environment (thus not requiring treatment, transport, and another place for management). The data collected proved that a secure management system for radioactive waste within the facility is possible. Conclusion: The management proposed by this work was able to safely contemplate all stages of waste management. This data is indispensable for the construction and licensing of the laboratory.
Palavras-Chave: radioactive waste management; solid wastes; iodine 125; brachytherapy; regulations; waste disposal
. Measurement of Iodine-125 radioactive solid waste derived from sources production laboratory for brachytherapy. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2974-2975, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31133. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Influência da irradiação com laser Er,Cr:YSGG sobre a resistência de união de braquetes ortodônticos. Brazilian Oral Research, v. 31, suppl. 2, p. 395-395, 2017. Abstract: A proposta deste estudo foi investigar os efeitos da irradiação com laser Er,Cr:YSGG na resistência de união da interface esmalte-braquete. Após aprovação pelo Comitê de Ética em Experimentação Animal da Universidade Federal de Pernambuco (protocolo número 23076.015869/2015-65), foram selecionados 40 incisivos bovinos, divididos aleatoriamente em quatro grupos (G) (n=10), três experimentais e um controle, com diferentes doses de irradiação com laser de Er,Cr:YSGG sobre a superfície do esmalte: G1 - 54,1 mJ/ 1,1 W, 20 Hz; G2 - 83 mJ/ 1,7W, 20 Hz; G3 - 120 mJ/ 2,41 W, 20 Hz; G4 - controle, condicionamento de esmalte com ácido fosfórico a 37%. Os espécimes foram analisados através da tomografia por coerência Óptica (OCT) e da microscopia eletrônica de varredura (MEV) para verificação das alterações promovidas no esmalte. Para análise estatística foram utilizados os testes de Tukey, ANOVA e o Qui-quadrado, adotando um nível de significância de 5%. O G3 apresentou a resistência de união mais elevada (8,0 MPa). A análise de ANOVA não revelou diferenças estatisticamente significativas entre os grupos (p = 0,1310). A análise qualitativa das imagens pelo OCT e MEV revelam que as superfícies irradiadas apresentaram microfissuras que auxiliam a penetração da resina.. Influência da irradiação com laser Er,Cr:YSGG sobre a resistência de união de braquetes ortodônticos. Brazilian Oral Research, v. 31, p. 395-395, 2017. suppl. 2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29206. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Incorporation of the methylene blue photosensitizer in the presence of glucose in strains of candida albicans with multidrug efflux systems. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, v. 49, n. 4, p. 438-438, 2017. Abstract: Background: Infectious diseases are responsible for 60% of deaths in developing countries.Candida albicans cause severe infection in immunocompromised patients and the commonly used treatments have not been effective against microbial resistance. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a new promising strategy to microbial inactivation based on the use of photosensitizer (PS) in the presence of oxygen and activation by light to form reactive oxygen species.C.albicanshas glucose sensors which could facilitate the entrance of the PS. The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of glucose in the photodynamic inactivation of C. albicans. Study: C. albicans ATCC 10231, YEM 12, YEM 13, YEM 14, and YEM15were aerobically grown on Sabouraud agar and incubated at 308C for 24 hours. Microbial inoculants were divided into 4 groups with and without glucose: Control; Only irradiation; PS toxicity and PDT groups with three irradiation times.After going throughthe treatments, the colony-forming units were counted and the data were subjected to statistical analysis (ANOVA) and Tukey test. To measure the concentration ofMB, fluorescence spectroscopy and flow cytometry were used. Results: We observed that yeast with overexpression of Major Facilitator Superfamily membrane pore tend to accumulate more MB in its cytoplasm, whereas strains that overexpress ABC pumps demonstrated the greater survival against the photodynamic challenge. Conclusion: PDT is an efficient strategy against C. albicans and the presence of glucose can intervene in the photodynamic effect. The presence of MB in the intracellular region of the yeast predisposes to greater photodynamic inactivation, however, its germicidal capacity is related to the type and characteristics of the microbial.. Incorporation of the methylene blue photosensitizer in the presence of glucose in strains of candida albicans with multidrug efflux systems. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, v. 49, n. 4, p. 438-438, 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27922. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Heavy metals presence in lipsticks: investigation of health impacts and their disposal in the environment. Applied Research in Toxicology, v. 2, suppl. 1, p. 57-57, 2017. Abstract: Lip cosmetics are involved in two major discussions: the public health and environmental problems. From this information, we intend to analyze the impact on human health, study the relationship among price, duration and color and investigate what are the possible impacts on the environment, assuming some waste disposal routes. The cosmetics analyzed were lipsticks, divided by brand, price and color. The first analysis was by x-ray fluorescence (XRF). Then, the raw material went through digestion with nitric and hydrochloric acids under heating, and diluted with distilled water, then filtered. The following readings were performed by optical emission spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma (ICP-OES). From the results of the analysis by XRF (found 18 metal elements), the matrix for analysis by ICP-OES is composed of: aluminum, calcium, cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, iron, potassium, manganese, nickel, lead, silicon and titanium. Toxic metals have been identified (Ni, Mn, Cd and Cr) in the samples. Although the examined lipsticks showed positive for toxic metals (Pb, Cd, Ni, Cr and Mn), their levels comply with national legislation, regard to limits for cosmetics and foods. However, it is important to note that the cosmetic and food laws have great differences in the limits for heavy metals. The study of disposal for lipsticks showed that even lipsticks that are most used, there is a waste of nearly 1/3 of the product due to the inner package. This information may help in a conscious consumption of lipsticks, including the risk associated with the use of a set of makeups (foundation, eyeshadows, mascara, blush and lipstick) with other cosmetics.. Heavy metals presence in lipsticks: investigation of health impacts and their disposal in the environment. Applied Research in Toxicology, v. 2, p. 57-57, 2017. suppl. 1. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28111. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Gamma irradiated soluble extracts of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites induced better humoral and cellular immune response due to preferential uptake by APCs scavenger receptors. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, v. 95, n. 5, S, p. 174-174, 2017. DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.abstract2016 Abstract: Toxoplasmosis occurs in one-third of the adult world population, without adequate vaccines and causing disease in fetus or specific groups. Aside to sterilizing effect, gamma radiation acts on antigens inducing enhanced antisera production against snake venoms or cell and humoral response to recombinant leprosy proteins. Gamma radiation affects proteins directly or indirectly in water by action of oxidant radicals from water radiolysis. Early reports showed gamma irradiated crotoxin had enhanced uptake by macrophages, limited by scavenger receptors competitors, as probucol. Irradiated tachyzoites induced adequate immune response with protection, attributed to mitotic death and DNA damage. Irradiated proteins could take a part in this process and we study the immune response induced by gamma irradiated soluble extracts of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, using mice immunized with native proteins as controls. Mice immunized with irradiated extracts without adjuvants showed significant protection after challenge with ME-49 (p<0.05) and RH (p<0.0001) strains compared to controls. There are increased specific and high avidity IgG production (p<0.05) when compare d to controls group. By flow cytometry and in vitro culture, spleens of mice immunized irradiated extract presented increased proliferation of CD4+, CD8+ and B cells and IFN-γ production as compared to controls. J774 cells had increased uptake of biotinylated irradiated extracts as compared to the uptake of native extract (p<0.05), due to longer and continuous uptake. All these data points to an alternative and effective uptake and immune processing of irradiated T. gondii extracts, probably due to specific receptor of oxidized proteins as scavenger receptors, resulting in enhanced immunity. This data also implies that irradiated proteins could be involved in the protection induced by irradiated parasites. Use of antigen gamma radiation can be a simple process to enhance vaccine efficiency, avoiding the use of adjuvants.
Palavras-Chave: immunity; protozoa; proteins; gamma radiation; parasitic diseases
. Gamma irradiated soluble extracts of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites induced better humoral and cellular immune response due to preferential uptake by APCs scavenger receptors. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, v. 95, n. 5, p. 174-174, 2017. S, DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.abstract2016. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31159. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Four years of estrogenic activity assessment in surface waters of São Paulo State, Brazil. Applied Research in Toxicology, v. 2, suppl. 1, p. 32-32, 2017. Abstract: Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) have the ability to alter the endocrine system of organisms. Such compounds are present in several industrial and domestic activities and reach the aquatic environment via wastewater discharges or agricultural surface runoff. The aim of this study was to determine the overall estrogenic activity of surface waters of São Paulo State, Brazil. For this purpose, 10 sites from the routine Surface Water Quality Program of CETESB were selected that were already surveyed for physical, chemical and biological variables from 2013 to 2016. Samples were extracted in solid phase and tested for estrogenic activity using bioluminescent yeast estrogen assay (BLYES). Results were expressed in 17-estradiol equivalent quotient (EEQ). Estrogenic activity was below the limit of quantification (0.1 EEQ) in 31.7% of 227 samples. All sites presented estrogenic activity at least once. The results have shown the presence of estrogenic activity in a range from 0.11 to 26.6 EEQ in the sampling sites in four years of study. Statistical analysis showed a positive correlation between estrogenic activity and the biochemical oxygen demand performed in the samples, indicating that this activity detected in most sites is related to wastewater discharges. Due to the presence of estrogenicity higher than 5.0 EEQ in a few sampling sites, further chemical analyses and other bioassays are recommended in order to provide a better understanding of the estrogenic activity present at these sites.. Four years of estrogenic activity assessment in surface waters of São Paulo State, Brazil. Applied Research in Toxicology, v. 2, p. 32-32, 2017. suppl. 1. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28109. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Fatigue limit of Y-TZP reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Dental Materials, v. 33, suppl. 1, p. e19-e19, 2017. DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.08.036 Abstract: Purpose/aim: To compare the Cyclic Fatigue Limit (CFL) of a control yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia pollycristal (Y-TZP) with a composite produced by adding multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNT) into Y-TZP. Materials and methods: CNT were coated with zirconium oxide and yttrium oxide to form a powder (CNT/ZYO) using a hydrothermal co-precipitation method. Powders made of Y-TZP + (CNT/ZYO) were produced using 99 vol% of Y-TZP and 1 vol% of CNT/ZYO. CAD-CAM blocks (42.5×16.0×16.0mm) were obtained by uniaxial pressing (67MPa/30 s) of each powder in a steel matrix. These blocks were partially sintered at argon atmosphere (1100 ◦C/1 h/5 ◦C/s) and then sectioned to produce 14 bar-shaped specimens (3.0×4.0×25.0mm/edges chamfered according to ISO6872:2008) of each material, which were sintered also in argon atmosphere (1.400 ◦C/4 h/5 ◦C/min). Density measured by Archimedes’ method was used to calculate the relative density (RD), based on the theoretical values for both materials (6.06 g/cm3). Flexural strength (FS) was measured in four-point bending with specimens immersed in water at 37 ◦C (inner and outer supports of 10 and 20 mm). CFL was determined in four-point bending, using the staircase method (10,000 cycles/5 Hz). In each cycle, the stress varied between the maximum stress (MS) and 50% of MS. The applied stress in the first specimen was 50% of FS. After 10,000 cycles, in case the specimen did not fracture, 10MPa was added to the next specimen. RD and FS were analyzed by Student’s t test (alpha = 5%). CFL was calculated according to: CLF =X0+d(SUMini/SUMni±0.5), where X0 is the lowest stress value tested, d is the stress added or subtracted to each cycle and n is the number specimens that survived or failed in each stress level. The lowest stress level was computed as i = 0, and the next one was computed as i=1, and so on. Fracture surfaces were fractographically analyzed. Results: Specimens containing nanotubes showed significantly lower RD compared to the control (p = 0.009). Nanotube addition also caused a 50% significant decrease in FS (p = 0.003). However, the FS coefficient of variation for the control was higher (17%) compared to that of the composite (10%). CFL calculated for the control was 2.5 times higher than that of the composite. The %CFL (CFL in terms of percentage of the FS) was also higher for the control. Fractography indicated fracture origins associated to surface defects and porous regions related to nanotube agglomerates. Conclusions: The processing method used to produce the composite Y-TZP/nanotubes needs to be improved since nanotube addition to Y-TZP caused a significant reduction of the relative density, strength and fatigue limit.. Fatigue limit of Y-TZP reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Dental Materials, v. 33, p. e19-e19, 2017. suppl. 1, DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.08.036. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28614. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Experiment to access Iodine-125 leakage in different vials. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 3146-3146, 2017. Abstract: Purpose: There are several challenges when developing a laboratory to produce radioactive sources. From choosing a prototype to radiation safety, the task is enormous. During the past 15 years, our research group is developing a laboratory to produce iodine-125 seed. These seeds are placed inside the cancer and release radiation directly in the target. The whole production line is full of new process and innovations. Among those, a new chemical reaction that deposit iodine-125 onto silver (core) was developed. This paper presents a comparison between vials in order to access their capability to retain radioactive iodine. Also, the fixation percentage in a silver core was taken into account. This information will be used to select a vial to be implemented at the iodine-125 sources manufacture laboratory. Methods: Vials made with polymers and glass was tested. Iodine-125 were placed in the vials overnight at rt. Seven vials with different materials (glass, dark glass, and plastics) were evaluated. Results: The selected vial (borosilicate glass 1 mL total volume) loss 17.61% of iodine in 24 hours and presented the highest iodine intake. It was noticeable that the vial material influenced both iodine intake and iodine loss. The goal is to maximize the reaction yield to result in a less costly product. Conclusion: We have selected the best vial for our reaction in regards to leakage and yield.
Palavras-Chave: iodine 125; leak detectors; silver; borosilicate glass
. Experiment to access Iodine-125 leakage in different vials. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 3146-3146, 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27822. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Efficiancy of hydrogen peroxide for cleaning production areas and equipments in the Laboratory for Brachyterapy Sources Production. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2828-2828, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304 Abstract: Purpose: A great challenge in the brachytherapy sources production is to fulfill the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) requirements, involving the process validation and of all supporting activities such as cleaning and sanitization. The increasingly strict requirements for quality assurance system, with several norms, normative resolutions and rules that must follow both medical products and radiochemical requirements, has led to a constant validation concerns. The main goal of GMP is to reduce inherent risks such as product contamination with microorganisms and cross-contamination. Methods: In the Laboratory for Brachytherapy Sources Production it was established a cleaning program for cleanrooms and hot cells using a hydrogen peroxide solution (6%). This work aims to assess the effectiveness of this cleaning agent in reducing and/or eliminating microbial load into the cleanrooms and equipments to acceptable levels in accordance with the current legislation. Results: The analysis was conducted using the results of the environmental monitoring program with settling contact plates in cleanrooms after the cleaning procedures. Furthermore, it was possible to evaluate the action of the sanitizing agent on the microbial population at the equipment and cleanrooms’ surfaces. It was also evaluated the best way to accomplish the cleaning program considering the dosimetry factor in each production process, hence the importance of radiological contamination. All the following environmental monitoring procedures presented satisfactory results, showing that the cleaning procedures was able to reduce and maintain the acceptable levels of viable and non-viable particles for the cleanroom classification (ISO 5 and ISO 7). The cleaning process with this sanitizer (hydrogen peroxide) can be performed quickly right before the production; allowing the production of brachytherapy sources without after use residues. Conclusion: This data will help the production of a clean and reliable product.
Palavras-Chave: radiopharmaceutical; isotope production; cleaning; equipment; clean rooms; pollution sources; contamination; hydrogen peroxide
. Efficiancy of hydrogen peroxide for cleaning production areas and equipments in the Laboratory for Brachyterapy Sources Production. Medical Physics, v. 44, n. 6, p. 2828-2828, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12304. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31132. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Efeito do laser de Femtossegundos no tratamento de superfície de cerâmicas à base de zircônia. Brazilian Oral Research, v. 31, suppl. 2, p. 403-403, 2017. Abstract: Este estudo objetivou analisar a superfície de cerâmicas à base de zircônia irradiadas por pulsos ultracurtos de um laser de Ti:Safira. Para isto, dois discos de zircônia (In-Ceram YZ® - Vita Zahnfabrik) com 15,3 mm de diâmetro foram irradiados por pulsos de 25 fs (1 fs=10-15 s) em 800 nm, com energia por pulso variando de 25 a 200 μJ, e taxa de repetição de 0,2 a 4 kHz. Cada irradiação varreu uma área de 1 × 1 mm2, com velocidades entre 0,2 e 4 mm/s, deslocamento lateral de 10 μm, e diâmetro de feixe de 40 ou 70 μm que resultaram em sobreposições de 65 ou 190 pulsos por posição, respectivamente. Uma amostra foi irradiada em atmosfera e a outra sob fluxo de argônio. Em cada uma foram feitas 24 irradiações com condições diferentes. As áreas foram analisadas por perfilometria óptica, Microscopia Eletrônica de Varredura e EDS. Foram escolhidas as áreas que apresentaram pequeno aumento de rugosidade (Ra) em relação ao material não irradiado - Ra=(0,32±0,02) μm - e menor alteração de cor, sem que houvesse alteração na composição. Os melhores resultados foram obtidos para irradiações em atmosfera por pulsos de 25 μJ, focalizados para 40 μm (densidade de energia de 2,0 J/cm2), e taxas de repetição de 0,2, 1 e 4 kHz, com rugosidades de (0,40±0,03) μm, (0,50±0,05) μm e (1,19±0,11) μm, respectivamente, e para pulsos de 50 μJ e 40 μm de diâmetro a 1 kHz, com Ra=(0,40±0,03) μm.. Efeito do laser de Femtossegundos no tratamento de superfície de cerâmicas à base de zircônia. Brazilian Oral Research, v. 31, p. 403-403, 2017. suppl. 2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29207. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 32
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

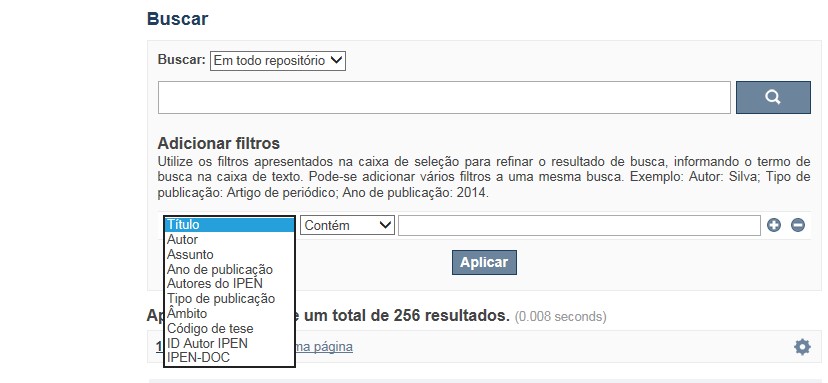
A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
