Navegação Livros - Capítulos por ano de publicação "2016"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Livros - Capítulos
- →
- Navegação Livros - Capítulos por ano de publicação
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Livros - Capítulos por ano de publicação "2016"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 31
-
. X and gamma ray secondary standard metrology. In: PEIXOTO, JOSE G.P. (Ed.). Ionizing radiation metrology. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Instituto de Radioproteção e Dosimetria, 2016. p. irregular,
Palavras-Chave: x radiation; gamma radiation; dosimetry; calibration; radiotherapy; radiation protection
. X and gamma ray secondary standard metrology. In: PEIXOTO, JOSE G.P. (ed.). Ionizing radiation metrology. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Instituto de Radioproteção e Dosimetria, 2016. p. irregular. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/26683. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Tratamento oxidativo em águas residuais da mineração de urânio com oxidação avançada de ozônio. In: PINHEIRO, ALEX G. (Colab.); SILVA, CARLA M. (Colab.); MENDES, ERLON (Colab.); WAJC, ISAC M. (Colab.); YAMANAKA, MARCOS H. (Colab.); QUADRI, MARINTHO B. (Colab.); SUZIN E SILVA, MIRNA M. (Colab.); GUIMARAES, NATALIA R. (Colab.); MOREIRA JUNIOR, PAULO F. (Colab.); MANFIOLETTI, SUELEN Z. (Colab.)ANGIOLETTO, ELIDIO (Coord.); CARVALHO, ELITA F.U. de (Coord.); BIAZINI FILHO, FRANCISCO L. (Coord.); LAGE FILHO, FREDERICO A. (Coord.); RIELLA, HUMBERTO G. (Coord.); SANTOS, IVAN (Coord.); DEPINTOR, JOSE C. (Coord.); BOSCOV, MARIA E.G. (Coord.); MENASCE, SAMY (Coord.); . Ozônio na recuperação de solos e recursos hídricos contaminados por mineração. Criciúma, SC: UNESC, 2016. p. 71-109, Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN.
Palavras-Chave: mining; waste water; environmental impacts; ground water; oxidation; uranium mines; manganese; ozone; removal; waste processing
. Tratamento oxidativo em águas residuais da mineração de urânio com oxidação avançada de ozônio. In: PINHEIRO, ALEX G. (colab.); SILVA, CARLA M. (colab.); MENDES, ERLON (colab.); WAJC, ISAC M. (colab.); YAMANAKA, MARCOS H. (colab.); QUADRI, MARINTHO B. (colab.); SUZIN E SILVA, MIRNA M. (colab.); GUIMARAES, NATALIA R. (colab.); MOREIRA JUNIOR, PAULO F. (colab.); MANFIOLETTI, SUELEN Z. (colab.)ANGIOLETTO, ELIDIO (coord.); CARVALHO, ELITA F.U. de (coord.); BIAZINI FILHO, FRANCISCO L. (coord.); LAGE FILHO, FREDERICO A. (coord.); RIELLA, HUMBERTO G. (coord.); SANTOS, IVAN (coord.); DEPINTOR, JOSE C. (coord.); BOSCOV, MARIA E.G. (coord.); MENASCE, SAMY (coord.); . Ozônio na recuperação de solos e recursos hídricos contaminados por mineração. Criciúma, SC: UNESC, 2016. p. 71-109. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27691. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Systemic effects. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 73-91, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_6 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a clinically approved practice for treatment of cancer and infectious diseases. PDT involves systemic or topical administration of a photosensitizer (PS), followed by irradiation of the target area with light of a wavelength matching the absorption band of the PS. In the presence of oxygen, photochemical reactions trigger the production of reactive oxygen species and, consequently, cell death by oxidative stress. Besides causing direct cytotoxicity to tumor cells, PDT induces destruction of the tumor vasculature releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines. Current literature supports that PDT is able to affect both the innate and adaptive responses of the immune system. In addition, PDT-induced adaptive immunity may attack distant untreated tumor cells and lead to development of antitumor memory immunity, which can potentially avoid the cancer relapse. Conversely, pro-inflammatory activity of PDT can also collaborate to resolve local infections since more neutrophils are recruited to the infected region.
Palavras-Chave: veterinary medicine; animals; photodynamic therapy; tumor cells; neoplasms; immunity
. Systemic effects. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 73-91. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_6. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28661. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Standard application in photon dosimetry. In: PEIXOTO, JOSE G.P. (Ed.). Ionizing radiation metrology. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Instituto de Radioproteção e Dosimetria, 2016. p. irregular,
Palavras-Chave: dosimetry; dosemeters; ionization chambers; calibration; uses; photons
. Standard application in photon dosimetry. In: PEIXOTO, JOSE G.P. (ed.). Ionizing radiation metrology. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Instituto de Radioproteção e Dosimetria, 2016. p. irregular. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/26682. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Radiation influence on edible materials. In: MONTEIRO, WALDEMAR A. (Ed.). Radiation Effects in Materials. London, UK: IntechOpen, 2016. p. 161-178, cap. 7. DOI: 10.5772/62430 Abstract: Innovations in the food industry are shaped both by new technologies available and by society’s requirements. A good knowledge on the chemistry and biological role of the macro-nutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and also energy and water) and micronutrients (minerals and vitamins) is required. Food production foundations include not only the design of the food products but also the materials, mechanics, ingredients, conversion and transformation all must be taken into consideration. Edible polymers are polymeric materials that can be easily consumed by human beings or lower animals in whole or part via the oral cavity and given harmless effect to the health. An edible polymer is originated from natural products such as polysaccharides, proteins and lipids, with the addition of plasticizers and surfactants. Radiation-processing technologies are used currently for numerous applications of commercial and economic importance, but it is an emerging application with the use of ionizing radiation to enhance properties of edible polymers such as carbohydrates or proteins. This chapter aims at supplying the state of the art about the effects of ionizing radiation on edible polymers: starch and vegetal proteins and also on gelatin that comes from animal origin.
Palavras-Chave: radiation effects; ionizing radiations; proteins; polysaccharides; films; nanotechnology
. Radiation influence on edible materials. In: MONTEIRO, WALDEMAR A. (ed.). Radiation Effects in Materials. London, UK: IntechOpen, 2016. cap. 7. p. 161-178. DOI: 10.5772/62430. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31162. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Photosensitizers. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 25-43, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_3 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) was discovered over 100 years ago when it was observed that certain dyes could kill microorganisms when exposed to light in the presence of oxygen. Since those early days, PDT has mainly been developed as a cancer therapy with regulatory approvals and clinical trials steadily accumulating for different types of cancer and different photosensitizer structures. A very important milestone for PDT was the introduction of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), which functions as a prodrug to induce endogenous porphyrin biosynthesis that acts as an endogenous photosensitizer produced by our cells. PDT with ALA and its derivatives have become mainstays of the clinical dermatologist’s practice covering everything from skin cancer, premalignant lesions, acne, and skin rejuvenation. Another milestone in PDT development was the realization that PDT may also be used as an effective antimicrobial modality and a potential treatment for localized infections. To some extent, this means that PDT has gone full circle and returned to its roots from when it was first discovered in 1900. In this chapter we discuss, in a contextualized fashion, what are the expected characteristics of an ideal photosensitizer and which are the main molecular frameworks used for development of synthetic, natural, and nanostructured photosensitizers.
Palavras-Chave: photosensitivity; photodynamic therapy; nanostructures; porphyrins
. Photosensitizers. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 25-43. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_3. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28658. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Photophysical and photochemical mechanisms. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 11-23, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_2 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) harnesses the power of light in an elegant method to produce cytotoxic agents in a spatially and temporally controlled manner and specifically damage target cells and tissues. For photodynamic reactions to occur, the PS molecule must absorb at least one photon to be promoted to a sufficiently long-lived excited state and then induce photodynamic reactions in an oxygenated environment. Such properties guarantee that PDT has an exceptionally broad action spectrum against tumors or pathogens, and resistance occurrence is restricted to only a few exceptions that can be avoided using simple strategies. To fully understand the intricacies of the mechanisms by which PDT acts, it is clear that one must take advantage of all the basic sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology). In fact, such conceptual complexity still maintains constant scientific investigations to deeply understand the molecular basis of PDT. Curiously, it might also be one of the reasons to explain why this hundred-year-old technique is still not generally applied in clinics or taught in standard courses of pharmacology. In this chapter, we will attempt to use a multidisciplinary approach, with simple technical language and a minimum of mathematics and equations, to allow any student with minimal training in basic sciences to understand all the fundamental mechanisms of PDT.
Palavras-Chave: photochemical reactions; photodynamic therapy; electromagnetic radiation; radiation sources
. Photophysical and photochemical mechanisms. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 11-23. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28657. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Oxide ceramics: the role of surface and grain boundaries for reliable functional applications. In: OHJI, TATSUKI (Ed.); SINGH, MRITYUNJAY (Ed.). Enginnering ceramics current status and future prospects. New York, NY: The American Ceramic Society and John Wiley & Sons, 2016. p. 415-426,
Palavras-Chave: oxides; grain boundaries; semiconductor resistors; sensors; solid oxide fuel cells; ceramics; surfaces; interfaces
. Oxide ceramics: the role of surface and grain boundaries for reliable functional applications. In: OHJI, TATSUKI (ed.); SINGH, MRITYUNJAY (ed.). Enginnering ceramics current status and future prospects. New York, NY: The American Ceramic Society and John Wiley & Sons, 2016. p. 415-426. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/26164. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Overview of radiation technology for environmental remediation in Brazil. In: INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY (Ed.). Radiation technology for cleaner products and processes. Vienna: IAEA, 2016. p. 26-37, (IAEA-TECHDOC-1786).
Palavras-Chave: brazil; ionizing radiations; water; waste water; organic compounds; environment; efficiency; evaluation
. Overview of radiation technology for environmental remediation in Brazil. In: INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY (ed.). Radiation technology for cleaner products and processes. Vienna: IAEA, 2016. p. 26-37. (IAEA-TECHDOC-1786). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/26572. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Other practices in PDT. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 197-207, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_13 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: In addition to clinical PDT applications regarding antimicrobial and antineoplastic activity, photodynamic reactions have also been used in several other practices such as for fish tank decontamination, water treatment, antiangiogenic therapy for age-related macular degeneration, decontamination of surfaces, and even inactivation of pathogens for blood transfusion. Nowadays, not all potentials of photodynamic reactions are commercially available yet, but they definitely deserve to be highlighted in this chapter as alternative applications of photodynamic reactions in veterinary medicine.
Palavras-Chave: veterinary medicine; photodynamic therapy; sterilization; water treatment; decontamination
. Other practices in PDT. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 197-207. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_13. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28666. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Multimodality dosimetry. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 93-109, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_7 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: PDT requires a multimodality approach for dosimetry because it works based on three essential components: light, photosensitizer, and molecular oxygen. Since these components are found in variable amounts inside target cells, PDT dosimetry is rather intricate. This chapter intends to address, with little mathematical complexity, the physical and chemical quantities that are most relevant for light and photosensitizer dosimetry as well as to present basic aspects of oxygen supply to achieve successful PDT interventions.
Palavras-Chave: veterinary medicine; photodynamic therapy; dosimetry; light sources; lasers
. Multimodality dosimetry. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 93-109. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_7. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28662. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Molecular damage. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 45-56, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_4 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) rapidly produces large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) to induce death of photosensitized cells. As previously described in Chap. 2, excited photosensitizer (PS) molecules can either donate electrons (type 1) or energy (type 2) to ground-state oxygen to produce superoxide radicals (O2•−) or singlet oxygen (1O2). Each type of ROS has characteristic chemical reactivity and reacts with different types of chemical bonds present in biomolecules and, consequently, will lead to different types of cell damage. Once again, what determines the mechanism of cell death directly depends on both: the PS localization site within the cell and total extent of oxidative stress produced during therapy (i.e., light dosimetry and efficiency of ROS generation). To elucidate the mechanisms of photooxidative damage and the consequent biological effects, this chapter will cover the most relevant chemical reactions related to oxidative damage caused by 1O2 and free radicals.
Palavras-Chave: veterinary medicine; photodynamic therapy; oxygen; molecular structure; photosensitivity
. Molecular damage. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 45-56. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_4. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28659. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Mineração de fosfato e produção de ácido fosfórico. In: REIS, ROCIO G. dos (Ed.). NORM: guia prático. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Edição do Autor, 2016. p. 89-98,
Palavras-Chave: phosphate minerals; phosphoric acid; fertilizers; radioisotopes
. Mineração de fosfato e produção de ácido fosfórico. In: REIS, ROCIO G. dos (ed.). NORM: guia prático. Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Edição do Autor, 2016. p. 89-98. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27030. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Mechanoluminescence of coordination compounds. In: OLAWALE, DAVID O. (Ed.); OKOLI, OKENWA O.I. (Ed.); FONTENOT, ROSS S. (Ed.); HOLLERMAN, WILLIAM A. (Ed.). Triboluminescence: theory, synthesis, and application. Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 39-63,
Palavras-Chave: luminescence; photoluminescence; chemical composition
. Mechanoluminescence of coordination compounds. In: OLAWALE, DAVID O. (ed.); OKOLI, OKENWA O.I. (ed.); FONTENOT, ROSS S. (ed.); HOLLERMAN, WILLIAM A. (ed.). Triboluminescence: theory, synthesis, and application. Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 39-63. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27379. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Low temperature ac electric field-assisted sintering of unitary anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell. In: PFEIFER, THOMAS (Ed.); MATYAS, JOSEF (Ed.); BALAYA, PALANI (Ed.); SINGH, DILEEP (Ed.); WEI, JOHN S. (Ed.). Ceramics for Energy Conversion, Storage, and Distribution Systems: ceramic transactions. v. 255. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2016. Abstract: Unitary planar solid oxide fuel cells (cathode La0.84Sr0.16MnO3 thin film/solid electrolyte ZrO2:8 mol% Y2O3 thin film/anode ZrO2:8 mol% Y2O3/NiO 55/45 vol.% 5.0 x 5.0 x 1.5 mm3 thick pellet) were prepared by electric field-assisted sintering. The application of multiple 300 V.cm-1 pulses at 1 kHz with 1-5 A limiting current at 1100 oC for 10 min produced single SOFC devices with dense electrolyte and porous anode and cathode. The electrical conductivity of the cells, measured at 590 oC by the impedance spectroscopy technique in the 5 Hz-13 MHz range in a HP4192A impedance analyzer, showed the increase in the electrical conductivity in comparison with the conventionally sintered cell. The microstructure of cross sections of the cells was observed in a scanning electron microscope. The images of the electric field-assisted sintered cells showed dense electrolyte and porous anode and cathode. Joule heating, provoked by the AC electric current pulses resulting from the application of the AC voltage, promoted NiO reduction at the anode, detected by EDX analysis in its intergranular region. L/L0 dilatometry shrinkage curves, J x t electric current pulses, Z'() x Z''() impedance plots and scanning electron microscopy micrographs show how anode-electrolyte-cathode ceramic cells can be sintered at temperatures lower than the usually required.
Palavras-Chave: solid oxide fuel cells; electric fields; sintering
. Low temperature ac electric field-assisted sintering of unitary anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell. In: PFEIFER, THOMAS (ed.); MATYAS, JOSEF (ed.); BALAYA, PALANI (ed.); SINGH, DILEEP (ed.); WEI, JOHN S. (ed.). Ceramics for Energy Conversion, Storage, and Distribution Systems: ceramic transactions. v. 255. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2016. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27411. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Irradiation of sugarcane bagasse for ethanol production. In: AL-ASSAF, SAPHWAN (Ed.); COQUERET, XAVIER (Ed.); DAHLAN, KHAIRUL Z.H.M. (Ed.); SEN, MURAT (Ed.); ULANSKI, PIOTR (Ed.). The Radiation Chemistry of Polysaccharides. Vienna, Austria: IAEA, 2016. p. 349-369,
Palavras-Chave: bagasse; biofuels; biomass; ethanol; irradiation; power generation; raw materials; saccharose; sugar cane; thermal power plants; wind power; ionizing radiations
. Irradiation of sugarcane bagasse for ethanol production. In: AL-ASSAF, SAPHWAN (ed.); COQUERET, XAVIER (ed.); DAHLAN, KHAIRUL Z.H.M. (ed.); SEN, MURAT (ed.); ULANSKI, PIOTR (ed.). The Radiation Chemistry of Polysaccharides. Vienna, Austria: IAEA, 2016. p. 349-369. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27025. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. How to enter PDT in clinical practice?. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 111-123, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_8 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: The photodynamic therapy stands out, not only for the few adverse effects to the veterinary patient but also for presenting environmental safety, not inducing microbial resistance and reducing generation of residual drugs on products intended for human consumption. After understanding the full potential of this new therapeutic modality through the previous chapters, the purpose of this chapter is to cover the main aspects to be considered by veterinarians to move PDT to clinical practice. It will be presented how the light source and photosensitizers should be chosen as well as the application modes for both antimicrobial and cancer PDT. Biosafety will also be addressed.
Palavras-Chave: veterinary medicine; photodynamic therapy; antimicrobial agents; light sources
. How to enter PDT in clinical practice?. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 111-123. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_8. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28663. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. History of PDT. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 1-10, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_1 Observação: Livro na íntegra disponível. Consulte a biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: This chapter presents the brightest historical milestones behind the development of photodynamic therapy (PDT). We initially present how photodynamic reactions were first observed by scientists from three different countries in the beginning of the twentieth century. Oskar Raab, from Germany, observed by accident that protozoan cells stained with fluorescent dyes were killed upon illumination, while Prime, in France, reported that human subjects who ingested also fluorescent dyes for an experimental treatment of neurological diseases developed severe erythema after short exposure to sunlight. Niels Finsen, from Denmark, was awarded with the third Nobel Prize of Medicine in the history for the development of light-based treatments for skin infections. Following, we describe how PDT slowly evolved until the 1960–1970s when new generations of less toxic photosensitizers were developed for diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors. Only then PDT really became a hot scientific area that began to attract many researchers to the field. We also describe the first huge medical and economic impact that PDT as the first effective treatment for age-related macular degeneration, the leading cause of adult blindness in the world. Finally, we go through the main discoveries in veterinary medicine over the past years for the treatment of localized tumors and infections in diverse animal species.
Palavras-Chave: photodynamic therapy; historical aspects; ultraviolet radiation; therapeutic uses
. History of PDT. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 1-10. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_1. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28656. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Future perspectives. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (Ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (Ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (Ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 209-222, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_14 Observação: Livro impresso disponível para consulta na biblioteca do IPEN. Abstract: Nowadays, it is clear that the activity of different photosensitizers (PSs) has a strong potential for moving photodynamic therapy (PDT) to clinical practice. Present technologies as dedicated light sources, new PSs, and nanotechnology are emerging strategies to promote PDT as a reliable, cost-effective, and safe approach to veterinary medicine. This chapter addresses an overview of emerging clinical applications and recent technologies to encourage veterinarians toward PDT.
Palavras-Chave: veterinary medicine; photodynamic therapy; photosensitivity; diseases; therapeutic uses
. Future perspectives. In: SELLERA, FABIO P. (ed.); NASCIMENTO, CRISTIANE L. (ed.); RIBEIRO, MARTHA S. (ed.). Photodynamic therapy in veterinary medicine: from basics to clinical practice. Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland: Springer, 2016. p. 209-222. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-45007-0_14. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/28667. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Fluoride bulk crystals growth. In: HASHMI, SALEEM (Ed.). Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering. Oxford: Elsevier, 2016. p. 1-6, DOI: 10.1016/b978-0-12-803581-8.03668-7 Abstract: Fluoride crystals have long presented a challenge for chemists and physicists, because their preparation often requires very specific procedures. Their synthesis usually requires the use of toxic and/or corrosive materials, procedures demanding suitable equipment, and safety operational norms. Additionally, most of the fluoride compounds are moisture sensitive. As a result, a dry working environment is needed. In spite of this, fluoride crystals have found many applications as dosimeters, information storage devices, X-ray monochromators, and, in particular, in the field of optics as laser hosts and other components such as windows, which has encouraged the development of research work on the preparation of large crystals. The successful preparation of bulk fluoride crystals is dependent upon a number of factors directly related to the crystal growth conditions of the most important is the purity of the raw material. The choice of high purity commercial salts will not always assure the growth of a crystal with high quality. First, the manipulation of fluorides without the correct procedures can easily introduce moisture contamination. Fluorides are very sensitive to water and oxygen, which are always present in the work environment. Second, commercial fluorides are rarely of sufficient purity, with respect to oxygen contaminants. Usually, starting materials are ‘five-nines’ (99.999%) pure with respect to the cation. Oxygen-related impurities, such as OH , COH , NO2 , present vibrational modes in the infrared range. Their presence, even in small concentrations, can be detrimental to the quality of infrared optical devices. In general, most simple fluoride crystals, such as alkali halides (LiF, NaF, RbF) or alkaline-earth fluorides (CaF2, SrF2, BaF2), are grown directly from commercial chemicals, after a preliminary treatment to eliminate moisture and oxygen contaminants. However, more complex fluoride compounds (e.g., LiSrAlF6 or BaY2F8) need to be carefully synthesized before the growth process. A preliminary treatment or synthesis of the raw material to be used for the crystal preparation is the first step in the growth of fluoride crystals.
Palavras-Chave: fluorides; crystal growth; crystal growth methods; rare earths; doped materials
. Fluoride bulk crystals growth. In: HASHMI, SALEEM (ed.). Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering. Oxford: Elsevier, 2016. p. 1-6. DOI: 10.1016/b978-0-12-803581-8.03668-7. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/27363. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 31
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
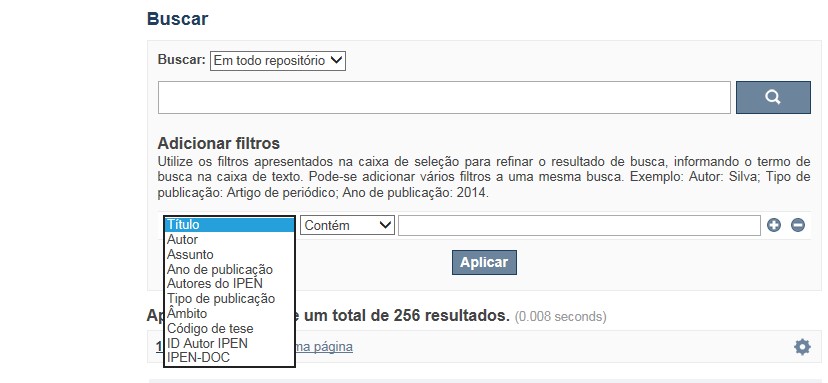
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
