Navegação Eventos - Resumos por Agências de fomento "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Eventos - Resumos
- →
- Navegação Eventos - Resumos por Agências de fomento
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Eventos - Resumos por Agências de fomento "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 104
-
. Adsorption isotherms for the removal of Am-241 in radioactive liquid wastes using magnetite nanoparticles. In: PAN AMERICAN CONGRESS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY, 1st, 27-30 de novembro, 2017, Guarujá, SP. Abstract... 2017. Abstract: Americium-241 (Am-241) is a radionuclide with half-life of 432 years, emitting alpha particles and low gamma energy and it is also considered radiotoxic. Am-241 is produced, in a low level, from nuclear fuel and laboratory wastes. Magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4) are iron oxides that possess highly magnetic properties, and its application for removal of water contaminants refers due to its high surface area which allows the adsorption capability and the facility to be prepared and removed from the aqueous medium. In This study, magnetite was synthesized by coprecipitation method largely described. Batch experiments were accomplished at room temperature, at pH 6 and the contacts varying from 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 minutes and at 30 minutes for the isotherms experiments. The solid containing magnetite and Am-241 were removed with a magnet and the solution analyzed in a gamma-ray spectrometer (Canberra Model GX2518) which could be quantified. Results show that magnetite possess a capability of removal up to 80% of Am-241 at room temperature, indicating that magnetite nanoparticles are a good sorbent for the removal of radionuclides. Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherms models were investigated and the parameters obtained. Langmuir’s isotherm showed constants of KL (75.7575 L/mg), Q (0.1617 mg/g) and R2 (0.9892) and Freundlich’s isotherm exhibited values of KF (2.6416 [(mg/g).(L/mg)1/n]), 1/n (0.7853 mg/g) and R2 (0.8395), which indicates that the Am- 241 removal from magnetite fits more suitable the Langmuir isotherm model. The thermodynamics parameters, such as the enthalpy and entropy of adsorption, the activation energy, as well as, the kinetics studies are under development.. Adsorption isotherms for the removal of Am-241 in radioactive liquid wastes using magnetite nanoparticles. In: PAN AMERICAN CONGRESS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY, 1st, 27-30 de novembro, 2017, Guarujá, SP. Abstract... 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29047. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Advances on Nafion-based composites for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. In: BRAZIL MRS MEETING, 16th, September 10-14, 2017, Gramado, RS. Abstract... São Carlos, SP: Aptor Software, 2017. p. 55-55. Abstract: PEMFC (Proton exchange membrane fuel cell) is considered a promising and efficient hydrogen fuelled electrical power source. However, PEMFC faces several technical problems, such as sluggish electrode reaction kinetics involving the limiting rate of the oxygen reduction and alcohol oxidation reactions, and high resistance to ion transport that could be surpassed with increasing of the operation temperature. The main impediment for such a temperature increase is the water dependent performance of the state-of-the-art Nafion electrolyte. Above 80 ºC water starts to evaporate considerably and Nafion microdomains begin to shrink, disrupting its percolative structure, leading from a conductor to insulator transition. In this work, the incorporation in-situ or ex-situ of an inorganic phase with hydrophilic properties, such as TiO2 and SiO2, into Nafion membranes has been evaluated as an interesting alternative to produce stable electrolytes able to operate at higher temperatures (130o C). The physical-chemistry and electrochemical characterisation has shown that the inorganic particles located in both the nonionic and ionic regions of the ionomer have important contributions to enhanced thermal stability and water uptake. Such features resulted in significant improvements of the PEMFCs using composite electrolytes tested at high operating temperature and low relative humidity. In addition, remarkable enhancement on the DEFC (Direct Ethanol Fuel Cell) performance (122 mW cm‑2) has been obtained as a result of an increase of ethanol oxidation reaction rate promoted by the combination of enhanced catalyst activity and high temperature of operation using stable composite Nafion-SiO2 electrolytes.. Advances on Nafion-based composites for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. In: BRAZIL MRS MEETING, 16th, September 10-14, 2017, Gramado, RS. Abstract... São Carlos, SP: Aptor Software, 2017. p. 55-55. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31196. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. AEOLUS calibration and validation activities at SPU Lidar Station - Brazil. In: EUROPEAN LIDAR CONFERENCE, November 18-20, 2020, Granada, Spain. Resumo expandido... 2020. p. 1-2.. AEOLUS calibration and validation activities at SPU Lidar Station - Brazil. In: EUROPEAN LIDAR CONFERENCE, November 18-20, 2020, Granada, Spain. Resumo expandido... 2020. p. 1-2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32325. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Aerobic co-oxidation of hemoglobin and aminoacetone. In: SILVA, FERNANDO de C. da (Org.) REUNIAO ANUAL DA SBQ, 45., 31 de maio - 3 de junho, 2022, Maceió, AL. Resumo... São Carlos, SP: Aptor Software, 2022. p. 164-164. Abstract: Aminoacetone (1-aminopropan-2-one), a putative minor biological source of methylglyoxal, reacts like other -aminoketones such as 6-aminolevulinic acid (first heme precursor) yielding electrophilic -oxoaldehydes, ammonium ion and reactive oxygen species by metal- and hemeprotein catalyzed aerobic oxidation 1,2. A wealth of reports implicates methylglyoxal in protein crosslinking and DNA addition, leading to age-related disorders, including diabetes 3,4. Importantly, methylglyoxal-treated hemoglobin adds four water-exposed arginine residues, which may compromise its physiological role and potentially serve as biomarkers for diabetes 5. In this work, we investigate the co-oxidation of aminoacetone and oxyhemoglobin in normally aerated phosphate buffer, leading to structural changes in hemoglobin, which might reportedly be attributed to the addition of aminoacetone-generated methylglyoxal to the protein. Hydroxyl radical-promoted chemical damage to hemoglobin may also occur in parallel, which is suggested by EPR-spin trapping studies with 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide and ethanol. Concomitantly, oxyhemoglobin is oxidized to methemoglobin, as indicated by characteristic CD spectral changes in the absorption Soret and visible regions. Overall, these findings may contribute to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying human diseases associated with hemoglobin dysfunctions (e.g., diabetes) and with aminoacetone in metabolic alterations related to excess of glycine and threonine (e.g., threoninemia, cri-du-chat syndrome).. Aerobic co-oxidation of hemoglobin and aminoacetone. In: SILVA, FERNANDO de C. da (org.) REUNIAO ANUAL DA SBQ, 45., 31 de maio - 3 de junho, 2022, Maceió, AL. Resumo... São Carlos, SP: Aptor Software, 2022. p. 164-164. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/33966. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Alteração da susceptibilidade de C. albicans resistente ao fluconazol após terapia fotodinâmica. In: VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (Ed.); SOARES, ALCIMAR B. (Ed.); FÉLIX, RODRIGO P.B. da C. (Ed.); VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (Org.); MAIA, JOAQUIM M. (Org.); PICHORIM, SÉRGIO F. (Org.); GAMBA, HUMBERTO R. (Org.); COSTA, EDUARDO T. (Org.) CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ENGENHARIA BIOMÉDICA, 25., 17-20 de outubro, 2016, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Resumo... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2016. p. 2336-2336. Abstract: Introdução: As doenças infecciosas causadas por fungos ainda representam um grande desafio para os profissionais de saúde e a comunidade científica, especialmente as infecções causadas por micro-organismos resistentes aos fármacos antifúngicos convencionais. Novas alternativas de tratamento foram estudadas, entre elas a terapia fotodinâmica (PDT) que surgiu como uma promissora modalidade terapêutica por causar a morte de micro-organismos a partir da associação de um fotossensibilizador e luz. Recentemente observamos que a PDT realizada em condições subletais aumenta a suscetibilidade do fungo Candida albicans ao fluconazol [1]. Dando continuidade a este estudo iniciamos a investigação em C. albicans que apresentam diferentes mecanismos de resistência aos antifúngicos. Assim, o presente trabalho teve o objetivo de avaliar o efeito antimicrobiano da associação de PDT e fluconazol em C. albicans que apresenta um sistema de efluxo responsável pela resistência ao antifúngico. Materiais e Métodos: Para a realização deste trabalho foi utilizado C. albicans YEM 13, uma cepa com expressão exacerbada de bomba de efluxo da família MFS (Major Facilitator Superfamily). As células foram submetidas a PDT com azul de metileno na concentração final de 50 μM e irradiadas com parâmetros subletais (=660 nm, 75 mW/cm2, 4 min)[1]. Para investigar a atividade antimicrobiana do fluconazol foram determinados os valores de concentração mínima inibitória (CMI) do crescimento celular. A CMI foi determinada pelo método de microdiluição em caldo de acordo com as normas estabelecidas pelo Comitê Europeu de Teste à Susceptibilidade Antimicrobiana (EUCAST)[2]. A solução de fluconazol (Sigma Aldrich, São Paulo, Brasil) foi preparada, considerando a potência do fármaco de 98% e a faixa de concentrações testadas foi de 0,125-64 μg/mL. Os valores de CMI foram determinados por meio da leitura da absorção em 530 nm, em espectrofotômetro (SpectraMax M4, Molecular Devices, EUA). Para cada grupo foi determinada a menor concentração da droga que promoveu a inibição ≥ 50% do crescimento em comparação ao controle livre de drogas. Foram avaliadas células C. albicans YEM 13 sem tratamento e previamente submetidas a PDT subletal. Foi utilizado como controle a cepa de C. albicans ATCC 90028 que não apresenta resistência ao fluconazol. Resultados: C. albicans ATCC 90028 apresentou valor de CMI de 0,5 μg/mL, dado compatível com os descritos na literatura. As amostras de célula YEM 13 que não foram submetidas à PDT apresentaram o valor de CMI de 64 μg/mL, que também coincide com o valor descrito na literatura [3]. Estes dados demonstram que a cepa YEM 13 apresenta um valor de CMI 128 vezes superior ao de uma cepa suscetível ao fluconazol (ATCC 90028). Confirmando nossa hipótese, o fluconazol foi mais ativo em C. albicans submetida previamente à PDT subletal. Dentro da faixa de 0,125-64 μg/mL, houve maior inibição do crescimento celular quando previamente submetido à PDT, resultando na redução do valor de CMI de 64 μg/mL para 32 μg/mL. Conclusões: Foi possível demonstrar que a PDT pode aumentar a susceptibilidade ao fluconazol em cepa de C. albicans que apresentam bombas de efluxo da família MFS. Estes resultados preliminares sugerem que a associação terapêutica entre a PDT e o fluconazol pode ser uma importante alternativa no tratamento de infecções por cepas de C. albicans que apresentam resistência a este antifúngico. Vale ressaltar que neste trabalho foram utilizadas condições subletais e resultados ainda mais promissores podem ser obtidos com a otimização dos parâmetros de irradiação.. Alteração da susceptibilidade de C. albicans resistente ao fluconazol após terapia fotodinâmica. In: VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (ed.); SOARES, ALCIMAR B. (ed.); FÉLIX, RODRIGO P.B. da C. (ed.); VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (org.); MAIA, JOAQUIM M. (org.); PICHORIM, SÉRGIO F. (org.); GAMBA, HUMBERTO R. (org.); COSTA, EDUARDO T. (org.) CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ENGENHARIA BIOMÉDICA, 25., 17-20 de outubro, 2016, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Resumo... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2016. p. 2336-2336. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31297. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Amazon CH4 budget and its controls based on atmospheric data from vertical profiles measurements. In: EGU General Assembly, May 4-8, 2020, Online. Abstract... Göttingen, Germany: Copernicus, 2020. Abstract: Wetland emissions are considered the main natural global Methane (CH4) source, but it is budget remains highly uncertain. Tropical regions like the Amazon, host some of the largest wetlands/seasonally flooded areas on the globe. However, tropical regions are still poorly observed with large-scale integrating observations. Here we present the first atmospheric sampling of the lower troposphere over the Amazon using regular vertical profile greenhouse gas and carbon monoxide (CO) observations at four sites. Since 2010 we collected bimonthly CH4, to provide solid seasonal and annual CH4 budgets with large spatial resolution. Vertical profiles are sampled using light aircraft, high-precision greenhouse gas and CO analysis of flask air, fortnightly between 2010 to 2018. The results show a regional variation in CH4 emissions. There are comparably high emissions from the northeast part of the Amazon exhibiting strong variability, with particularly high CH4 fluxes in the beginning of the wet season (January to March). A second period of high emissions occurs during the dry season. The cause of the high emissions is unclear. In the other three sites located further downwind along the main air-stream are observed lower emissions, that represents approximately 25-30% of what is observed in the northeast region and with a clear annual seasonality. In addition, these data show an interannual variability in emissions magnitude, so we discuss how these data can be correlate to climate variables (like temperature and precipitation) and with human-driven changes (like biomass burning) that could be influencing this variability. Over the full period the Amazon (total area of around 7.2 million km2) was a source of CH4, of approximately 46 ± 6 Tg/year, which represent 8% of the global CH4 flux to the atmosphere. Using a CO/CH4 emission ratio calculated in this study we find a biomass burning contribution varying between 10 and 23% of the total flux at each site.
Palavras-Chave: methane; atmospheres; carbon monoxide; greenhouse gases; wetlands
. Amazon CH4 budget and its controls based on atmospheric data from vertical profiles measurements. In: EGU General Assembly, May 4-8, 2020, Online. Abstract... Göttingen, Germany: Copernicus, 2020. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31676. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Analyzing the effects of biomass in the Amazon region on the São Paulo urban boundary layer. In: EUROPEAN LIDAR CONFERENCE, November 18-20, 2020, Granada, Spain. Resumo expandido... 2020. p. 1-2.. Analyzing the effects of biomass in the Amazon region on the São Paulo urban boundary layer. In: EUROPEAN LIDAR CONFERENCE, November 18-20, 2020, Granada, Spain. Resumo expandido... 2020. p. 1-2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32326. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Antimicrobial activity of Graphene Oxide/Silver nanocomposite obtained by Electron Beam. In: PAN AMERICAN CONGRESS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY, 1st, 27-30 de novembro, 2017, Guarujá, SP. Abstract... 2017. Abstract: Graphene oxide is a carbon-based nano material that has a high specific surface area, high chemical stability, excellent electrical and thermal conductivities, high mechanical resistance, the oxygen groups facilitate dispersion in polar solvents and its functionalization. In the literature, is described several methods of metal incorporation on graphene oxide surface using toxic reagents or with long periods of reaction. The objective of this work is to develop an innovative and sustainable method of incorporating silver into graphene oxide that does not involve toxic reagents or generated residues. in a short reaction time at room temperature beyond the use of the as an alternative process to the chemical processes traditional.A silver solution in the complex form was added to a dispersed graphene oxide in water/isopropanol solution. The mixture wassubmitted to a dose of radiation ranged from 150 to 400 KGy using a electron beam acelerator. The nanocomposite GO/Ag characterization was performed by thermogravimetry analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XDR), scanning transmission electron microscope coupled to the energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (TEM/EDS). The antimicrobial activity of GO/Ag was observed by Escherichia coli, a Gram negative bacterium and Bacillus subtilis a Gram positive bacterium in solid culture medium. The minimum inhibitory concentration of GO/Ag was 50 mg/L. .It is noteworthy that the incorporation of silver occurred at the same time the reduction of graphene oxide without the generation of toxic chemical residues.. Antimicrobial activity of Graphene Oxide/Silver nanocomposite obtained by Electron Beam. In: PAN AMERICAN CONGRESS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY, 1st, 27-30 de novembro, 2017, Guarujá, SP. Abstract... 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29060. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Assessment of burn wounds status using mid-infrared spectroscopy. In: SBFOTON INTERNATIONAL OPTICS AND PHOTONICS CONFERENCE, October 7-9, 2019, São Paulo, SP. Abstract... Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE, 2019. p. 20-21. Abstract: Burns are one of the major causes of morbidity and the most costly traumatic injuries worldwide. Better understanding of the molecular mechanisms associated with wound healing might provide improved clinical strategies to speed up the tissue repair process and reduce the global impact of burns on public health services. The traditional techniques used to assess the biochemical events related to wound repair are laborious, time-consuming and require multiple staining. Thus, the present study aims to evaluate the feasibility of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in order to monitor the progress and healing status of burn wounds. Third-degree burn injuries were induced on Wistar rats by water vapor exposure. Afterwards, biopsies specimen was extracted for further histopathological examination and spectroscopic evaluation at 4 time-points (3, 7, 14 and 21 days). Raw spectral data were offset-corrected and normalized by amide I band area. The second derivatives were compared by the Principal Component Analysis (PCA). On days 3 and 7, when compared to healthy group, biomolecules bands were most prominent. However, on days 14 and 21, these molecular bands decreased. Therefore, our pairwise comparison revealed that metabolic activity induced by thermal injury decreases as the healing process progresses. Our findings show that FTIR spectroscopy can monitor the biochemical development induced by burn injury and detect the status of wound repair.. Assessment of burn wounds status using mid-infrared spectroscopy. In: SBFOTON INTERNATIONAL OPTICS AND PHOTONICS CONFERENCE, October 7-9, 2019, São Paulo, SP. Abstract... Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE, 2019. p. 20-21. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32225. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Assessment of osteoporosis through laser speckle imaging: an in vitro model. In: BRAZILIAN CONGRESS IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, 27th, October 26-30, 2020, Vitória, ES. Abstract... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2020. p. 66-67.. Assessment of osteoporosis through laser speckle imaging: an in vitro model. In: BRAZILIAN CONGRESS IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, 27th, October 26-30, 2020, Vitória, ES. Abstract... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2020. p. 66-67. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31678. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Avaliação da biodistribuição do radiofármaco Fluorestradiol-18F em animais sadios e com modelo tumoral. In: CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE MEDICINA NUCLEAR, 34., 4-7 de setembro, 2020, Online. Resumo expandido... São Paulo, SP: Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Nuclear, 2020. Abstract: O Fluorestradiol-18F (FES-18F) é um radiofármaco promissor para utilização, por método não-invasivo de tomografia de emissão de pósitrons (PET) no diagnóstico de câncer de mama ER+. Estudos pré-clínicos em animais sadios e com modelo tumoral desenvolvido com células MCF-7 apresentaram captação do FES-18F nos órgãos com receptores de estrogênio, tumor e significativa captação no fígado e intestinos, com perfil metabólico semelhante ao estradiol.. Avaliação da biodistribuição do radiofármaco Fluorestradiol-18F em animais sadios e com modelo tumoral. In: CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE MEDICINA NUCLEAR, 34., 4-7 de setembro, 2020, Online. Resumo expandido... São Paulo, SP: Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Nuclear, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31975. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Avaliação da espessura da epiderme em hemangioma por optical coherence tomography. In: VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (Ed.); SOARES, ALCIMAR B. (Ed.); FÉLIX, RODRIGO P.B. da C. (Ed.); VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (Org.); MAIA, JOAQUIM M. (Org.); PICHORIM, SÉRGIO F. (Org.); GAMBA, HUMBERTO R. (Org.); COSTA, EDUARDO T. (Org.) CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ENGENHARIA BIOMÉDICA, 25., 17-20 de outubro, 2016, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Resumo... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2016. p. 2331-2331. Abstract: Introdução: Os Hemangiomas são lesões vasculares que comumente encontradas na região da cabeça e pescoço, atingindo cerca de 10% das crianças ao redor do mundo [1]. O diagnóstico precoce pode levar ao tratamento das lesões e redução de suas consequências estéticas e psicológicas causadas ao paciente. A biopsia excisional é o padrão ouro para diagnostico a nível celular, porém é uma técnica invasiva e que pode causar efeitos colaterais. As alternativas não invasivas disponíveis são a tomografia computadorizada (CT), a imagem por ressonância magnética (MRI) e o ecografia por ultrassom (US) [1, 2]. Tanto o CT quanto o MRI apresentam um custo proibitivo para aplicações clínicas de rotina. Já o US está presente em hospitais e possui custo mais acessível com aplicações no diagnóstico vascular. A imagens US atinge camadas profundas com resolução e alguns milímetros no do tecido biológico, não atendendo aos hemangiomas que aparecem nas camadas mais superficiais da pele. Uma possível alternativa é a técnica Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) que produz imagens em seção transversal com resolução micrométrica do tecido biológico utilizando luz. Ela encontra aplicações na dermatologia [3] e pode ser usado para caracterização funcional, óptica ou morfológica de tecido biológico. O objetivo deste trabalho foi avaliar as diferenças de espessura da epiderme em regiões de lesão vascularizada e normal utilizando a técnica OCT. Materiais e Métodos: As imagens OCT foram adquiridas utilizando-se um sistema OCT swept source com resolução axial de 9 μm e lateral de 18 μm. As imagens possuem 512x1024 pixel (axial x lateral) e foram adquiridas a uma taxa de 25 quadros / s. Este estudo foi aprovado pelo Comitê de Ética do IMIP (protocolo no. 728.993). Neste estudo fo ram utilizadas imagens da mão de um paciente nas regiões de hemangioma e pele sadia, possibilitando a identificação de suas diferenças. Foi implementado um algoritmo em ambiente Matlab para determinar a espessura da epiderme em todas as 541 imagens de lesão vascularizada e as 50 de pele normal. Resultados: Através da medição automatizada da espessura da epiderme na região de lesão e sadia (figura 1) foi possível observar a distribuição de profundidade em cada uma destas regiões. A região de lesão possui uma distribuição de profundidade mais estreita e com espessura menor que a de pele normal. Já a região de pele normal apresenta uma distribuição mais larga, porém com dois valores de maior probabilidade, isso se deve tanto a presença de glândulas mais visíveis na pele sadia quanto a uma maior presença de papilas dérmicas na junção derme-epiderme. Conclusões: A medição da espessura da epiderme mostrou-se válida como um possível marcador da presença de hemangioma. O uso desta abordagem poderia ser complementar a outros marcadores possíveis de serem extraídos do sinal OCT. A ampliação do painel de estudo e comparação com outras técnicas padrão ouro deverá ser realizada em futuros estudos.. Avaliação da espessura da epiderme em hemangioma por optical coherence tomography. In: VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (ed.); SOARES, ALCIMAR B. (ed.); FÉLIX, RODRIGO P.B. da C. (ed.); VIEIRA NETO, HUGO (org.); MAIA, JOAQUIM M. (org.); PICHORIM, SÉRGIO F. (org.); GAMBA, HUMBERTO R. (org.); COSTA, EDUARDO T. (org.) CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ENGENHARIA BIOMÉDICA, 25., 17-20 de outubro, 2016, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Resumo... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2016. p. 2331-2331. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31294. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Avaliação de propriedades de consolidados fabricados por manufatura aditiva usando a fusão seletiva a laser em pós aço inoxidável AISI 316L. In: CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ENGENHARIA E CIÊNCIA DOS MATERIAIS, 24., 6-10 de novembro, 2022, Águas de Lindóia, SP. Resumo... 2022. Abstract: Neste estudo foi utilizado como material partida o pó de aço inoxidável AISI 316L para fabricação de consolidados em dimensões padronizadas, usando do processo de Fusão Seletiva a Laser (FSL), que é uma técnica de fabricação por manufatura aditiva (MA). Foram variados diversos parâmetros de processo tais como, potência e velocidade do feixe, distância entre os passes do feixe laser (hachura), estratégia de varredura e sentido de fabricação, visando estudar o efeito na: porosidade aberta, densidades geométrica e hidrostática, rugosidade e microestrutura. Verificou-se que o uso da relação potência do laser e velocidade de movimentação do laser com intervalos diferentes de distância entre os passes foi acertado na fabricação de amostras consolidadas com baixa porosidade aberta, elevada densidade geométrica e hidrostática (acima de 98% da densidade teórica) e baixa rugosidade. A microestrutura observada apresentou uma morfologia refinada, do tipo celular e dendrítica dentro dos grãos proveniente da alta velocidade de resfriamento, elevado gradiente de temperatura e variações de concentração de elementos de liga . A região de fratura indicou características com morfologia dúctil, com a presença de poros isolados e pequenas micro cavidades (“dimples”).. Avaliação de propriedades de consolidados fabricados por manufatura aditiva usando a fusão seletiva a laser em pós aço inoxidável AISI 316L. In: CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ENGENHARIA E CIÊNCIA DOS MATERIAIS, 24., 6-10 de novembro, 2022, Águas de Lindóia, SP. Resumo... 2022. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/33763. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Biochemical changes in serum of obese mice related to photoactivation of brown adipose tissue. In: CONGRESSO DA SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE BIOFISICA, 43., 27-30 de setembro, 2018, Santos, SP. Resumo... Rio de Janeiro: Sociedade Brasileira de Biofísica, 2018. p. 35-35. Abstract: Obesity is closely related to the development of insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes. Mammal fat consists of white and brown adipose tissues (WAT and BAT). Although most fat is energy-storing WAT, brown adipocytes dissipate energy as heat. Thus, the thermogenic capacity of BAT and its activation makes it an interesting target for treating metabolic syndrome (MS). On the other hand, photobiomodulation (PBM) has proven to be beneficial to manage the chronic inflammatory component of obesity and hyperglycemia by irradiating WAT. However, PBM has still not been used to activate BAT. In this work, obese and hyperglycemic mice were treated with PBM, and their BAT was irradiated. The mouse serum was collected and submitted to attenuated total reflection (ATR)- Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to evaluate the biochemical changes promoted by PBM. Five animals were fed with standard food (normal diet – ND) and used as negative control. The remaining 10 animals were submitted to a hyperlipidic diet (high fat – HF) and their body mass, Lee index and glycemia were measured weekly during 15 weeks to induce MS. After MS establishment, the HF animals were divided into two groups: HF and HF660. The HF660 group was exposed to six irradiation sessions using a 662 ± 20 nm LED. The radiant exposure was 5.7 Jcm-2 at 19 mWcm-2 per session, delivered at 300 s, on days 1, 3, 7, 10, 14 and 21. The HF group was sham-irradiated. After the treatment ended, the mouse serum was collected from cardiac puncture under deep anesthesia. Serum samples were prepared and analyzed by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. The lipid absorptions were responsible for the clearest differences among the IR spectra. An intense C=O stretching absorption at 1742 cm-1 was noticed only for HF group. Acyl CH2 stretching absorptions at 2853 and 2925 cm−1 were also more pronounced in HF group. After PBM, these major lipid peaks decreased their vibrational modes. In fact, hierarchical cluster analysis identified the similarities between the spectra and grouped ND and HF660 groups into a same cluster. Taking together, our findings suggest that PBM applied to the BAT is able to promote biochemical changes in serum of obese mice mainly in lipid bands.. Biochemical changes in serum of obese mice related to photoactivation of brown adipose tissue. In: CONGRESSO DA SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE BIOFISICA, 43., 27-30 de setembro, 2018, Santos, SP. Resumo... Rio de Janeiro: Sociedade Brasileira de Biofísica, 2018. p. 35-35. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29723. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Borate and silicate glasses as high-dose linear response dosimeters. In: INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON CERAMICS, 7th; CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CERÂMICA, 62., June 17-21, 2018, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Abstract... 2018. p. 829-829. Abstract: The search for new sensor materials is a continuous effort in materials engineering field. Aspects such as lower production costs and better sensitivity response, are of great technological importance and the main goals on this quest. The food and medical industries are the ones that benefit most from this research. In the food industry, for example, one of the processes that have been widely used is the application of high doses of gamma radiation in fruits and vegetables. Ionizing radiation destroys bacteria and fungi, increasing the shelf life of foods. In this way, there is the need for the development of dosimeters to monitor the dose used which can reach up to 20,000 times of the lethal ones for humans. Glasses are being considered for high-dose dosimetry applications, since its production costs are lower compared to other materials. However, it must fit another desirable characteristic, which is the linear response with respect to the radiation dose exposure. When glasses are exposed to high-dose gamma radiation, their optical absorption spectra changes. Although there is not a full agreement on the cause of that change in the optical spectra, it is believed that this is a combination of color centers produced by the entrapment of either electron-hole generated and/or due to some oxidized transition metal impurities. In this work, small rectangular pieces (1 x 1 x 4) mm3 of commercial soda-lime glasses, lithium and sodium diborates were irradiated with doses up to 10000 Gy, using a 60Co Gamma Cell-220 system. The samples were characterized by UV-Vis and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrometry. The dose-response data showed good linear relationships at 250 nm (R2=0.9972). The highest linearity was shown for lithium diborate, sodium diborate and commercial soda-lime glass, respectively. Based on the data presented, it is also shown that these glasses may be used as Yes/No in situ detectors.
Palavras-Chave: ionizing radiations; borates; boron compounds; silicates; dosemeters; food industry; food processing; gamma radiation; radiation detectors
. Borate and silicate glasses as high-dose linear response dosimeters. In: INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON CERAMICS, 7th; CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CERÂMICA, 62., June 17-21, 2018, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Abstract... 2018. p. 829-829. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29702. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Breast cancer estrogen and progesterone receptors evaluation using FTlR spectroscopy imaging: a pilot study. In: IUPAB CONGRESS; ANNUAL SBBF MEETING; ANNUAL SBBQ MEETING, October 26-30, 2020, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Abstract... 2020. Abstract: INTRODUCTION. Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in woman worldwide with an incidence of 2.09 million and 627 thousand deaths in 2018. Histopathology is the gold standard method for cancer diagnosis and identification of therapeutic targets, however it still presents interpretation difficulties, especially when comparing different cancer subtypes. OBJETICVE: The aim of this study was to evaluate Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in the diagnose and differentiation of molecular differences between two different breast cancer subtypes: positive and negative for estrogen (ER) and progesterone (PR) receptors. METHODS: Two human breast cell lines, BT474 (ER and PR positive) and SKBR3 (ER and PR negative), were inoculated in Balb/c nude mice. Tumors were collected when reached 0.5 cm3, processed by formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. 5μm thick tissue cuts were fixed in low-e slides (MirrIR, Kevley Technologies). Spectral images were performed in a micro-FTIR (Cary 660, Agilent Technologies) with 32 x 32 FPA of 5.5 μm pixel size. Scattering correction (RMieS-EMSC) was performed using MATLAB and remaining processing using Python. Groups differentiation were evaluated by PCA from 1350 to 1000 cm-1 second derivatives. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: Groups were split in two clusters, separated by PC-1 with a 99 % accuracy in both groups and 45 % of explained variance. The absorptions in the selected region for the PCA were mainly related to DNA, RNA and protein content. The main contribution was presented by the 1238 cm-1 peak, which was correlated with nucleic acids symmetrical stretching. Hyperspectral image built from this peak presented a spatial correlation with the microscope white light imaging, indicating that possible region for histopathological correlation might be present. CONCLUSAO: Our pilot study shows that FTIR spectroscopy imaging can distinguish ER/PR positive from negative breast cancer subtypes.
Palavras-Chave: neoplasms; mammary glands; diagnostic techniques; histology; fourier transformation; infrared spectra
. Breast cancer estrogen and progesterone receptors evaluation using FTlR spectroscopy imaging: a pilot study. In: IUPAB CONGRESS; ANNUAL SBBF MEETING; ANNUAL SBBQ MEETING, October 26-30, 2020, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Abstract... 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32354. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Carbon supported hybrids nanostructures PtSn with CeO2 nanorods for Direct Ethanol Fuel Cells. In: REUNIAO ANUAL DA SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE QUIMICA: CONSTRUINDO O AMANHA, 41., 21-24 de maio, 2018, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Resumo... São Paulo: Sociedade Brasileira de Química, 2018. Abstract: New energetic sources have been the focus of current researches, including on fuel cells. This device has as its operating principle the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy, making possible the use of renewable energy sources [1]. In the fuel cells operation are applied nanostructured electrocatalysts capable of oxidizing organic molecules such as ethanol [2]. This work was carried out using PtSn-based electrocatalysts with ceria nanorods (CeO2), synthesized by chemical reduction method via sodium borohydride [2], and supported on carbon Vulcan XC 72 (20% w/w). The synthesized materials have the following mass metal ratios: Pt/C; Pt3Sn1/ C and Pt3Sn1_20%NR/ C, with % of the Pt3Sn1 load replaced by ceria nanorods in the last nanomaterial, in order to reduce the costs of noble metals such as platinum. The evaluation of the activity for ethanol oxidation is given by polarization and power density curves, according to Figure 1. From the polarization curve it was observed that the Pt3Sn1_20%NR/ presented higher open circuit potential value (572 mV), and power density higher than the Pt/C composite material. The Pt3Sn1/C material presented a higher value of power density related to the others, but Pt3Sn1_20%NR/C generated a power density for ethanol oxidation relatively close to the best activity material, by the supply of oxygenated species improved the electrocatalytic activity for CO oxidation, making its application possible.. Carbon supported hybrids nanostructures PtSn with CeO2 nanorods for Direct Ethanol Fuel Cells. In: REUNIAO ANUAL DA SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE QUIMICA: CONSTRUINDO O AMANHA, 41., 21-24 de maio, 2018, Foz do Iguaçu, PR. Resumo... São Paulo: Sociedade Brasileira de Química, 2018. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29719. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. CaSiO3 polycrystal for neutron, proton and carbon detection. In: RUBIO, MARCELO (Ed.); TIRAO, GERMAN (Ed.) INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON RADIATION PHYSICS, 14th, October 7-11, 2018, Córdoba, Argentina. Abstract... Córdoba: Centro de Excelencia en Productos y Procesos, 2018. p. 20-20.. CaSiO3 polycrystal for neutron, proton and carbon detection. In: RUBIO, MARCELO (ed.); TIRAO, GERMAN (ed.) INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON RADIATION PHYSICS, 14th, October 7-11, 2018, Córdoba, Argentina. Abstract... Córdoba: Centro de Excelencia en Productos y Procesos, 2018. p. 20-20. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30222. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Células a combustível de membrana de troca aniônica de alto desempenho baseadas em ionômeros sólidos / High performance anion exchange membrane fuel cells based on ionomers. In: SIMPÓSIO BRASILEIRO DE ELETROQUÍMICA E ELETROANALÍTICA, 21., 17-21 de abril, 2017, Natal, RN. Resumo... Campinas, SP: Galoá, 2017. Abstract: Alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells (APEFC) have received increased attention in recent years as an alternative to well-established PEMFC because the alkaline medium enables more efficient and faster electrochemical reactions using nonnoble catalysts. The development of stable and conductive polymeric materials employed as anion-exchange membranes (AEM) and anion-exchange ionomers (AEI) has been the focus of substantial efforts. In this work, ETFE (poly(ethylene-cotetrafluoroethylene)) powders were electron-beamed radiation-grafted (RG) with vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) monomer and then either aminated with trimethylammonium (TMA) or N-methylpyrrolidinium (MPY). The resulting powders were employed as the AEI in the gas diffusion electrodes in single cell H2/O2 APEFCs (along with RG-AEMs). The results showed that the degree of grafting (DoG), and consequently the ionexchange capacity (IEC), are strongly dependent on the radiation dose. RG-AEI made from ETFE irradiated at 100 kGy (total absorbed dose) and functionalised with TMA (ETFE100TMA) and MPY (ETFE100MPY) exhibit IEC values of 2.05 and 1.91 meq.mol-1, respectively. The H2/O2 power density curves (Fig. 1) for APEFC with ETFE100TMA in both anode and cathode; ETFE100MPY in both anode and cathode, and ETFE100TMA in anode and ETFE100MPY in cathode, revealed high performances (> 800 mW cm-2). The best performance was observed for with the ETFE100TMA anode and ETFE100MPY cathode (maximum power density of 1.1 W.cm-2).. Células a combustível de membrana de troca aniônica de alto desempenho baseadas em ionômeros sólidos. In: SIMPÓSIO BRASILEIRO DE ELETROQUÍMICA E ELETROANALÍTICA, 21., 17-21 de abril, 2017, Natal, RN. Resumo... Campinas, SP: Galoá, 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31190. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Characterization by atomic force microscope (AFM) of graphene oxide and graphene oxide-PEG-NH2 incorporated in bovine pericardium. In: PAN AMERICAN CONGRESS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY, 1st, 27-30 de novembro, 2017, Guarujá, SP. Abstract... 2017. Abstract: Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a technique that allows images from the surface topography with high spatial resolution at Nano metric scales. AFM has being used in several fields in science such as Biology, Medicine, Chemistry and Pharmaceuticals. In this study, the tecnhique was used to characterize graphene oxide and graphene oxide functionalized with amino-PEG (GO-PEG-NH2) in the bovine pericardium (BP) surface. The treatment of BP with GO and (GO-PEG-NH2) improved the mechanical properties of the biomaterial that will be used in the manufacture of cardiovascular device that is used to replace heart valves. For the BP coating, two different pathways were tested: 1) chemical pathway using solution containing 1-Ethyl-3- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and GO; and 2) in physical adsorption the incorporation were performed by ultrassom. The same procedure was performed to incorporate GO-PEG-NH2. The images of the BP with its modified surface were obtained by AFM and proof the efficiency in the two incorporation processes. The study also demonstrated the applicability of AFM to characterize incorporated nanomaterial in the biological samples.. Characterization by atomic force microscope (AFM) of graphene oxide and graphene oxide-PEG-NH2 incorporated in bovine pericardium. In: PAN AMERICAN CONGRESS OF NANOTECHNOLOGY, 1st, 27-30 de novembro, 2017, Guarujá, SP. Abstract... 2017. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/29057. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 104
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

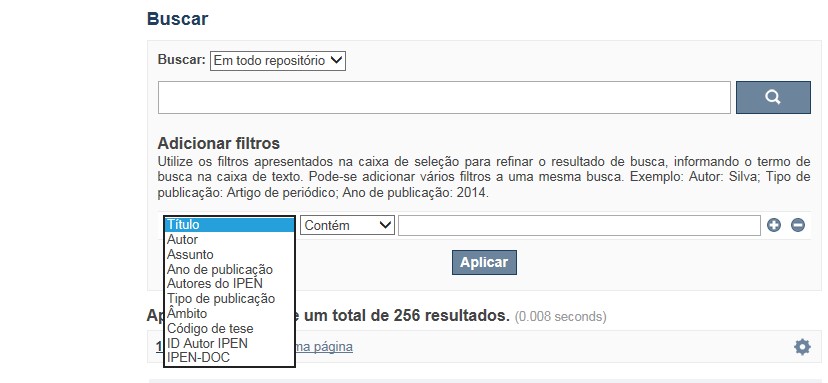
A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
