Navegação Livros - Capítulos por ano de publicação "2020"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Livros - Capítulos
- →
- Navegação Livros - Capítulos por ano de publicação
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Livros - Capítulos por ano de publicação "2020"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 30
-
. Two-dimensional metal oxide nanomaterials for sustainable energy applications. In: ZAFEIRATOS, SPYRIDON (Ed.). 2D Nanomaterials for Energy Applications. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2020. p. 39-72, cap. 2. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-816723-6.00002-2
Palavras-Chave: nanomaterials; metals; oxides; energy sources
. Two-dimensional metal oxide nanomaterials for sustainable energy applications. In: ZAFEIRATOS, SPYRIDON (ed.). 2D Nanomaterials for Energy Applications. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2020. cap. 2. p. 39-72. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-816723-6.00002-2. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30885. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Study on closed-die forging in stainless steel as standard ASTM F138 in grain size function. In: ÖCHSNER, ANDREAS (Ed.); ALTENBACH, HOLM (Ed.). Engineering Design Applications II: Structures, Materials and Processes. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2020. p. 133-153, (Advanced Structured Materials, 113). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-20801-1_10 Abstract: Forging is a bulk deformation process in metal working commonly employed in the manufacture of metallic materials prostheses. Depending on the compressive loads applied to the material, structures (grain sizes) are formed which increase its strength. By forging an ASTM F138 stainless steel, the heating of material in a suitable temperature is of fundamental importance to be formed without the presence of folds arising from the process and as a result we can obtain a proper microstructure. This work aims to define the accurate temperature in relation to the strain rate applied in the hot die forging process. Besides, it is used a closed-die forging in which cavity has different thickness that stimulates the profile of an orthopedic plate. Four ranges of temperature used in the process vary between 1000 and 1200 °C, with a strain rate ranging from 400 to 600 s−1.Results demonstrate that there is a transitional temperature close to 1050 °C, where temperatures of 1000–1040 °C provide satisfactory grain size and temperatures of 1100 and 1200 °C, showed limitations in grain size, greater than those recommended by ASTM F 621.
Palavras-Chave: stainless steels; standardization; forging; grain size; strain rate; austenitic steels
. Study on closed-die forging in stainless steel as standard ASTM F138 in grain size function. In: ÖCHSNER, ANDREAS (ed.); ALTENBACH, HOLM (ed.). Engineering Design Applications II: Structures, Materials and Processes. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2020. p. 133-153. (Advanced Structured Materials, 113). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-20801-1_10. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31326. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Simulação computacional de recristalização de grãos. In: . Engenharia no Século XXI. Belo Horizonte, MG: Poisson, 2020. p. 100-105, v. 16, cap. 12. DOI: 10.36229/978-65-86127-70-6.CAP.12 Abstract: Um modelo de Monte Carlo bidimensional foi desenvolvido para simular a recristalização de grãos na presença de uma partícula circular imóvel para diferentes valores de energias armazenadas. Para energias armazenadas maiores que um valor crítico (H/J = 2,01) a propagação da recristalização pôde facilmente transpor a partícula imóvel, levando a uma densidade aleatória dos grãos e a uma influência insignificante da partícula imóvel na cinética da recristalização. Para energias armazenadas mais baixas (H/J = 0,1), a partícula imóvel limita a propagação da recristalização, levando à uma recristalização incompleta.
Palavras-Chave: computerized simulation; monte carlo method; recrystallization; grain growth
. Simulação computacional de recristalização de grãos. In: . Engenharia no Século XXI. Belo Horizonte, MG: Poisson, 2020. v. 16, cap. 12. p. 100-105. DOI: 10.36229/978-65-86127-70-6.CAP.12. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32234. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Radiation, Plant Proteins and Sustainability. In: BADSHAH, MALIK (Ed.). Prime Archives in Biosciences. Hyderabad, India: Vide Leaf, 2020. DOI: 10.37247/PABsc.1.2020.8
Palavras-Chave: ionizing radiations; proteins; sustainability; nutrition; radiation doses; plants; food; safety
. Radiation, Plant Proteins and Sustainability. In: BADSHAH, MALIK (ed.). Prime Archives in Biosciences. Hyderabad, India: Vide Leaf, 2020. DOI: 10.37247/PABsc.1.2020.8. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31484. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Production and characterization of PBAT reinforced with clay and graphene oxide nanosheets: a comparative study. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 689-699, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_68 Abstract: The poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), a biodegradable polymer, is among the most promising materials to be considered as environmentally friendly high performance biodegradable plastics. However, the mechanical properties of PBAT are not the best for several applications. According to the literature, the properties of the biodegradable polymer can be improved by addition of a small amount of nanofillers, such as clay, silica, and graphene. The objective of this study is to compare the effect of the addition of Cloisite clay and graphene oxide (GO) on the properties of flexible films based on PBAT matrix. The composite films based on PBAT with addition of Cloisite (2.0 wt%) and PBAT composite films with addition of Cloisite and GO (0.1–0.2 wt%) were prepared by extrusion, using a twin-screw extruder and a flat die single extruder. The effects of the addition of Cloisite clay and graphene oxide on mechanical and thermal properties of films were evaluated by mechanical and water absorption tests, FE-SEM, XRD, and Raman analysis.
Palavras-Chave: graphene; oxide minerals; nanocomposites; polymers; butenes; biodegradation; mechanical properties; flexibility
. Production and characterization of PBAT reinforced with clay and graphene oxide nanosheets: a comparative study. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 689-699. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_68. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31860. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Processing and characterization of polyethylene-AgNPs films: biocide effect. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 679-688, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_67 Abstract: Low-density-polyethylene (LDPE) and Linear-low-density-polyethylene (LLDPE) nanocomposites films containing silver nitrate (AgNO3) and surfactant oleic acid (AO) were manufactured via extrusion and subsequently characterised. The films were evaluated by scanning electronmicroscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Further, the antibacterial properties of the films were investigated against Escherichia coli (Gram-negative) and Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive) bacteria.The results indicated that LDPE nanocomposite films containing AgNPs have the potential to be used in antimicrobial packaging for food applications.
Palavras-Chave: nanocomposites; polyethylenes; silver nitrates; oleic acid; germicides
. Processing and characterization of polyethylene-AgNPs films: biocide effect. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 679-688. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_67. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31859. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Preliminary neutronic assessment of iron based alloy fuel cladding. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files). Abstract: Nowadays two important nuclear fuel performance requirements have been addressed: high burnup in order to improve fuel cycle economic aspect and accident tolerant fuel to enhance the safety under accident condition. The accident tolerant fuel particularly becomes very important issue after Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident in 2011. The initiatives of R&D program toward to accident tolerant fuel comprises different countries, organizations and including fuel vendors. The Accident Tolerant Fuel (ATF) can be defined as enhanced fuel which can tolerate loss of active cooling system capability for a considerably longer time period and the fuel/cladding system can be maintained without significant degradation and can also improve the fuel performance during normal operations and transients, as well as design-basis accident (DBA) and beyond design-basis (BDBA) accident. Different materials have been proposed as fuel cladding candidates considering thermo-mechanical properties and lower reaction kinetic with steam and slower hydrogen production, besides that an evaluation of the neutronic aspects for several cladding candidates is important and shall be evaluated. Depending of the outcome of this evaluation, the fuel enrichment level changes to higher than actual level shall be necessary to overcome the neutron absorption penalty. The aim of this work is to perform a preliminary neutronic assessment of fuel cladding based on iron alloy considering a standard PWR fuel rod (fuel pellet and dimension). The main purpose of the assessment is to quantify the penalty due to increase of neutron absorption in the cladding materials and some others fuel parameters are evaluated in order to overcome such penalty. In addition to neutronic assessment, the criticality safety aspects due to increase of fuel enrichment level are briefly presented and discussed.
Palavras-Chave: absorption; accident-tolerant nuclear fuels; beyond-design-basis accidents; cooling systems; design-basis accidents; enrichment; fuel cycle; fuel pellets; fuel rods; iron alloys; pwr type reactors; radiation accidents; reactor accidents; safety
. Preliminary neutronic assessment of iron based alloy fuel cladding. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31920. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Obtenção e caracterização de BaxSr1-xCoyFe1-yO3±δ para preparação de camada funcional do eletrodo catódico das células a combustível do tipo IT-SOFC. In: HOLZMANN, HENRIQUE A. (Org.); DALLAMUTA, JOÃO (Org.); MAZUR, VIVIANE T. (Org.). As engenharias e seu papel no desenvolvimento autossustentado. Ponta Grossa, PR: Atena, 2020. p. 294, cap. 19. DOI: 10.22533/at.ed.46620300619 Abstract: A demanda mundial por energia elétrica é uma tendência crescente, desta maneira há necessidade de diversificar e buscar por novas matrizes energéticas. Insere-se neste contexto, as células a combustível de Óxido Sólido de Temperatura Intermediária (Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells - IT-SOFC), que converte diretamente a energia de reações químicas em água e em energia elétrica e também em energia térmica (calor). As células a combustível do tipo IT-SOFC por utilizarem materiais cerâmicos em sua concepção, são capazes de suportarem temperaturas até 800ºC e sem perderem suas propriedades físicas, químicas, elétricas e microestruturais. O presente trabalho tem como objetivo a síntese e a caracterização do material particulado de BaxSr1-xCoyFe1- yO3±δ – BSCF (variando os valores de x iguais a 0,4; 0,6 e 0,5), visando sua utilização para fabricação de componente catódico de IT-SOFC. O particulado de BSCF foi obtido por meio do método de complexação por EDTA – Citratos, que consiste nas reações de estado sólido e reações em fase líquida. A reação em fase líquida consiste no processo de complexação em que os agentes quelantes atraem os íons metálicos presentes na solução precursora. A caracterização do material particulado BSCF foi realizada por difração de raios X (DRX), Espectroscopia de raios X por energia dispersiva (EDS), Análise Química por Fluorescência de raios X (identificação dos elementos constituintes na composição), Análise de Microscopia Eletrônica de Varredura - MEV (observação de morfologia e do tipo de aglomeração das partículas), e Picnometria por Gás Hélio (medidas de densidade real) e BET. Os resultados da caracterização dos particulados para a confecção do material catódico do BSCF apresentaram adequados para fabricação de componente catódico de IT-SOFC.
Palavras-Chave: fuel cells; ceramics; solid oxide fuel cells; synthesis; energy; edta; x-ray fluorescence analysis
. Obtenção e caracterização de BaxSr1-xCoyFe1-yO3±δ para preparação de camada funcional do eletrodo catódico das células a combustível do tipo IT-SOFC. In: HOLZMANN, HENRIQUE A. (org.); DALLAMUTA, JOÃO (org.); MAZUR, VIVIANE T. (org.). As engenharias e seu papel no desenvolvimento autossustentado. Ponta Grossa, PR: Atena, 2020. cap. 19. p. 294. DOI: 10.22533/at.ed.46620300619. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31575. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Neutronic screening of potential candidate for accident tolerant fuel. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Resumo expandido... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files).
Palavras-Chave: accident-tolerant nuclear fuels; beryllium oxides; cladding; fuel rods; monte carlo method; pwr type reactors; reactivity; stainless steels; uranium dioxide; uranium silicides; zircaloy
. Neutronic screening of potential candidate for accident tolerant fuel. In: . Light Water Reactor Fuel Enrichment beyond the Five Per Cent Limit: Perspectives and Challenges. Resumo expandido... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. (IAEA-TECDOC-1918 - Supplementary Files). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31922. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Nanotheranostics in oncology and drug development for imaging and therapy. In: FAINTUCH, JOEL (Ed.); FAINTUCH, SALOMAO (Ed.). Precision Medicine for Investigators, Practitioners and Providers. London, UK: Academic Press, 2020. p. 453-458, cap. 44. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819178-1.00044-7
Palavras-Chave: theranostics; nanotechnology; neoplasms; nanomaterials; drugs; nanoparticles; carcinogenesis
. Nanotheranostics in oncology and drug development for imaging and therapy. In: FAINTUCH, JOEL (ed.); FAINTUCH, SALOMAO (ed.). Precision Medicine for Investigators, Practitioners and Providers. London, UK: Academic Press, 2020. cap. 44. p. 453-458. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819178-1.00044-7. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30873. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Moving ahead towards sustainable development-AHWR, an amicable approach for nuclear reactors. In: JAIN, VINOD K. (Ed.); RATTAN, SUNITA (Ed.); VERMA, ABHISHEK (Ed.). Recent Trends in Materials and Devices. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2020. p. 203-210, cap. 21. (Springer Proceedings in Physics, 256). DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-8625-5_21 Abstract: With a constant urge of digging the unraveled, India has come far ahead in taking an evolutionary step in the field of nuclear science. There has been a recent breakthrough in nuclear reactor advancements. India is using advanced heavy water reactors which function on thorium as one of its fuel components. It can be used in conjunction with plutonium or low enriched uranium. This has been a massive lead as it produces energy at commercial levels and leaves lesser residual actinides having long half-life and inert thorium oxide. This has optimized the energy production rate up to 50% with respect to its production of burnt fuels. This research focuses on bringing an insight on recent advancements in terms of researches and scientific projects that are being conducted in India and how its result would ascent with the current sustainability models such as “Green Chemistry”, a program developed two decades ago in United States and England which defines its requirement for efficient transformation of reagents in obtaining desired results. This revolutionary uplift in nuclear science must reach global acceptance and execution. Considering the ample resources nature earth has bestowed us with, Brazil has remained away from the thorium fueled reactor project studied 50 years ago and there is no light put towards any future research prospects either. Being the second largest reserve of thorium on the entire planet, AHWR can become a mass advantage if explored and taken into deeper accounts.
Palavras-Chave: thorium; heavy water; reactor safety; radioactive wastes; enriched uranium
. Moving ahead towards sustainable development-AHWR, an amicable approach for nuclear reactors. In: JAIN, VINOD K. (ed.); RATTAN, SUNITA (ed.); VERMA, ABHISHEK (ed.). Recent Trends in Materials and Devices. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2020. cap. 21. p. 203-210. (Springer Proceedings in Physics, 256). DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-8625-5_21. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31908. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Mitochondrial effects of low-level light. In: RAI, VIKRANT (Ed.). Laser Therapies: Types, Uses and Safety. New York, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2020. p. 95-118, cap. 3. Abstract: Since the discovery of light amplified by stimulated emission of radiation – Lasers – in 1967, the effects of light on the improvement of tissue healing, promoting pain relief, decreasing inflammation and swelling, as well as preventing further tissue damage, have been known and constantly studied. Due to these useful properties for health, the interest of researchers for photobiomodulation has been growing, especially with the advent of light-emitting diodes and other light sources with various wavelengths. There are many known effects of light at the molecular level, and most of them occur in the mitochondria (especially by the interaction of light with cytochrome-C oxidase), such as increased ATP production, differential gene expression due to the induction of transcription factors, and altered oxidative status due to the modulation of oxidative stress. This chapter provides up-to-date information regarding those molecular and cellular mechanisms of low-level light according to wavelength, light dose, and other parameters, as well as some of its consequences in the cellular and tissue levels. The concept of the Arndt-Schulz curve, regarding the biphasic dose response to low-level light, is also explained.
Palavras-Chave: light sources; visible radiation; animal tissues; low dose irradiation; therapy; electromagnetic radiation; biological repair
. Mitochondrial effects of low-level light. In: RAI, VIKRANT (ed.). Laser Therapies: Types, Uses and Safety. New York, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers, 2020. cap. 3. p. 95-118. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32346. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Mechanical and morphological properties of hybrid composites based on recycled LDPE/EVA blend reinforced with clay and babassu fiber residues. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 661-669, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_65 Abstract: Over the years the consumption of plastic products made of conventional polymers has produced a large amount of waste which has led to disposal problems worldwide. Among the alternatives to minimize these problems are reuse and recycling practices. Then, the recycling of plastic and the use of recycled materials to produce new materials reinforced with nanoparticles from natural resources can be an alternative to reduce inappropriate waste disposal. The objective of this study is to investigate the effects of the addition of clay and non-treated babassu fiber residues on the mechanical and morphological properties of composite based on recycled LDPE/EVA blend. Composite materials containing 1–3 wt% of babassu residues and 1 wt% of clay were prepared using a twin-screw extruder machine and flat die single extrusion process, in order to prepare hybrid composites sheets. The sheets prepared by recycled LDPE/EVA blend and its composites were characterized by tensile tests, XRD, and FE-SEM analysis and the correlation between properties was discussed.
Palavras-Chave: mixers; recycling; polymers; films; fibers; composite materials; hybridization
. Mechanical and morphological properties of hybrid composites based on recycled LDPE/EVA blend reinforced with clay and babassu fiber residues. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 661-669. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_65. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31858. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Investigation on mechanical and thermal behaviours of PBAT/PLA blend reinforced with reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 631-639, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_62 Abstract: The aim of this study was to process and investigate the changes in the mechanical and morphological properties of the biodegradable nanocomposites based on polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blend (PBAT/PLA blend) due to the incorporation of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanosheets. The biodegradable polymeric nanocomposites were prepared by melting extrusion process using a twin-screw extruder machine. The influence of the RGO nanosheets incorporation on mechanical and thermal properties of PBAT/PLA blend was investigated by tensile Thermogravimetric (TG), X-Ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and tensile test analysis. Results showed that incorporation of the small amount ofRGO(0.1wt.%) ofRGOnanosheets in the blend matrix of PBAT/PLA resulted in an important gain of mechanical properties of the blend. This result indicates that a very small amount of RGO nanosheets addition in the PBAT/PLA can lead to obtaining materials with superior properties suitable for several industrial applications.
Palavras-Chave: polymers; graphene; oxides; biodegradation; mechanical tests
. Investigation on mechanical and thermal behaviours of PBAT/PLA blend reinforced with reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 631-639. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_62. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31857. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Inhibition of flame propagation in nanocomposites with expanded polystyrene recycled clay, gypsum, and titanium dioxide. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 609-618, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_60 Abstract: The large amount of plastic waste found in the environment, landfills, and dumps boost research into the recycling of polymer materials, which could reduce the amount of polymer discarded. In Brazil, the sector that most consumes polymers is the civil construction that could consume recycled polymerswithout concerns with the properties due to applications of low mechanical exigency. However, for applications in this sector, it is necessary that the materials have some resistance to the propagation of flames. This work discusses the flame retardance in nanocomposites with recycled polystyrene matrix and particles of nanoargila, titanium dioxide, and gypsum. The results of the X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), field emission scanning electronmicroscopy (FE-SEM), and flammability test. The results showed that glycerol, added during recycling, can plasticize recycled expanded polystyrene while maintaining the flame resistance properties of the material with flame retardant. It can also be concluded that some particles may delay the propagation of the flame in the composite.
Palavras-Chave: clays; titanium oxides; gypsum; polystyrene; flames
. Inhibition of flame propagation in nanocomposites with expanded polystyrene recycled clay, gypsum, and titanium dioxide. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 609-618. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_60. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31856. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Influência do espaçamento dendrítico secundário na dureza da liga Cu-14Al-5Ni-5Fe obtida por solidificação unidirecional. In: TULLIO, FRANCIELE B.M. (Org.). Engenharia na prática: importância teórica e tecnológica. Ponta Grossa, PR: Atena, 2020. p. 199-210, cap. 19. DOI: 10.22533/at.ed.08820240819 Abstract: O objetivo deste trabalho é analisar a influência dos espaçamentos dendríticos secundários na dureza da liga Cu-14Al-5Ni- 5Fe após o processo de solidificação. A liga foi solidificada em um dispositivo de solidificação direcional ascendente sendo o calor extraído através de refrigeração à água em uma base de aço SAE 1020. As medições dos espaçamentos dendríticos secundários foram obtidas por meio de microscopia óptica com software acoplado. As variáveis térmicas de solidificação como velocidade de deslocamento da isoterma liquidus (VL) e taxa de resfriamento (TR) foram avaliadas em função da distância da superfície de extração de calor. A dureza e os espaçamentos dendríticos secundários foram correlacionados com as posições dos termopares devidamente dispostos no lingote. Em função dos resultados obtidos, conclui-se que maiores taxas de resfriamento apresentam espaçamentos dendríticos secundários mais refinados que propiciam maiores valores de dureza.
Palavras-Chave: solidification; bronze; copper base alloys; hardness; dendrites
. Influência do espaçamento dendrítico secundário na dureza da liga Cu-14Al-5Ni-5Fe obtida por solidificação unidirecional. In: TULLIO, FRANCIELE B.M. (org.). Engenharia na prática: importância teórica e tecnológica. Ponta Grossa, PR: Atena, 2020. cap. 19. p. 199-210. DOI: 10.22533/at.ed.08820240819. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31675. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Influence of the reduced graphene oxide incorporation on properties of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 599-607, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_59 Abstract: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of incorporation of the reduced graphene oxide on properties of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). The incorporation of 0.5 and 1.5 wt% of RGO into ABS matrix was carried out by melting extrusion process using a twin-screw extruder and injection molding machine. The properties of ABS/RGO nanocomposite samples were investigated by tensile and impact Izod tests, FE-SEM, and XRD analysis. The results showed that the incorporation of small amount of RGO into ABS matrix led to obtaining of polymeric nanocomposite with superior mechanical properties when compared with original properties of ABS matrix.
Palavras-Chave: graphene; oxides; acrylonitrile; butadiene; styrene; mechanical tests
. Influence of the reduced graphene oxide incorporation on properties of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 599-607. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_59. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31855. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Improvement properties of polypropylene by graphene oxide incorporation. In: LI, JIAN (Ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (Ed.); LI, BOWEN (Ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (Ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (Ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (Ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (Ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (Ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (Ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (Ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 581-589, (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_57 Abstract: Due to the remarkable properties of graphene oxide (GO) and its possibility of functionalization,GOhas been used in many applications such as nanocomposites. GO nanosheets have been shown to improve the properties of the polypropylene (PP) matrix, for instance, its strength, gas barrier, thermal, and electrical conductivity. As PP has relatively low cost and varied applications, this work aims to study the changes in its thermal, morphological, and mechanical properties, due to the incorporation of GO in the PP matrix. GO was synthesized from graphite by a modified Hummers method. The nanocomposites PP/GO with 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3 wt% of GO in the PP matrix were obtained using a twin-screw extruder and an injection molding machine via a melt blending process. The nanocomposites PP/GO were characterized by FE-SEM and Izod impact test. In addition, the GO nanosheets were also characterized by Raman spectroscopy, ATR-FTIR, FE-SEM, and XRD, therewith correlation between properties was discussed.
Palavras-Chave: graphene; oxides; polypropylene; nanocomposites
. Improvement properties of polypropylene by graphene oxide incorporation. In: LI, JIAN (ed.); ZHANG, MINGMING (ed.); LI, BOWEN (ed.); MONTEIRO, SERGIO N. (ed.); IKHMAYIES, SHADIA (ed.); KALAY, YUNUS E. (ed.); HWANG, JIANN-YANG (ed.); ESCOBEDO-DIAZ, JUAN P. (ed.); CARPENTER, JOHN S. (ed.); BROWN, ANDREW D. (ed.). Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials. Cham, CZ, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 581-589. (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-36628-5_57. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31854. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Galectins in host defense against microbial infections. In: HSIEH, SHIE-LIANG (Ed.). Lectin in Host Defense Against Microbial Infections. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2020. p. 141-167, cap. 6. (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1204). DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-1580-4_6 Abstract: Galectins are differentially expressed in a variety of cell types, including immune cells, and characterized by the affinity for β-galactoside–containing glycans. There are fifteen galectin members in mammals. Galectins are primarily located intracellularly, but can be secreted outside the cells. They exhibit pivotal roles during microbial infection, such as pathogen recognition and innate and adaptive immunity, and this review aims to discuss the functions of endogenous galectins during infection by four main types of microbes (bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites). Extracellular galectins are known to exert a bacteriostatic effect on some bacteria via association with bacterial glycans, whereas cytosolic galectins are recognized to control antibacterial autophagy by binding to luminal host glycans of ruptured endo-lysosomes. With regard to fungal infections, most studies deal with galectin-3. Galectin-3 modulates fungal burdens, the adaptive immune responses, and mortality in fungi-infected mice, which has been shown to be associated with its ability to manipulate fungicidal functions in neutrophils and cytokine expression in dendritic cells. Some viral infections, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza virus infections, can be regulated by galectin-1 and -3, and they affect various aspects of viral infections, including viral binding, replication, budding, transmission, and infection-associated inflammation. Functions of galectins during a number of different parasitic infections have been identified in studies using galectin-knockout mice. Different parasitic infections have consistently demonstrated a role of galectins in tuning T helper immune responses in infected hosts.
Palavras-Chave: parasites; viruses; bacteria; fungi; immunity; immune reactions; galactose
. Galectins in host defense against microbial infections. In: HSIEH, SHIE-LIANG (ed.). Lectin in Host Defense Against Microbial Infections. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2020. cap. 6. p. 141-167. (Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1204). DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-1580-4_6. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31909. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Entrepreneurial university and Its engagement in the triple helix system: roadmapping to leading innovation on early stage: the technology transfer office whole. In: ABU-TAIR, ABID (Ed.); LAHRECH, ABDELMOUNAIM (Ed.); AL MARRI, KHALID (Ed.); ABU-HIJLEH, BASSAM (Ed.). Proceedings of the II International Triple Helix Summit. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 21-33, (Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, 43). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-23898-8_3 Abstract: This paper presents as main contribution the standardization of complex areas in the development and empirical demonstration of a managerial roadmap tool applied to the TTO (Technological Transfer Office) scenario, which primary role is to anticipate trends in technological and innovative skills at the level of firm to meet the demands from smart cities solutions, among University engagement and Industry. Implementing roadmapping on early stage in innovation provides convergence in key-technologies at the Nuclear an Energy Research Institute, addressing structural, regional, institutional role in Intellectual Property and complementarities to development market front-to-end through chains in health, environment, food, agriculture, energy, chemistry, education, entertainment and arts in the context of the knowledge economy.
Palavras-Chave: convergence; market; technology transfer; educational facilities
. Entrepreneurial university and Its engagement in the triple helix system: roadmapping to leading innovation on early stage: the technology transfer office whole. In: ABU-TAIR, ABID (ed.); LAHRECH, ABDELMOUNAIM (ed.); AL MARRI, KHALID (ed.); ABU-HIJLEH, BASSAM (ed.). Proceedings of the II International Triple Helix Summit. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020. p. 21-33. (Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, 43). DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-23898-8_3. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31919. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 30
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
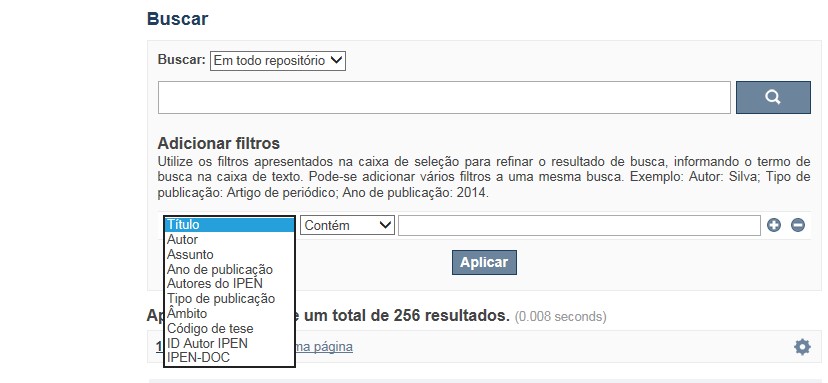
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
