Navegação Eventos - Artigos por ano de publicação "2020"
- Página inicial
- →
- IPEN
- →
- Eventos - Artigos
- →
- Navegação Eventos - Artigos por ano de publicação
- Sobre
- Perfil Técnico
- Política de funcionamento
- Ajuda
- Apresentação
Navegação Eventos - Artigos por ano de publicação "2020"
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 40
-
. Virtual magnetic TL-based channel modeling of SWIPT systems assisted by MTMs. In: MATOS, LENI J. de (Ed.) SIMPÓSIO BRASILEIRO DE MICRO-ONDAS E OPTOELETRÔNICA, 19.; CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ELETROMAGNETISMO, 14., 8-12 de novembro, 2020, Online. Anais... São Caetano do Sul, SP: SBMO, 2020. p. 674-678. Abstract: This paper describes a general methodology for the description of inductive power and data transfer based on virtual magnetic transmission-lines (VMGTLs). This approach presents a better physical insight on the channel behavior since the model correctly preserves the energy flow between the transmitting and receiving coils. Particularly, the virtual-TL analogy clarifies the mechanism of transmission gain improvement between any two coils assisted by MTM lenses. Based on the results of this work, these lenses do not enhance the magnetic coupling between the drivers, as usually claimed, but create conditions to propagating near-field modes to increase their power transfer. This approach also reveals that MTMs could be employed not only for the increasing of power transfer but also for enlarging the inductive channel bandwidth.
Palavras-Chave: metamaterials; power transmission lines; magnetic fields; computer networks; data transmission systems
. Virtual magnetic TL-based channel modeling of SWIPT systems assisted by MTMs. In: MATOS, LENI J. de (ed.) SIMPÓSIO BRASILEIRO DE MICRO-ONDAS E OPTOELETRÔNICA, 19.; CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE ELETROMAGNETISMO, 14., 8-12 de novembro, 2020, Online. Anais... São Caetano do Sul, SP: SBMO, 2020. p. 674-678. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31779. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Three-level Nd:YLF Raman laser directly pumped by a beam shaped diode bar. In: KUDRYASHOV, ALEXIS V. (Ed.); PAXTON, ALAN H. (Ed.); ILCHENKO, VLADIMIR S. (Ed.); ARMANI, ANDREA M. (Ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE LASE, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 1126614-1 - 1126614-8. (Proceedings SPIE 11266, Laser Resonators, Microresonators, and Beam Control XXII). DOI: 10.1117/12.2544844 Abstract: Low heat generation can be obtained when pumping Nd:YLF at wavelengths of 872 nm and 880 nm and emitting at the three-level transition of 908 nm. These transitions show very low quantum defect with efficiencies of 0.96 and 0.97, respectively. However, the low average absorption cross-section at these wavelengths makes efficient absorption even for longitudinal pump setups difficult. Using a beam-shaped pump diode instead of a fiber-coupled diode bar may be an effective means of increasing absorption because it can provide for π-polarized radiation which shows higher absorption cross section. In this work, a Nd:YLF was pumped at 872 nm by a diode bar using beam-shaping. Results were compared to pumping at 872 and 880 nm with non-polarized fiber-coupled diodes. Stimulated Raman scattering was also obtained with a KGW crystal generating first Stokes emissions at 990 nm and 976 nm.
Palavras-Chave: laser radiation; raman spectra; neodymium lasers; yttrium; lithium; beam shaping; energy levels
. Three-level Nd:YLF Raman laser directly pumped by a beam shaped diode bar. In: KUDRYASHOV, ALEXIS V. (ed.); PAXTON, ALAN H. (ed.); ILCHENKO, VLADIMIR S. (ed.); ARMANI, ANDREA M. (ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE LASE, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 1126614-1 - 1126614-8. (Proceedings SPIE 11266, Laser Resonators, Microresonators, and Beam Control XXII). DOI: 10.1117/12.2544844. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31560. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. The RMB project: fuel cycle management. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Abstract: The Brazilian Nuclear Energy Commission (CNEN) decided to construct a new research reactor, named RMB (Brazilian Multipurpose Reactor). It is a 30 MW open pool-type research reactor using low enriched uranium fuel, and several associated facilities and laboratories. To establish an infrastructure for producing fuel assemblies for RMB operation and uranium targets for Mo-99 production, the RMB technical secretary has developed a coordinated project for the fuel cycle management system, putting together the fuel technology actors in Brazil. The goals of this coordinated project were: (i) to have a centrifuge cascade enriching uranium up to 20 wt% with the capacity to supply RMB yearly needs; (ii) to upgraded the CNEN existing infrastructure to produce nuclear fuel assemblies and uranium targets for the RMB yearly needs; (iii) to produce a set of fuel assemblies for a real RMB mockup core at the IPEN/MB-01 Critical Facility of CNEN. The RMB project design incorporates structures, systems and components (SSC) for interim storage of spent fuels for the hole plant lifetime. This paper presents details of the coordinated project that gives support and sustainability to the RMB fuel cycle supply and the spent fuel SSC designed.
Palavras-Chave: rmb reactor; fuel cycle; slightly enriched uranium; molybdenum 99; fuel assemblies
. The RMB project: fuel cycle management. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31845. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. The RMB project: technical and management development status. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Abstract: The Brazilian Nuclear Energy Commission (CNEN) decided to construct a new research reactor, named RMB (Brazilian Multipurpose Reactor). This reactor will be part of a new nuclear research center, to be built on a site about 100 kilometers from São Paulo city, in the southeast part of Brazil. It is a 30 MW open pool-type research reactor using low enriched uranium fuel, and several associated facilities and laboratories in order to produce radioisotopes for medical and industrial use; to use thermal and cold neutron beams in scientific and technological research; to perform neutron activation analysis; and to perform materials and fuel irradiation tests. This project started in September 2008 and is nowadays at the development stage before construction. This article presents updated information on the technical design and the safety features regarding the reactor and the overall installation. It also presents an update on the nowadays overall development status of the RMB project and lessons learned related to the complexity of the project management.
Palavras-Chave: cold neutrons; design; isotope production; neutron beams; nuclear fuels; program management; reactor planning; rmb reactor; slightly enriched uranium; urban areas
. The RMB project: technical and management development status. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31844. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. The IPEN/CNEN contribution to IAEA FUMAC benchmark using modified fuel performance code based on stainless steel as cladding under steady state, transient and accident conditions. In: TECHNICAL MEETING ON MODELLING OF FUEL BEHAVIOUR IN DESIGN BASIS ACCIDENTS AND DESIGN EXTENSION CONDITIONS, May 13-16, 2019, Shenzhen, China. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. p. 1-9. Abstract: The IPEN/CNEN (Brazil) participated in IAEA Coordinated Research Project on Fuel Modeling in Accident Conditions (FUMAC) among others 18 countries (Argentina, Belgium, Bulgaria, China, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Japan, Norway, Republic of Korea , Russian Federation , Spain , Sweden , Ukraine and United States of America), which aim was focused in modelling, predicting and improving the understanding of the behaviour of nuclear fuel under accident conditions in order to better understanding and enhanced safety of nuclear fuel. A serie of LOCA (Loss of Coolant Accident) experiments data were made available for the participants to perform simulation using their fuel performance codes and the outcome gives an idea about fuel codes limitation considering LOCA simulation and possible improvement needed in the existing models related to LOCA condition.The IPEN/CNEN (BRAZIL) proposal for FUMAC-CRP was to modify existing fuel performance codes (FRAPCON and FRAPTRAN) considering stainless steel as cladding material and perform a simulation comparing to zircaloy cladding performance under steady state and accident condition. The HALDEN LOCA Experiments (IFA 650-9, IFA-650-10 and IFA-650-11) were selected and modeled to perform the LOCA accident simulation considering the original cladding (zircaloy) and compared to stainless steel cladding.
Palavras-Chave: design-basis accidents; reactor accident simulation; numerical data; reactor sites; nuclear fuels; stainless steel; cladding; international cooperation
. The IPEN/CNEN contribution to IAEA FUMAC benchmark using modified fuel performance code based on stainless steel as cladding under steady state, transient and accident conditions. In: TECHNICAL MEETING ON MODELLING OF FUEL BEHAVIOUR IN DESIGN BASIS ACCIDENTS AND DESIGN EXTENSION CONDITIONS, May 13-16, 2019, Shenzhen, China. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. p. 1-9. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31849. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. The IEA-R1 62 years of operation: experiences and lessons learned. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Abstract: Early in 1956, the Atomic Energy Institute (IEA, from the acronym in portuguese) was founded with the aim of installing the nuclear research reactor purchased from the American company Babcock & Wilcox in the framework of the “Atoms for Peace” program. The start-up was on September 16, 1957, where the first criticality in the Southern hemisphere was achieved. The IEA-R1 is a pool type, light water cooled and moderated, beryllium and graphite reflected research reactor. Although designed to operate continuously at up to 5 MW, it operated at 2 MW for 40 years and only rather recently started operating at 5 MW. This year IEA-R1 completed 62 years of operation. The reactor is the core of the Nuclear and Energy Research Institute – IPEN (former IEA) – with its laboratories working for radiopharmaceutical applications, in the areas of radiological protection, nuclear fuel cycle, nuclear engineering, and radiation applications among others. Throughout this period it underwent several reforms, renovations and changes of management. In 2000 an Integrated Management System (IMS) has been structured, based on ISO-9001, in order to keep the operation safe, which implied certain procedures together with a continuous modernization program, and to comply with the regulatory requirements at the date as well. The first certification dates to 2002 and since then the reactor has been successfully renewing its ISO certification. The history, experiences and lessons learned during the 62 years of the IEA-R1 operation are described and shared in this paper.
Palavras-Chave: iear-1 reactor; information dissemination; isotope applications; knowledge management; licensing regulations; nuclear engineering; radiation protection; radiopharmaceuticals
. The IEA-R1 62 years of operation: experiences and lessons learned. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31841. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Temperature generation and transmission in root dentin during Nd:YAG laser irradiation for preventive purposes. In: BRAZILIAN CONGRESS IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, 27th, October 26-30, 2020, Vitória, ES. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2020. p. 1031-1035. Abstract: High-intensity lasers are widely used in dental procedures and the heating produced on the surface is necessary to ensure protective activity against the development of caries and erosion lesions. However, caution should be exercised regarding the spread of heat to the pulp, periodontal tissue and alveolar bone, which can cause harm to these tissues. This study sought to evaluate the generation and transmission of heat in the root dentin and adjacent tissues during irradiation with Nd:YAG laser for preventive activity. For that, 15 lower incisor human teeth had an area of 9 mm2 of root dentin irradiated with Nd:YAG laser (λ=1.064 μm, 10 Hz, 60 mJ/pulse, 84.9 J/cm2) for 30s. During irradiations, pulpal temperature was evaluated by fast-response thermocouples, while surface temperature and heat distribution on surrounding tissues were measured by infrared thermography. It was observed a mean surface temperature increase of 293.48±30.6° C in root dentin surface, and 15.85 ± 39.6° C below the irradiated area, 11.72 ± 8.7° C above the irradiated area, 19.77 ± 4.9° C at 1 cm laterally and 7.03 ± 2.7° C at 2 cm laterally to the irradiated area. The mean pulpal temperature augment registered was 6.5±1.4° C. It can be concluded that Nd:YAG laser irradiation promoted surface temperature rises that suggest chemical changes on dentin; however, the temperature increases generated in the adjacent tissues (region of periodontal ligament) and in the pulp chamber may be dangerous in future clinical application considering the irradiation time of 30 s made in this study. Therefore, this laser protocol can be used as long as the irradiation time is reduced in future studies.
Palavras-Chave: dentistry; dentin; neodymium lasers; yttrium compounds; teeth; caries
. Temperature generation and transmission in root dentin during Nd:YAG laser irradiation for preventive purposes. In: BRAZILIAN CONGRESS IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, 27th, October 26-30, 2020, Vitória, ES. Proceedings... Rio de Janeiro, RJ: Sociedade Brasileira de Engenharia Biomédica, 2020. p. 1031-1035. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31681. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. A systemic approach to information and cyber security. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEAR SECURITY, February 10-14, 2020, Vienna, Austria. Proceedings... 2020. p. 1-6. Abstract: Design Based Threat, or DBT, is a common principle for physical and cyber protection, which is based on threat assessments. The protection, cyber or physical, will be planned based on the type of the identified threat. While we acknowledge the importance of the DBT, we argue that following this line of reasoning may limit our ability to grasp other vulnerabilities the system may have due to the following assumptions: a) The system will behave according to the way we think it should, based on a predetermined fashion. b) If each component of the system is reliable, then the system will be reliable. Systems theory assumes that accidents are a result of systemic factors, and does not have a single root-cause, generally a failure, that starts a chain of events leading to the accident. Moreover, systems theory assumes that security and safety are emergent properties of a system that result from the interactions between the components of that system. Therefore, accidents are a problem of control of the interactions between the components of the system rather than a problem of failures of components. In the systemic approach a cyber security system is treated as part of the whole socio-technical complex system, where humans are components of the system and interact with the computerized controls. The organizational culture permeates the entire system affecting decisions and, consequently, the interactions between the components. Weak safety and security cultures will eventually contribute for the system to migrate to hazardous states leading to losses or accidents. The paper analyzes the roles of organizational, safety and security cultures, as underlying factors that can lead to the deterioration of the hierarchical control structure, which is supposed to keep the interactions between the components of the system within desirable constraints.
Palavras-Chave: cybernetics; security; risk assessment; information systems; organizational models; management
. A systemic approach to information and cyber security. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NUCLEAR SECURITY, February 10-14, 2020, Vienna, Austria. Proceedings... 2020. p. 1-6. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31576. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Sustainability management system model for operating organisations of nuclear research reactors. In: EUROPEAN RESEARCH REACTOR CONFERENCE, October 12-15, 2020, Online. Proceedings... Brussels, Belgium: European Nuclear Society, 2020. Abstract: United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development establishes 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Nuclear and isotopic techniques contribute directly to achieving the SDGs related to energy, human health, food production, water management and environmental protection. This paper proposes a sustainability management system model for operating organisations of nuclear research reactors, supported by four sustainability pillars: institutional, economic, environmental and social. Each pillar of sustainability is formed by categories of indicators found in bibliographic references and validated by nuclear and sustainability academic experts, by using Delphi method. The management system model proposed has a high-level structure based on standards established by International Organisation for Standardization (ISO), considers safety requirements of International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and corporate sustainability requirements found in bibliographic references. Stakeholders’ requirements and expectations are inputs of the management system. The focus of the management system is nuclear safety and the organisation's commitment to sustainable development. A method for validating the sustainability management system, a sustainable development matrix to assess the maturity of sustainability management over time, and a sustainable value model, which evaluates the path taken by the organisation towards sustainable development, are tools that support the management system proposed. The management system outputs are management decisions that comply with organisation's policy, objectives and processes; products that meet stakeholders' requirements and expectations; and a Sustainability Report that contains sustainability indicators addressed by institutional, economic, environmental and social dimensions.
Palavras-Chave: information systems; sustainability; management; standardization; iso; safety standards; nuclear facilities
. Sustainability management system model for operating organisations of nuclear research reactors. In: EUROPEAN RESEARCH REACTOR CONFERENCE, October 12-15, 2020, Online. Proceedings... Brussels, Belgium: European Nuclear Society, 2020. Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31698. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Study of long term SF6 mole fractions in Amazon and Brazilian coast. In: CROTWELL, ANDREW (Ed.); LEE, HAEYOUNG (Ed.); STEINBACHER, MARTIN (Ed.) WMO/IAEA MEETING ON CARBON DIOXIDE, OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES AND RELATED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES, 20th, September 2-5, 2019, Jeju Island, South Korea. Proceedings... Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2020. p. 107-110. (GAW Report 255).
Palavras-Chave: sulfur fluorides; surfaces; greenhouse gases; coastal regions; concentration; greenhouse effect
. Study of long term SF6 mole fractions in Amazon and Brazilian coast. In: CROTWELL, ANDREW (ed.); LEE, HAEYOUNG (ed.); STEINBACHER, MARTIN (ed.) WMO/IAEA MEETING ON CARBON DIOXIDE, OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES AND RELATED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES, 20th, September 2-5, 2019, Jeju Island, South Korea. Proceedings... Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2020. p. 107-110. (GAW Report 255). Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31692. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Reactivity initiated accident assessment for ATF cladding materials. In: TECHNICAL MEETING ON MODELLING OF FUEL BEHAVIOUR IN DESIGN BASIS ACCIDENTS AND DESIGN EXTENSION CONDITIONS, May 13-16, 2019, Shenzhen, China. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. p. 155-161. (IAEA-TECDOC-1913). Abstract: Following the experience that came from the Fukushima Daiichi accident, one possible way of reducing risk in a nuclear power plant operation would be the replacement of the existing fuel rod cladding material (based on zirconium alloys) by another materials which could fulfill the requirements of the accident tolerant fuel (ATF) concept. In this sense, ATF should be able to keep the current fuel system performance under normal operation conditions; moreover, it should present superior performance than the existing conventional fuel system (zirconium-based alloys and uranium dioxide) under accident conditions. The most challenging and bounding accident scenarios for nuclear fuel systems in Pressurized Water Reactors (PWR) are Loss of Coolant Accident (LOCA) and Reactivity Initiated Accident (RIA), which are postulated accidents. This work addresses the performance of ATF using iron-based alloys as cladding material under RIA conditions. The evaluation is carried out using modified versions of the coupled system FRAPCON/FRAPTRAN. These codes were modified to include the material properties (thermal, mechanical, and physics) of an iron-based alloy, specifically FeCrAl alloy. The analysis is performed using data available in the open literature related to experiments using conventional PWR fuel system (zirconium-based alloys and uranium dioxide). The results obtained using the modified code versions are compared to those of the actual existing fuel system based on zircaloy-4 cladding using the original versions of the fuel performance codes (FRAPCON/FRAPTRAN).
Palavras-Chave: accident-tolerant nuclear fuels; charges; cladding; comparative evaluations; currents; fuel rods; fuel systems; fukushima daiichi nuclear power station; hazards; zircaloy 4; iron; loss of coolant; nuclear power plants; operation; performance; pwr type reactors; reactivity-initiated accidents; steady-state conditions; uranium dioxide
. Reactivity initiated accident assessment for ATF cladding materials. In: TECHNICAL MEETING ON MODELLING OF FUEL BEHAVIOUR IN DESIGN BASIS ACCIDENTS AND DESIGN EXTENSION CONDITIONS, May 13-16, 2019, Shenzhen, China. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. p. 155-161. (IAEA-TECDOC-1913). Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31065. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Polydispersed Nd3+:YVO4+SiO2 powders for highly efficient random lasers. In: JIANG, SHIBIN (Ed.); DIGONNET, MICHEL J.F. (Ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE OPTO, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 112760N-1 - 112760N-8. (Proceedings SPIE 11276, Optical Components andMaterials XVII). DOI: 10.1117/12.2545028 Abstract: Random lasers are cheap and easy to fabricate, having several different applications such as early cancer detection, encryption and Speckle-free imaging. However, few fabricated random lasers present high efficiency, which limits their possible applications. In a recent work, our group achieved a record efficiency by developing random lasers that use compacted, polydispersed yttrium vanadate doped with neodymium (Nd3+:YVO4 ) powders to create separate regions for gain and light diffusion. Large particles are responsible for the light diffusion, while the small particles that occupy the spaces between them create gain pockets, absorbing the pumped light. In this work, this strategy is refined by using passive particles (SiO2) for light diffusion, restricting the laser active particles to the gain pockets. The first attempt with this strategy used 30% of Nd3+:YVO4 small powders and 70% of large SiO2 particles. Without any further optimization, the result achieved is already 40% of the highest obtained efficiency in the previously studied Nd3+:YVO4 polydisperse sample, showing a promising result to further improve this new strategy and reach even larger efficiencies with less laser active material.
Palavras-Chave: randomness; lasers; optical pumping; gain; absorption
. Polydispersed Nd3+:YVO4+SiO2 powders for highly efficient random lasers. In: JIANG, SHIBIN (ed.); DIGONNET, MICHEL J.F. (ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE OPTO, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 112760N-1 - 112760N-8. (Proceedings SPIE 11276, Optical Components andMaterials XVII). DOI: 10.1117/12.2545028. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31562. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Optical-coherence-tomography-based algorithm for handwriting forensic analysis. In: JALALI, BAHRAM (Ed.); KITAYAMA, KEN-ICHI (Ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE OPTO, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 112990P-1 - 112990P-8. (Proceedings SPIE 11299, AI and Optical Data Sciences). DOI: 10.1117/12.2543356 Abstract: This work describes a new method for handwriting forensic analysis using optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. The region of interest (ROI) in documents signature to be analyzed were pre-selected with a traditional optical analyzer (Docucenter 2000 – Projectina®) equipped with different wavelengths light sources and bandpass filters coupled detector. The ROI where then submitted to OCT to 3D imaging (OCP930SR, Thorlabs Inc.) with optical resolution of 6.0 microns. One original and 5 falsified signatures were produced by 5 different individuals, using a block of 5 sheets of white sulfite paper A4 size and weight of 75 g/m^2, using the same blue ballpoint pen and in the same surface. For pressure pen calibration, were developed a system computer controlled to maintain the pressure constant during writing linear traces, 15 different pressure configuration were applied to each linear trace, resulting in a relation between deformation and applied pressure. An autonomous algorithm was developed to make surface detection, across OCT tomographic images, correct the paper surface curvature, detect and measure deformation on paper due to pen pressure, generating a new image in false color from differential pressure, based in previous calibration. This new image can be considered as a “fingerprint pressure” signature. This methodology may assist the forensic expert in correctly determining the authorship of a signature.
Palavras-Chave: coherent radiation; tomography; crime detection; nuclear forensics; pressure measurement; hands
. Optical-coherence-tomography-based algorithm for handwriting forensic analysis. In: JALALI, BAHRAM (ed.); KITAYAMA, KEN-ICHI (ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE OPTO, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 112990P-1 - 112990P-8. (Proceedings SPIE 11299, AI and Optical Data Sciences). DOI: 10.1117/12.2543356. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31563. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. New plate-type core of the IPEN/MB-01 research reactor facility for validation of RMB project. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Abstract: The IPEN/MB-01 research reactor had its first criticality in November 1988 and, ever since, has been of major importance in Brazilian reactor physics researches, achieving international level for experiments comparison and validation (benchmarks). In this facility it is possible to build many different core configurations (i.e., rectangular, square and cylindrical), once versatility and flexibility were both taken into account on its initial project. The core is a fissile material assembly, inserted in a water tank, where the chain reaction is self-maintained and controlled at low power levels, so that, in normal operation, the feedback effects of temperatures are negligible. The core is intended for neutrons simulation of light water moderated reactors allowing the experimental verification of the calculation methods, reactor cell and mesh structures, control rods effectiveness, isothermal reactivity coefficients and core dynamics due to reactivity insertions. The first standard IPEN/MB-01 core had UO2 rod-type fuel, 4.3 % enriched in U-235 and using B4C and Ag-In-Cd rods for safety and control of the reactor. The facility is located at IPEN/CNEN-SP (Nuclear and Energy Research Institute), in Sao Paulo - Brazil. Within the scope of the new research reactor project, the Brazilian Multipurpose Reactor (RMB), it was designed a new critical configuration for the IPEN/MB-01. After thirty years of work, the rod-type fuels were replaced by plate-type fuels, in order to validate the RMB calculation methodologies, as well as the nuclear data libraries used. The RMB is an open pool-type reactor with maximum power of 30 MW, being the core a 5x5 configuration, consisting of 23 fuel elements, made of U3Si2-Al, having a medium density of 3.7 gU/cm3 and 19.75% enriched in U-235, and two positions available in the core for materials irradiation devices. The production of radioisotopes, silicon doping, neutron activation analysis, nuclear fuels and structural materials testing and the development of scientific and technological research using neutron beams are the main targets of the RMB enterprise. The new IPEN/MB-01 core has a 4×5 configuration, having 19 fuel elements, consisting of U3Si2-Al, 2.8 gU/cm³ and 19.75% enriched in U-235, plus one aluminum block. The IPEN/MB-01 new plate-type fuel assembly uses Cadmium wires as burnable poison, as the one used in RMB core for controlling the core power density and excess of reactivity during its operation. The core is also reflected by 4 boxes of heavy water (D2O), inserted in a moderator tank of light water. The maximum nominal power is 100 W and, for a safe operation, the critical assembly has both safety and auxiliaries’ systems. This paper presents a description of the new core and the principal neutronic parameters. The new core of the IPEN/MB-01 will be certainly a world class benchmark core for the core physics calculation of research reactors.
Palavras-Chave: burnable poisons; control rod worths; cylindrical configuration; fuel elements; heavy water; neutron activation analysis; neutron beams; reactor cores; rmb reactor; uranium 235
. New plate-type core of the IPEN/MB-01 research reactor facility for validation of RMB project. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/30986. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Nd:YLF/KGW intracavity Raman laser in DBMC configuration at 1147 and 1163 nm in TEM00. In: CLARKSON, W. ANDREW (Ed.); SHORI, RAMESH K. (Ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE LASE, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 112590K-1 - 112590K-7. (Proceedings SPIE 11259, Solid State Lasers XXIX: Technology and Devices). DOI: 10.1117/12.2545092 Abstract: A Nd:YLF / KGW intracavity Raman laser in DBMC (double-beam-mode-controlling) configuration has been investigated in this work. The fundamental wavelength laser was generated using a Nd:YLF crystal pumped in DBMC configuration generating an emission wavelength of 1053 nm in σ-polarization. A VBG (volume-Bragg-grating) equipped diode emitting at 797 nm was used as pump source. The KGW crystal has two strong Raman lines, 768 cm-1 and 901 cm-1, generating two Raman wavelengths at 1147 nm and 1163 nm, respectively. The DBMC technique allows to produce TEM00 stable output in a side-pumped configuration with no requirement to introduce any additional mode selection technique, thus achieving high efficiency for fundamental TEM00 operation. The high power density of the fundamental laser combined with intracavity Stokes conversion produces an efficient Raman laser. Allying both techniques, the Nd:YLF in DBMC configuration and the intracavity Raman generation, it was possible to generate an output power at 1163 nm of 3.2 W corresponding to a diode-to-Raman conversion efficiency of 8% with slope efficiency of 8.8 %. For the emission at 1147 nm, 3.5 W of output power was achieved with a diode-to-Raman conversion efficiency of 11% and slope efficiency of 9%. The beam quality was M2 =1.9 and 1.1 in the horizontal and vertical direction, respectively. This is, to our knowledge, the first report of a side-pumped Nd:YLF/KGW intracavity Raman laser in DBMC configuration.
Palavras-Chave: raman spectra; raman effect; optical pumping; diode-pumped solid state lasers
. Nd:YLF/KGW intracavity Raman laser in DBMC configuration at 1147 and 1163 nm in TEM00. In: CLARKSON, W. ANDREW (ed.); SHORI, RAMESH K. (ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE LASE, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 112590K-1 - 112590K-7. (Proceedings SPIE 11259, Solid State Lasers XXIX: Technology and Devices). DOI: 10.1117/12.2545092. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31558. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Monitoring network for nuclear research laboratory using WSN and IoT devices. In: INTERNATIONAL MULTI-CONFERENCE ON COMPLEXITY, INFORMATICS AND CYBERNETICS, 11th, March 10-13, 2020, Florida, USA. Proceedings... Florida, USA: International Institute of Informatics and Systemics, 2020. p. 108-111. Abstract: This work presents a proposal of implementation of an automatic monitoring system for environments who does experimentation and manipulation of ionizing radioactive particles, having as a base scenario the structures off nuclear energy research laboratories through sensors coupled to integrated microprocessor circuit boards, to carry out the communication between the sensors a Wireless Sensor Network with star topology was raised by resorting in the Internet of Things paradigm. For the network security, the concept of layered access level was applied, specifically, access level according to the criticality off the process and environment whose the sensors are exposed to.
Palavras-Chave: neural networks; internet; computer networks; monitoring; sensors
. Monitoring network for nuclear research laboratory using WSN and IoT devices. In: INTERNATIONAL MULTI-CONFERENCE ON COMPLEXITY, INFORMATICS AND CYBERNETICS, 11th, March 10-13, 2020, Florida, USA. Proceedings... Florida, USA: International Institute of Informatics and Systemics, 2020. p. 108-111. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/32627. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Measuring stables isotopes of CO2 (13C and 17,18O) in vertical profiles over the Amazon. In: CROTWELL, ANDREW (Ed.); LEE, HAEYOUNG (Ed.); STEINBACHER, MARTIN (Ed.) WMO/IAEA MEETING ON CARBON DIOXIDE, OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES AND RELATED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES, 20th, September 2-5, 2019, Jeju Island, South Korea. Proceedings... Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2020. p. 129-132. (GAW Report 255).
Palavras-Chave: carbon; emission; greenhouse gases; greenhouse effect; carbon dioxide
. Measuring stables isotopes of CO2 (13C and 17,18O) in vertical profiles over the Amazon. In: CROTWELL, ANDREW (ed.); LEE, HAEYOUNG (ed.); STEINBACHER, MARTIN (ed.) WMO/IAEA MEETING ON CARBON DIOXIDE, OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES AND RELATED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES, 20th, September 2-5, 2019, Jeju Island, South Korea. Proceedings... Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2020. p. 129-132. (GAW Report 255). Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31695. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Measuring photoelastic dispersion coefficients in material samples with digital holography. In: BJELKHAGEN, HANS I. (Ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE OPTO, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 113060P-1 - 113060P-7. (Proceedings SPIE 11306, Practical Holography XXXIV: Displays, Materials, and Applications). DOI: 10.1117/12.2544874 Abstract: Polarized Digital Holography (PHD) is a fast and efficient tool for analyzing mechanical effects in materials. Especially when the task requires non-invasive techniques that do not damage the material in study, the use of PHD has great perspectives. The most common methods of digital reconstruction use the convolution theory to discretize the Huygens- Fresnel integral. When external stresses are applied to photoelastic materials, the relationship between these stresses and phase differences observed by polarization holography is an intrinsic characteristic of the material called the photoelastic dispersion coefficient. In photoelasticity, this coefficient depends on the wavelength. By using PHD the authors show in the present paper that the photoelastic dispersion coefficient also depends on the wavelength in Holography. A Mach- Zehnder interferometer, modified with the inclusion of linear polarizers, was built to verify this effect in a sample of photoelastic material. In this set-up, two coherent light sources with different wavelengths were used. For the analysis, a digital method was created that correlated the mean stresses differences on the photoelastic material sample and the mean phases differences at each distinct wavelength.
Palavras-Chave: interferometry; holography; stresses; polarization; photoelasticity
. Measuring photoelastic dispersion coefficients in material samples with digital holography. In: BJELKHAGEN, HANS I. (ed.) SPIE PHOTONICS WEST; SPIE OPTO, February 1-6, 2020, San Francisco, USA. Proceedings... Washington, USA: SPIE, 2020. p. 113060P-1 - 113060P-7. (Proceedings SPIE 11306, Practical Holography XXXIV: Displays, Materials, and Applications). DOI: 10.1117/12.2544874. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31564. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Measurement program of GHG vertical profiles at Amazon. In: CROTWELL, ANDREW (Ed.); LEE, HAEYOUNG (Ed.); STEINBACHER, MARTIN (Ed.) WMO/IAEA MEETING ON CARBON DIOXIDE, OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES AND RELATED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES, 20th, September 2-5, 2019, Jeju Island, South Korea. Proceedings... Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2020. p. 111-115. (GAW Report 255).
Palavras-Chave: environment; environmental impacts; greenhouse gases; fires; forests; carbon sources; deforestation
. Measurement program of GHG vertical profiles at Amazon. In: CROTWELL, ANDREW (ed.); LEE, HAEYOUNG (ed.); STEINBACHER, MARTIN (ed.) WMO/IAEA MEETING ON CARBON DIOXIDE, OTHER GREENHOUSE GASES AND RELATED MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES, 20th, September 2-5, 2019, Jeju Island, South Korea. Proceedings... Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2020. p. 111-115. (GAW Report 255). Disponível em: http://200.136.52.105/handle/123456789/31693. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
-
. Main experiments performed at the IPEN/MB-01 RR using UO2 fuel rods core. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Abstract: This paper aims to show the main experimental utilization of the IPEN/MB-01 zero power reactor during the last 30 years with 3663 operations cycles. The IPEN/MB-01 reactor it was mainly used to validation of calculation methodology used in nuclear reactor cores design.
Palavras-Chave: fuel rods; reactor cores; reactor design; uranium dioxide; validation
. Main experiments performed at the IPEN/MB-01 RR using UO2 fuel rods core. In: INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH REACTORS: ADDRESSING CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES TO ENSURE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUSTAINABILITY, November 25-29, 2019, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Proceedings... Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency, 2020. Disponível em: http://repositorio.ipen.br/handle/123456789/31843. Acesso em: $DATA.Como referenciar este itemEsta referência é gerada automaticamente de acordo com as normas do estilo IPEN/SP (ABNT NBR 6023) e recomenda-se uma verificação final e ajustes caso necessário.
Itens para a visualização no momento 1-20 de 40
Buscar no repositório
Navegar
Minha conta
Visualizar
A pesquisa no RD utiliza os recursos de busca da maioria das bases de dados. No entanto algumas dicas podem auxiliar para obter um resultado mais pertinente.
✔ É possível efetuar a busca de um autor ou um termo em todo o RD, por meio do Buscar no Repositório , isto é, o termo solicitado será localizado em qualquer campo do RD. No entanto esse tipo de pesquisa não é recomendada a não ser que se deseje um resultado amplo e generalizado.
✔ A pesquisa apresentará melhor resultado selecionando um dos filtros disponíveis em Navegar
✔ Os filtros disponíveis em Navegar tais como: Coleções, Ano de publicação, Títulos, Assuntos, Autores, Revista, Tipo de publicação são autoexplicativos. O filtro, Autores IPEN apresenta uma relação com os autores vinculados ao IPEN; o ID Autor IPEN diz respeito ao número único de identificação de cada autor constante no RD e sob o qual estão agrupados todos os seus trabalhos independente das variáveis do seu nome; Tipo de acesso diz respeito à acessibilidade do documento, isto é , sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, ID RT apresenta a relação dos relatórios técnicos, restritos para consulta das comunidades indicadas.

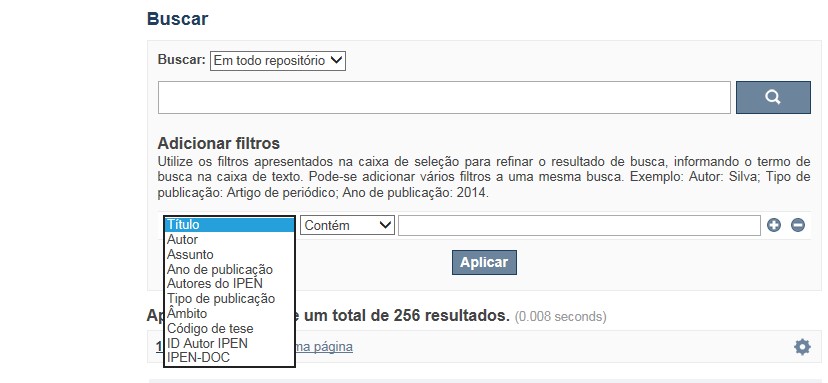
A opção Busca avançada utiliza os conectores da lógica boleana, é o melhor recurso para combinar chaves de busca e obter documentos relevantes à sua pesquisa, utilize os filtros apresentados na caixa de seleção para refinar o resultado de busca. Pode-se adicionar vários filtros a uma mesma busca.
Exemplo:
Buscar os artigos apresentados em um evento internacional de 2015, sobre loss of coolant, do autor Maprelian.
Autor: Maprelian
Título: loss of coolant
Tipo de publicação: Texto completo de evento
Ano de publicação: 2015
✔ Para indexação dos documentos é utilizado o Thesaurus do INIS, especializado na área nuclear e utilizado em todos os países membros da International Atomic Energy Agency – IAEA , por esse motivo, utilize os termos de busca de assunto em inglês; isto não exclui a busca livre por palavras, apenas o resultado pode não ser tão relevante ou pertinente.
✔ 95% do RD apresenta o texto completo do documento com livre acesso, para aqueles que apresentam o ![]() significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
significa que e o documento está sujeito as leis de direitos autorais, solicita-se nesses casos contatar a Biblioteca do IPEN,
[email protected]
.
✔ Ao efetuar a busca por um autor o RD apresentará uma relação de todos os trabalhos depositados no RD. No lado direito da tela são apresentados os coautores com o número de trabalhos produzidos em conjunto bem como os assuntos abordados e os respectivos anos de publicação agrupados.
✔ O RD disponibiliza um quadro estatístico de produtividade, onde é possível visualizar o número dos trabalhos agrupados por tipo de coleção, a medida que estão sendo depositados no RD.
✔ Na página inicial nas referências são sinalizados todos os autores IPEN, ao clicar nesse símbolo ![]() será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
será aberta uma nova página correspondente à aquele autor – trata-se da página do pesquisador.
✔ Na página do pesquisador, é possível verificar, as variações do nome, a relação de todos os trabalhos com texto completo bem como um quadro resumo numérico; há links para o Currículo Lattes e o Google Acadêmico ( quando esse for informado).
ATENÇÃO!
ESTE TEXTO "AJUDA" ESTÁ SUJEITO A ATUALIZAÇÕES CONSTANTES, A MEDIDA QUE NOVAS FUNCIONALIDADES E RECURSOS DE BUSCA FOREM SENDO DESENVOLVIDOS PELAS EQUIPES DA BIBLIOTECA E DA INFORMÁTICA.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
1. Portaria IPEN-CNEN/SP nº 387, que estabeleceu os princípios que nortearam a criação do RDI, clique aqui.
2. A experiência do Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares (IPEN-CNEN/SP) na criação de um Repositório Digital Institucional – RDI, clique aqui.
O Repositório Digital do IPEN é um equipamento institucional de acesso aberto, criado com o objetivo de reunir, preservar, disponibilizar e conferir maior visibilidade à Produção Científica publicada pelo Instituto, desde sua criação em 1956.
Operando, inicialmente como uma base de dados referencial o Repositório foi disponibilizado na atual plataforma, em junho de 2015. No Repositório está disponível o acesso ao conteúdo digital de artigos de periódicos, eventos, nacionais e internacionais, livros, capítulos, dissertações, teses e relatórios técnicos.
A elaboração do projeto do RI do IPEN foi iniciado em novembro de 2013, colocado em operação interna em julho de 2014 e disponibilizado na Internet em junho de 2015. Utiliza o software livre Dspace, desenvolvido pelo Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Para descrição dos metadados adota o padrão Dublin Core. É compatível com o Protocolo de Arquivos Abertos (OAI) permitindo interoperabilidade com repositórios de âmbito nacional e internacional.
O gerenciamento do Repositório está a cargo da Biblioteca do IPEN. Constam neste RI, até o presente momento 20.950 itens que tanto podem ser artigos de periódicos ou de eventos nacionais e internacionais, dissertações e teses, livros, capítulo de livros e relatórios técnicos. Para participar do RI-IPEN é necessário que pelo menos um dos autores tenha vínculo acadêmico ou funcional com o Instituto. Nesta primeira etapa de funcionamento do RI, a coleta das publicações é realizada periodicamente pela equipe da Biblioteca do IPEN, extraindo os dados das bases internacionais tais como a Web of Science, Scopus, INIS, SciElo além de verificar o Currículo Lattes. O RI-IPEN apresenta também um aspecto inovador no seu funcionamento. Por meio de metadados específicos ele está vinculado ao sistema de gerenciamento das atividades do Plano Diretor anual do IPEN (SIGEPI). Com o objetivo de fornecer dados numéricos para a elaboração dos indicadores da Produção Cientifica Institucional, disponibiliza uma tabela estatística registrando em tempo real a inserção de novos itens. Foi criado um metadado que contém um número único para cada integrante da comunidade científica do IPEN. Esse metadado se transformou em um filtro que ao ser acionado apresenta todos os trabalhos de um determinado autor independente das variáveis na forma de citação do seu nome.
