Navegação Livros - Capítulos por Agências de fomento "Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Livros - Capítulos
- →
- Navegação Livros - Capítulos por Agências de fomento
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Livros - Capítulos por Agências de fomento "Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-7 de 7
-
. Biocompatible glasses applied in cancer treatment: magnetic hyperthermia and brachytherapy. In: BAINO, FRANCESCO (Ed.); KARGOZAR, SAEID (Ed.). Bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics: fundamentals and applications. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley-American Ceramic Society, 2022. p. 537-579, cap. 22. DOI: 10.1002/9781119724193.ch22. Biocompatible glasses applied in cancer treatment: magnetic hyperthermia and brachytherapy. In: BAINO, FRANCESCO (ed.); KARGOZAR, SAEID (ed.). Bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics: fundamentals and applications. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley-American Ceramic Society, 2022. cap. 22. p. 537-579. DOI: 10.1002/9781119724193.ch22. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/33734. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Electrochemical applications of metal−organic frameworks: overview, challenges, and perspectives. In: GHOSH, POOJA (Ed.); KUMAR, SMITA S. (Ed.); SINGH, LAKHVEER (Ed.). Metal−Organic Frameworks for Carbon Capture and Energy. Washington, DC, USA: American Chemical Society, 2021. p. 395-453, cap. 15. (ACS Symposium Series, 1393). DOI: 10.1021/bk-2021-1393.ch015 Abstract: Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are materials constructed by linking multitopic organic ligands and metal ions or clusters by means of strong coordination bonds. These materials have attracted growing interest, due to their highly tunable composition, structure, and chemical functionalities, from which arise a great variety of remarkable topologies and properties. MOFs can be produced in different ways and theirmain characteristics are very high surface area, low density, reasonable thermal stability, and possibility of surface modification, due to the organic portion of the material. Such properties allow their use in wide range of applications, exploiting the ability to preconcentrate gases and other analytes in their cavities, as a result of the specific pore sizes and/or diverse functional groups of MOFs. This chapter describes and discusses the synthesis of MOFs and the applications of these materials in electrocatalytic processes, electrochemical sensors, photoelectrocatalytic processes, and degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters.
Palavras-Chave: organometallic compounds; electrochemistry; photoelectrolysis; carbon dioxide; emission
. Electrochemical applications of metal−organic frameworks: overview, challenges, and perspectives. In: GHOSH, POOJA (ed.); KUMAR, SMITA S. (ed.); SINGH, LAKHVEER (ed.). Metal−Organic Frameworks for Carbon Capture and Energy. Washington, DC, USA: American Chemical Society, 2021. cap. 15. p. 395-453. (ACS Symposium Series, 1393). DOI: 10.1021/bk-2021-1393.ch015. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32899. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Lasers in caries and erosion prevention: fluoride synergy and spectroscopy monitoring. In: ROMANOS, GEORGIOS E. (Ed.). Laser Light Therapy in Dentistry: Efficacy, Uses and Limitations. New York, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2021. p. 123-171, cap. 6. (Dentistry and Oral Sciences). DOI: https://doi.org/10.52305/YICB6320 Abstract: The use of laser radiation has shown benefits in different areas of human health. In Dentistry, laser radiation at high or low intensity is widely used as an adjunct strategy to the traditional therapeutic techniques in different specialties, and the observed effects depend both on the parameters of the radiation used, as well as on the tissues to be treated and their clinical condition. High intensity lasers are used for cutting both hard and soft tissues, as well as for hemostasis, vaporization, removal of decayed tissue, calculus, biofilm, and for decontamination. Also, lasers can be used for preparing dental hard tissue for prosthetic treatment, as well as to non-invasively remove ceramic or resin restorations, crowns, and laminates. Still, due to its thermal effect, lasers have shown promising results in preventing the appearance and progression of caries and erosion lesions in enamel and dentin. These thermal effects can also enhance the action of other preventive strategies, among which the topical application of fluoride stands out. The compositional effects of Nd:YAG (λ = 1,064 nm), Er:YAG (λ = 2,094 nm) and Er,Cr:YSGG (λ = 2,078 nm) laser wavelengths, applied under different conditions and in association or not with fluoride, have been evaluated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, a non-destructive technique that allows the broad evaluation of the same sample in different periods; for this reason, it is an extremely attractive technique for monitoring the treatments. Infrared thermography was also used in order to guide the choice of safe irradiation parameters tested for future clinical use of these lasers. These aspects will be detailed in this chapter.. Lasers in caries and erosion prevention: fluoride synergy and spectroscopy monitoring. In: ROMANOS, GEORGIOS E. (ed.). Laser Light Therapy in Dentistry: Efficacy, Uses and Limitations. New York, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2021. cap. 6. p. 123-171. (Dentistry and Oral Sciences). DOI: https://doi.org/10.52305/YICB6320. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/33282. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este item
Esta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Processing and characterization of polyethylene-AgNPs films: biocide effect. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 679-688, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_67 Abstract: Low-density-polyethylene (LDPE) and Linear-low-density-polyethylene (LLDPE) nanocomposites films containing silver nitrate (AgNO3) and surfactant oleic acid (AO) were manufactured via extrusion and subsequently characterised. The films were evaluated by scanning electronmicroscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Further, the antibacterial properties of the films were investigated against Escherichia coli (Gram-negative) and Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive) bacteria.The results indicated that LDPE nanocomposite films containing AgNPs have the potential to be used in antimicrobial packaging for food applications.
Palavras-Chave: nanocomposites; polyethylenes; silver nitrates; oleic acid; germicides
. Processing and characterization of polyethylene-AgNPs films: biocide effect. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 679-688. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_67. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31859. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Removal of Crystal Violet dye from aqueous solution using ash-based adsorbent materials. In: DUFFET, VICTOR (Ed.). Crystal Violet: Production, Applications and Precautions. Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2019. p. 1-40, cap. 3. Abstract: Crystal Violet (CV) is widely used for various purposes and enters into the aquatic systems from the effluents of textile, paint, medical and biotechnological industries. A considerable amount of this dye is lost during manufacturing and processing operations. Contaminated wastewater containing CV must be treated before releasing in the environment because it is highly cytotoxic and carcinogenic to mammalian cells, present mitotic poisoning nature and is nonbiodegradable being classified as a recalcitrant molecule. This chapter reports the removal of CV dye from water using surfactant-modified zeolite from coal fly ash (MZSF), surfactant-modified zeolite from coal bottom ash (MZSB) and nanosilica from sugarcane waste ash (SiO2NP). The adsorbent materials were characterized to obtain chemical and mineralogical composition and others physicochemical properties. The adsorption kinetic of CV onto adsorbents was discussed using the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and Elovich models. The Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models were used to describe the equilibrium adsorption data. The maximum adsorption capacities were 36.7 mg g-1 and 21.1 mg g-1 for CV/MZSF and CV/MZSB, respectively. The adsorption process of CV/SiO2NP achieves equilibrium in 60 min of contact time, and the maximum adsorption capacity was 117.98 mg g-1. Application of the adsorbent materials synthesized from agricultural waste and coal combustion products can ensure the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of treating effluent containing CV dye, especially effluent from the textile industries generated in large quantity.
Palavras-Chave: methyl violet; zeolites; coal; ashes; silica; nanomaterials
. Removal of Crystal Violet dye from aqueous solution using ash-based adsorbent materials. In: DUFFET, VICTOR (ed.). Crystal Violet: Production, Applications and Precautions. Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2019. cap. 3. p. 1-40. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30872. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Synthesis of nanocrystalline zeolite Na-A from coal fly ash and different aluminum sources: application for heavy metals removal. In: GRAY, MIRIAM (Ed.). Coal Fly Ash. Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2018. p. 1-33, cap. 4. Abstract: This chapter describes the synthesis process to obtain zeolite Na-A from coal fly ash via fusion with NaOH followed by hydrothermal reaction. Coal fly ash is a low cost source of both silica and alumina. The molar ratio of SiO2/Al2O3 for zeolite 4A formation was achieved by the addition of sodium aluminate solution or aluminum waste from tertiary industry as aluminum sources. The effects of temperature and time at the fusion step and the hydrothermal reaction time on crystalline products were investigated. The synthesized products were studied for their purity and yield as well as were characterized by different techniques such as Xray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and cation exchange capacity (CEC), among others. Analysis of the properties of the raw materials and the products demonstrates that the by-products can be used to produce a high purity zeolite A. The optimum conditions related to the synthesis was set and the samples were pure, highly crystalline and white. The synthesized zeolites were used for both the removal of Cd (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solution. The results showed that coal fly ash and aluminum source can be transformed into zeolite A, which is considered as value-added material with adsorption properties.
Palavras-Chave: synthesis; zeolites; nanocrystals; coal; fly ash
. Synthesis of nanocrystalline zeolite Na-A from coal fly ash and different aluminum sources: application for heavy metals removal. In: GRAY, MIRIAM (ed.). Coal Fly Ash. Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2018. cap. 4. p. 1-33. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30087. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. The potential of micro- and nano-sized fillers extracted from agroindustry residues as reinforcements of thermoplastic-based biocomposites: a review. In: IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); LI, JIAN (Ed.); VIEIRA, CARLOS M.F. (Ed.); MARGEM, JEAN I. (Ed.); BRAGA, FABIO de O. (Ed.). Green Materials Engineering. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2019. p. 89-100, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-10383-5_10 Abstract: Currently, the relevance of reuse of agroindustrial waste to obtain fillers in micro- and nano-sizes for the development of biocomposite materials has grown significantly. Production processes based on sustainable and low carbon development have increased interest in more environmentally friendly polymer composites, which have made the origin of reinforcement materials a determining factor for their application in this segment. This work presents a review of the developments of our team in the field of thermoplastic biocomposites reinforced with micro- and nano-sized fillers extracted from agroindustry residues. The different residues from Brazilian agroindustry available for the extraction of micro- and nano-sized fillers for the production of polymer biocomposites, the methods of the extraction and treatments of these natural fillers are presented; and its application as reinforcements in thermoplastic-based biocomposite are discussed in this review.
Palavras-Chave: agriculture; agricultural wastes; environmental impacts; bagasse; biodegradation; thermoplastics; composite materials; fillers; polymers
. The potential of micro- and nano-sized fillers extracted from agroindustry residues as reinforcements of thermoplastic-based biocomposites: a review. In: IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); LI, JIAN (ed.); VIEIRA, CARLOS M.F. (ed.); MARGEM, JEAN I. (ed.); BRAGA, FABIO de O. (ed.). Green Materials Engineering. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2019. p. 89-100. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-10383-5_10. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30081. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-7 de 7
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

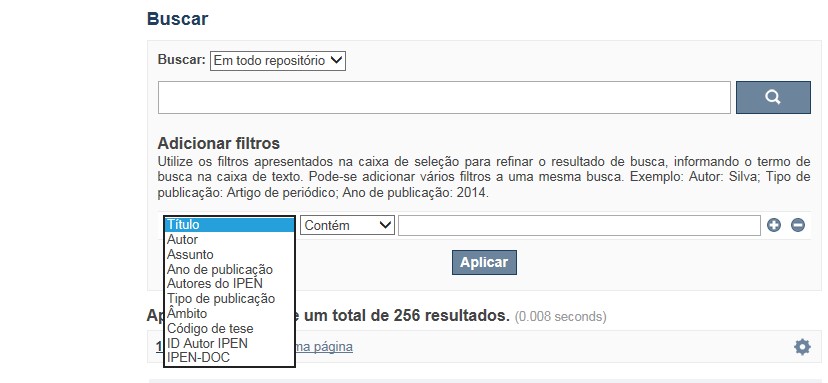
A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
